Section 11: Block Storage Service – Cinder
35. Overview of Storage in Openstack
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729394#overview
Ephemeral
- Type: Block
- VM File systems
- Persistent across reboots
- Deleted when the VM is destroyed
Block
- Type: Block
- Persistent
- Can only be attached to a single instance at a time
- But can be unmounted and remounted to another instance
Object
- Type: Object
- Used for storing binary objects (files, etc.)
- Like S3 or DropBox
- Managed by Swift
- Images are stored as Objects
Shared File system
- Good for sharing file systems in a multi-tenant environment
- Can be mounted on multiple instances at the same time.
- Managed by the Manilla project
36. Cinder – Introduction and Capabilities
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729402#overview
Cinder Block Storage
- Persistent block level storage devices for use with compute instances
- Block device lifecycle management
- One to one relationship between instances
- Like a usb drive.
- Can only be in one server at a time
- but can be moved.
- managed snapshots
- Managed volume types
- Mostly Linux LVM
- Others available
- Fully integrated into Nova and Horizon allowing self service.
- create. resize, migrate, delete, etc.
Volumes
- Persistent R/W block storage
- Attach as secondary volumes
- Good for Databases
- Can be used as root volumes to boot instances
- Lifecycle management
- Create, delete, extend
- Attach / detach
- Manages volume management
Snapshots
- Read only copy of a volume
- Create / delete snapshots
- Create a volume out of snapshot
- An instance can use a snapshot as a boot source
Backup
- Admin operation
- Done from CLI
- Stored in Swift
- Needs a container
- Create/restore
- `cinder backup-create “volumeid”`
Quotas
- Enforced per project
- Number of volumes
- storage space in GB
- Number of Snapshots
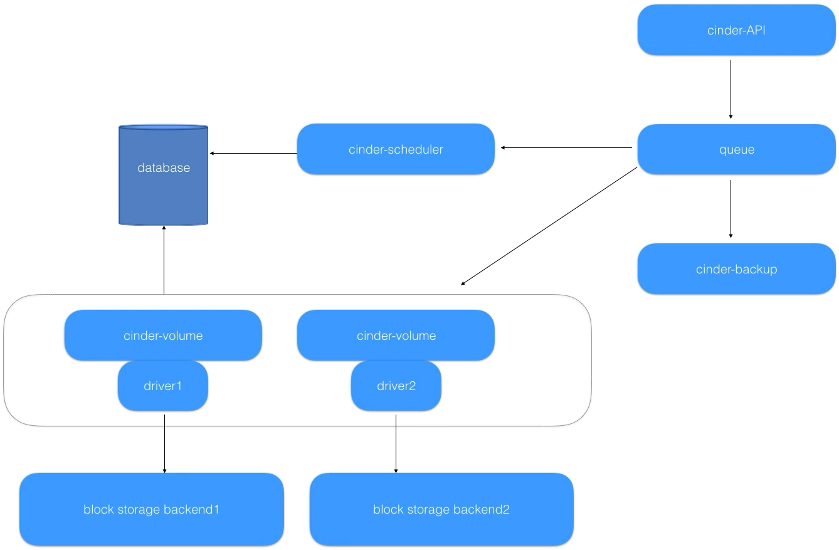
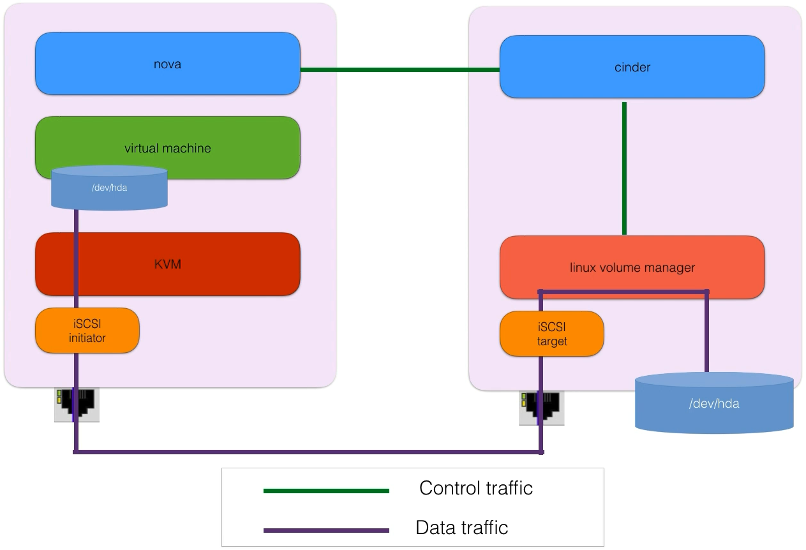
37. Cinder Architecture
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729408#overview
Example of Data and Control Traffic for Cinder
38. Managing Cinder from CLI
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6738324#overview
Cinder direct commands
cinder service-list cinder service-disable cinder service-enable
Openstack Unified Client commands
openstack command list | grep openstack.volume -A 40
- backup (create / delete / list / restore/ set / show)
- Deprecated for volume backup commands
- consistency group
- volume backup (create / delete / list / restore/ set / show)
- volume (create / delete / host set / list / migrate / set / show)
- volume qos *
- Limit iops and writes per second
- volume service (list / set)
- volume snapshot (create / delete / list / set / show / unset)
- volume transfer request accept
- volume type (create / delete / list / restore/ set / show)
- Logical constructs
- Example can create volume type for top performance for SSD
Create Volume
openstack volume create --size <GB> <name>
Attach
- Can be attached on the fly!
Section 12: Object Storage Service – Swift
39. Introduction to Swift Object Storage Service
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6731472#overview
Swift Object Overview
- Scalable, distributed, replicated object storage
- Simple, powerful REST API
- HTTP
- Supports many users
- Pooled Storage capacity
What is an Object
- File
- Metadata
- tags
- location
- anything else
Why Swift
- Accessible from almost everywhere
- Pure software based
40. Characteristics of Swift
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6731476#overview
Data Consistency
- Strict consistency (Block)
- All replicas are written to completion in all regions and zones before the write operation is considered successful
- Failure to write ANY replicas / parity results in a failed transaction
- Eventual Consistency (object)
- All replicas written at the same time but only most (>50%) needed to be declared successful
- Failed replicas handed separately
Durability with Replicas
- Swift stored multiple replicas
- 3 replicas is default
- Good balance between durability and cost
- Can be changed
- Stores Md5 checksums with each object
- returned in header so client can verify
Data Placement
- Tries to be as far away as possible
41. Swift Architecture
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6731478#overview
Swift API
- PUT and GET
- Can even use a web browser
Components
- Can be load balanced
- Proxy
- Account Service
- Container Service
- Object Service
- Replication and consistency tools
42. Managing Swift from CLI
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6738326#overview
Can be deployed on an Openstack cluster or even stand alone. Does not require Openstack to function.
View object storage accounts
openstack object store account show +------------+---------------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +------------+---------------------------------------+ | Account | AUTH_a5444c1b501c4bc882871fbdc93e883f | | Bytes | 0 | | Containers | 0 | | Objects | 0 | +------------+---------------------------------------+
List containers
openstack container list < empty >
Create 2 containers
openstack container create container1 +---------------------------------------+------------+------------------------------------+ | account | container | x-trans-id | +---------------------------------------+------------+------------------------------------+ | AUTH_a5444c1b501c4bc882871fbdc93e883f | container1 | txfb49336776ee4fcc84928-0061e5eed7 | +---------------------------------------+------------+------------------------------------+ openstack container create container2 +---------------------------------------+------------+------------------------------------+ | account | container | x-trans-id | +---------------------------------------+------------+------------------------------------+ | AUTH_a5444c1b501c4bc882871fbdc93e883f | container2 | tx9da0771e5eef45b2bb333-0061e5ef40 | +---------------------------------------+------------+------------------------------------+ openstack container list +------------+ | Name | +------------+ | container1 | | container2 | +------------+
Create an Object
# openstack object create <container_name> <file_name> openstack object create container1 keystonerc_admin +------------------+------------+----------------------------------+ | object | container | etag | +------------------+------------+----------------------------------+ | keystonerc_admin | container1 | eeb224b479b7c3f2ed4f7fbcc9666b43 | +------------------+------------+----------------------------------+
Accessing your files
- CLI – Hard Way
- Meh, lots of work
- Create via Horizon and make public
CLI Commands
openstack command list | grep object_store -A 20
- container (create / delete / list / save / set / show / unset)
- object (create / delete / list / save / set / show / unset)
- object store account (set / show / unset)
- managing the account