https://wiki.thomasandsofia.com/openstack-essentials-1-4/
https://wiki.thomasandsofia.com/openstack-essentials-11-12/
Section 5: Horizon Dashboard
13. Overview
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729054#overview
- Dashboard and Horizon are often used interchangably
- Dashboard is the UI
- Horizon is the underlying code (API I rec’n)
14. Dashboard Walkthrough
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729072#overview
Create a user
- Identity > Users > [+ Create User]
- Name, Password
- Assign to ‘admin’ project as a _member_
- [ X ] Enabled
- [Create User]
Create a project and assign users
- Identity > Projects > [+ Create Project]
- Create the Project
- [Project Information] tab
- Domain ID and Domain Name are disabled and set to Default since no domains have been established.
- Name: firstproject
- [Project Information] tab
- Add the users
- [Project Members] tab
- Under “All Users” Click [+] next to user name
- Under “Project Members” use drop down and assign roles.
- Don’t forget to add the Admin as a Member and an Admin!
- [Create Project]
Setting Quotas
- Identity > Projects > Locate dropdown to right of ProjectName > Manage Quotas
- Compute, RAM, Disk etc.
Logging In
- Make sure to select the correct Project
Horizon Overview
No notes. Watch the video
Section 6:CLI Client
openstack command list
15. Working from the CLI
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6732850#overview
Openstack CLI Overview
- OS credentials mean nothing to the Openstack Application
- Openstack commands are translated to respective API commands
- Credentials are assigned to environmental variables in `/root/keystonerc_admin`
keystonerc_admin File
cd /root cat keystonerc_admin
- OS_USERNAME
- OS_PASSWORD
Running Commands
Running without credentials error
openstack server list Missing value auth-url required for auth plugin password
Logging in
source keystonerc_admin [root@localhost ~(keystone_admin)]#
- This sets the environmental variables in the file to your session.
Now run the command
openstack server list < blank - there are no servers to list! >
Errors
If getting authentication errors, run the export command to see what variables have been set
export < Long list of variables here! >
Adding new CLI Users
Copy the current file to a new filename
cp keystonerc_admin operator1_rc
Edit the new file
- Change the username and password
- Keep the URL the same (must be the API Url)
- You could assign new project here, but not necessary now
unset OS_SERVICE_TOKEN export OS_USERNAME=operator export OS_PASSWORD='16charhexpassword' export OS_REGION_NAME=RegionOne export OS_AUTH_URL=http://IP.ADD.RE.SS:5000/v3 export PS1='[\u@\h \W(operator1)]\$ ' export OS_PROJECT_NAME=admin export OS_USER_DOMAIN_NAME=Default export OS_PROJECT_DOMAIN_NAME=Default export OS_IDENTITY_API_VERSION=3
Login as the new user
source operator1_rc [root@localhost ~(operator1)]#
Switch back to Admin
source keystonerc_admin [root@localhost ~(keystone_admin)]#
16. Unified CLI Client
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6732860#overview
Most command have transitioned to new format
- nova boot > openstack server create
- neutron net-create > openstack network create
- glance image-list > openstack image list
- cinder create > openstack volume create
Not all command have transitioned so you may find times you need to use the old school technique.
Section 7: Identity Service – Keystone
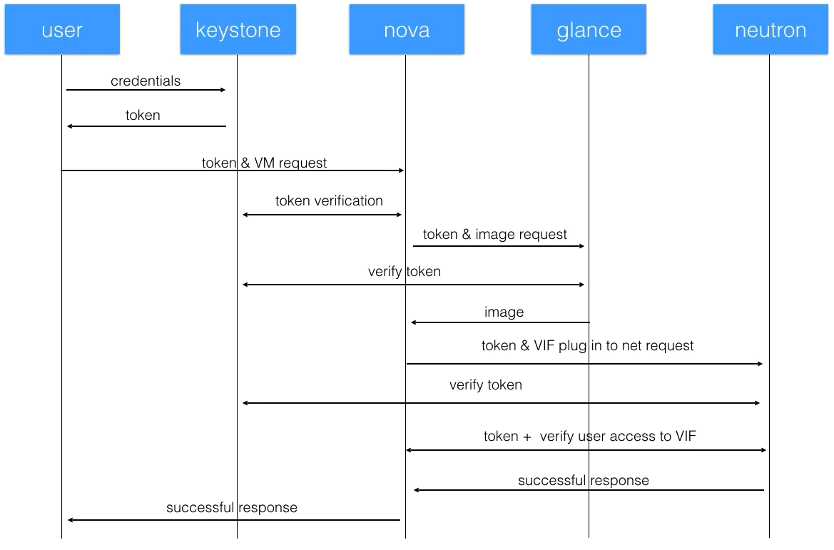
17. Introduction & Important Identity Concepts
- Provides central authentication for users and projects.
- Everything you want to do in Openstack requires authentication
- Supports
- LDAP
- AD
- MySQL
- provides a token for subsequent auth requests
- Tokens have roles embedded in them
- Generally expire in 24hrs, but modifiable
- Like a wrist band.
- You show your ID and pay at the door (Authentication)
- You get a color coded wrist band for the rides you can go on
- The
Concepts
- User:
- User, system, service, or anything that requires access
- Project (or Tenant)
- Container that groups or isolates resources or identity objects
- Projects might map to
- Customer
- Account
- Organization
- Tenant
- Role
- Group of users with a defined set of privileges to perform a specific set of operations.
- Users can be granted access to any role
- Globally scoped (all projects)
- Project scoped
- Token
- Alpha-numeric text string (key) that allows access to APIs and resources
- These tokens include a list of roles
- Catalog
- Directory services for Openstack API
- By registering with Keystone
- Don’t need to discover application API addresses/endpoints each time.
Tell me like I’m 5.
- Tokes are like a wrist band at an amusement park
- You show your ID and pay at the door (Authentication)
- You get a color coded wrist band for the rides you can go on (Token)
- They give you a map to these rides (Catalog)
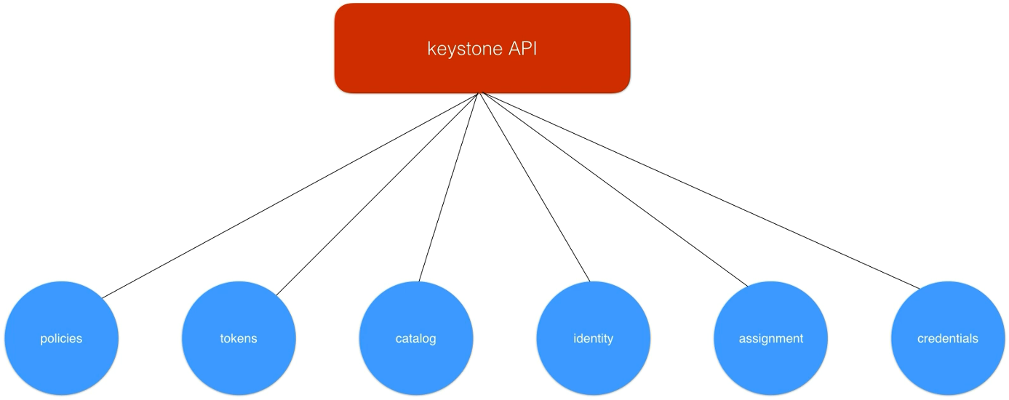
18. Keystone Architecture
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729088#overview
Polices and authorization
Each service has it’s own role based policies.
- stored in json file (policy.json)
Architecture
- Stored in SQL database
19. Managing Keystone from CLI
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6732892#overview
Section 8: Image Service – Glance
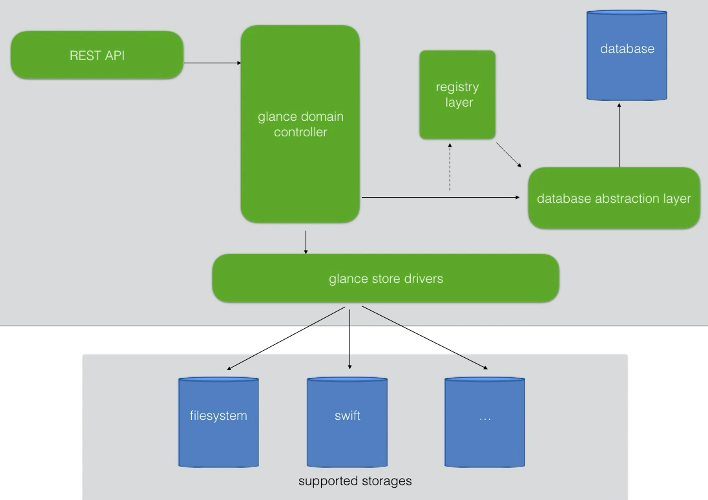
20. Overview and Architecture
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729094#overview
- Stores VM disk images
- New VMs are NOT created from fresh installs.
- Instead, use a pre-built image to pull up the OS
- Nova gets a copy of the image from Glance and spins up from it.
- Like booting from a Live CD
Supported Images
- Raw
- Machine (kernel, ramdisk outside of image, aka AMI)
- VHD (Hyper-V)
- VDI (VirtualBox)
- Qcow2 (Qemu/KVM)
- VMDK (VMware)
- OVF (VMware, Others)
Link for downloading Glance Images
- https://docs.openstack.org/image-guide/obtain-images.html
- One is CirrOS
- Only 13MB
- Very limited but great for testing!
21. Managing Glance from CLI
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6732890#overview
Seach for Commands
openstack command list | grep openstack.image -A 15
- image add project
- Adds an image to a project.
- Good for admins to use
- image create
- Saves the local file to the Glance repository
- image delete
- image list
- This will also show the Image ID
- image member list
- image remove project
- Removes an image from a project.
- image save
- Saves image in Glance repository to a local file
- image set
- Set image properties or tags
- image show <name or id>
- Displays the image’s properties
- image unset
- Unsets image properties or tags
Get CirrOS
curl -o /tmp/cirros-0.3.4.img http://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.5.1/cirros-0.5.1-x86_64-disk.img
Username: cirros
Password: gocubsgo
Note: I was unable to use curl to access the file. Instead, since my Openstack VM has access to my LAN, I used SCP to pull it from my workstation. Worked great!
- Had to switch back to the admin user using the source command. Easy enough.
Create the Image in Glance
openstack image create --min-disk 2 --private --disk-format qcow2 --file /tmp/cirros-0.5.1-x86_64-disk.img cirros
- –min-disk: Minimum disk size in GB
- –private: Make private to the user creating the image.
Note: Had to switch back to the admin user using the source command. I was still as operator1.
View the image details
openstack image show cirros +------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | checksum | 1d3062cd89af34e419f7100277f38b2b | | container_format | bare | | created_at | 2022-01-16T01:02:35Z | | disk_format | qcow2 | | file | /v2/images/56355c14-2a6b-4980-9af8-7cda2940754c/file | | id | 56355c14-2a6b-4980-9af8-7cda2940754c | | min_disk | 2 | | min_ram | 0 | | name | cirros | | owner | a5444c1b501c4bc882871fbdc93e883f | | properties | os_hash_algo='sha512', os_hash_value='553d220ed5...', os_hidden='False' | | protected | False | | schema | /v2/schemas/image | | size | 16338944 | | status | active | | tags | | | updated_at | 2022-01-16T01:02:35Z | | virtual_size | None | | visibility | shared | +------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Note: I did not use the –private switch. As such, my image is not protected. 🙂
Section 9 Networking Service – Neutron
22. Introduction to Neutron
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729110#overview
Benefits
- Rich topologies
- Overlapping IP addresses
- Technology agnostic
- Not limited to vlans or flat networks
- Pluggin architecture
- Load balancing, vpn, firewalls, etc
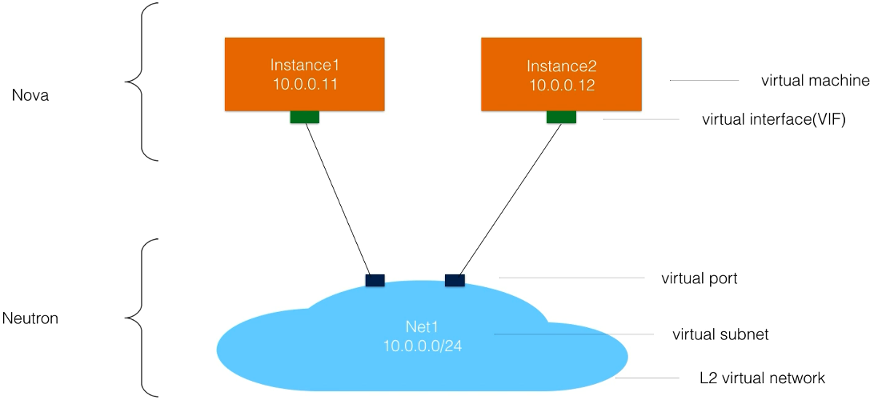
Base Terminology and Abstractions
Core Resources
- Networks
- Ports
- Subnets
23. Neutron Architecture
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729118#overview
- REST API
- Exposes logical resources: subnets, ports, etc.
- Plugin
- Optional extension support
- ml2 is primary
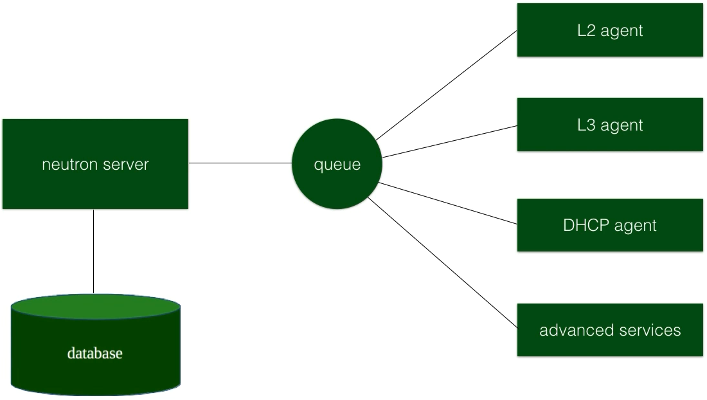
- Queue
- Enables bidirectional agent communications
Architecture
- Message Queue
- Exchanges messages with other Neutron agents
- L2 (Layer 2) Agent
- Responsible for wiring up ports and devices and connecting them into a shared broadcast domain.
- Generally reside on the hypervisor on Compute node.
- DHCP Agent
- Auto-configure IP address, networking, DNS, yadda yadda
- Can use another agent called “config drive” which would not require you to use DHCP
- L3 (Layer 3) Agent
- Provides connectivity between different networks
- Advanced Services
- Special agents for LB, FW, VPN, etc.
Note: When running these agents in the real world, you will see many copies of each!
Plugin Extensions
- Plugins are registered with the API and discovered at startup
- Common extensions include
- DHCP, L3, Quota, Security Groups, Provider Networks
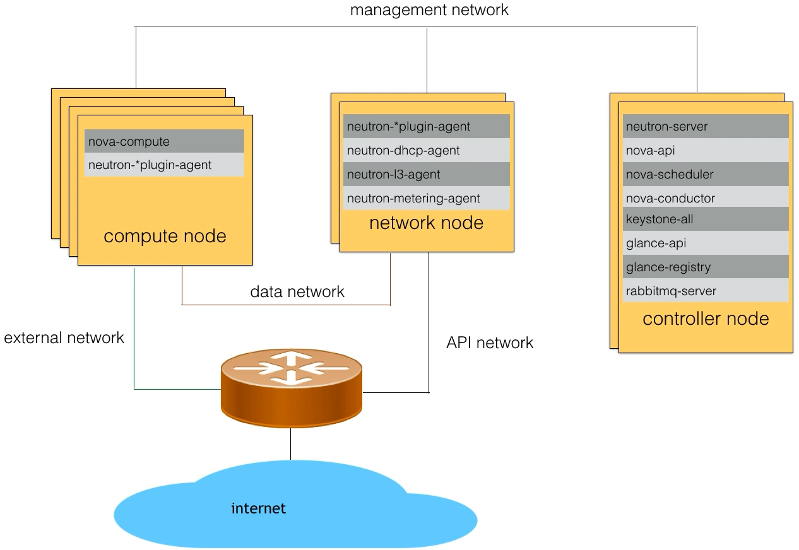
Where Neutron Components Reside
24. Provider and Project Networks
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729142#overview
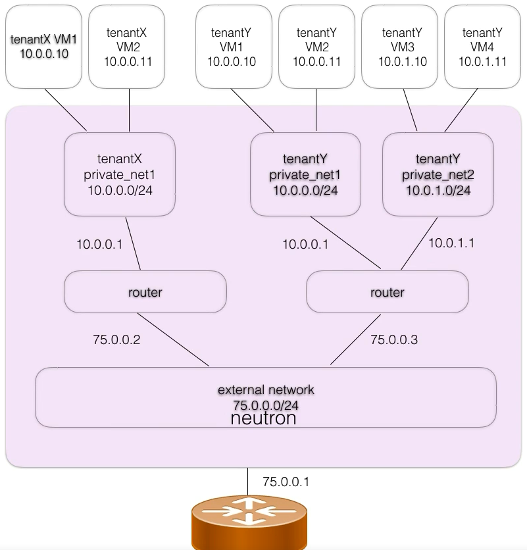
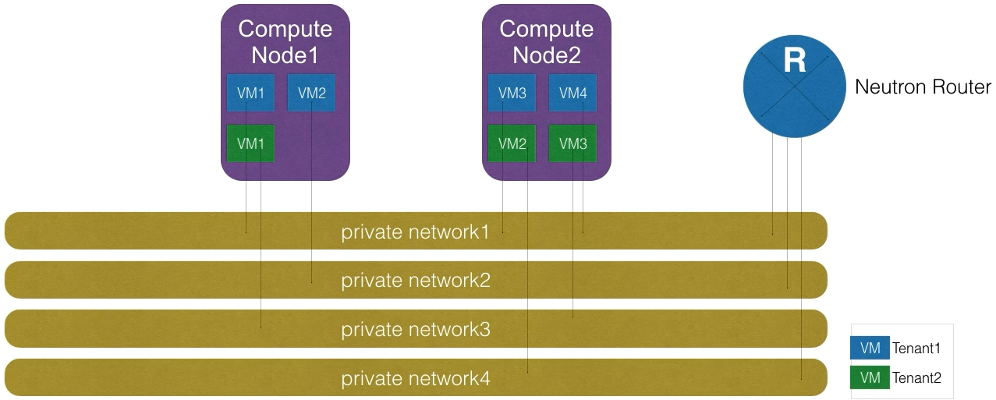
Multi Tenancy
- Can provide per-tenant networking
- Virtual, isolated networks can be created inside Openstack projects
- Only have routes to the outside world if you create them.
- Design your networks according to the needs of your environment.
- If you need a Router, add it.
- If you need a Load Balancer, add it.
- If you need Outside connectivity, add it.
Project vs Provider Networks
Project networks
- The terms Project and Tenant can be use interchangeably
- Created by normal users
- Details about how they are physically realized are hidden from these users.
- Created to be used by the instances in their project.
- All software defined and live in their project environments.
- Must attach their Upstream Interfaces to Provider Networks for access to external resources.
- Supports
- Local
- Flat (No vLANS. Everything on the same network)
- VLAN
- VXLAN
- GRE (General Routing Encapsulation)
Provider networks
- Sole purpose for a Provider Network is to have access to the Outside (non-Openstack) world.
- vLAN numbers have to match existing vLANs.
- Are created by Administrators
- These admin specify how the network is physically realized
- These usually match some existing network in the datacenter
- Often used to give Projects direct access to a Public network that can be used to reach either the Internet or perhaps some Intranet networks outside of Openstack.
- Great for integrating some VMs in Openstack with some bare-metal machines in a specific VLAN
- Supports
- Flat
- VLAN (802.1Q tagged)
- VXLAN
- GRE
- Only support Layer 2 connectivity for instances
- As such, they lack supporting for features such as Routers and Floating IP Addresses
25. Network Technologies Supported
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729158#overview
Local Network
- Isolated networks that live on a single compute node.
- Good for test and POC environments
Flat Network
- No segmentation
- No 802.1Q tagging or other mechanisms
- Single broadcast domain
- Not scalable
VLAN
- Layer 2 Implementation
- Separate broadcast domains
- IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Tagging
- Improves security by network segmentation
- Implemented by almost all router and switches
- Supported by most NIC cards
- Limited to 4096 VLANs
- Although note that some of these are reserved….
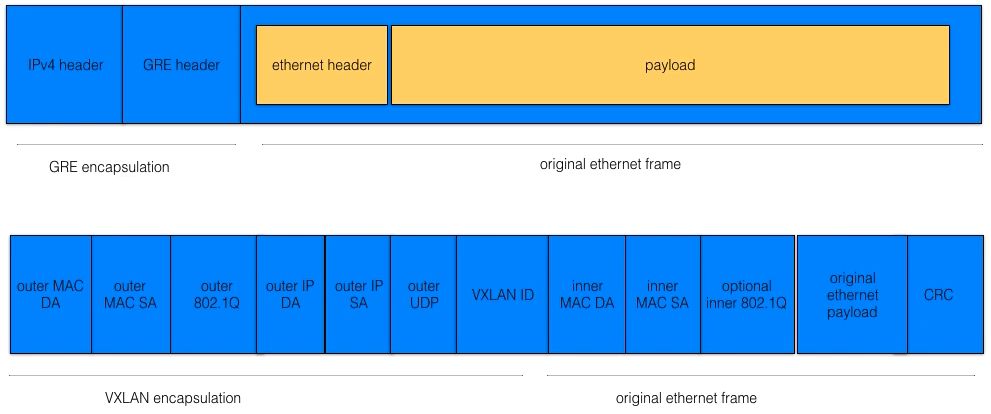
Tunneling Technologies (GRE and VXLAN)
- Both are Layer 3 protocols
- GRE (General Routing Encapsulation)
- MAC in IP encapsulation
- Not supported by most NICs
- More CPU Overhead
- VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN)
- MAC in UDP encapsulation
- 24 VLAN address bits support 16.7M VLANs
26. Common Neutron Agents
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729166#overview
L2 Agent
- Runs on Compute node
- Communicated with Neutron server via RPC message queue
- Main job is to Watch and Notify when devices are added/removed
- Wires up new devices
- Network segment
- Security Group rules
OVS L2 Agent
- Open vSwitch (Open Source Virtual Switch)
- http://openvswitch.org
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x-F9bDRxjAM
- Network segmentation
- VLAN, GRE, VXLAN
L3 Agent
- Responsible for
- routing traffic inside the Openstack cloud
- Handles NAT
- Runs on the Network node
- Uses Linux namespaces and Metadata agent (optional)
- Supports HA
- Uses (VEERP?) to sync states between primary and failover?
27. Neutron Features and Functionality
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729174#overview
Security Groups
- Set of IP Tables rules
- Stateful
- Applied per VIF (Virtual Interface)
- VMs with multiple VIFs supported
- By default
- all outgoing is allowed
- all incoming dropped
NAT
- Usually Linux servers with IP Tables functionality that perform this
- Layer 3 agent
- Source Address Translation
- Convert Private IPs to Public
- The public IP is the Floating IP
- Destination Address Translation
- Used for applications
- Port Address Translation
Floating IPs
- Neutron L3 Agent’s task
DVR – Distributed Virtual Routing
Network Namespaces
- Critical to Neutron
- Isolated copy of network stack
- scope limited to each namespace
- Each namespace has it’s own network devices, routing tables, IP addresses, etc.
- Can resute addresses
- Explicity configuration needed to connect
- View using
IP netns
28. Managing Neutron from CLI
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6733868#overview
openstack command list | grep openstack.network -A 70
STOPPED TAKING NOTES HERE REDUE from here on!
Section 10: Compute Service – Nova
29. Introduction to Nova
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729180#overview
Introduction
- One of the two original openstack projects
- runs on all hypervisor nodes
- Provides instance lifecycle management
- Multiple Hypervisors supported
- Nova is NOT a hypervisor!
- Nova uses the hypervisor’s API or requires an agent to talk to it.
Hypervisors Supported
- KVM (Kernel based VM)
- QEMU (Quick Emulator)
- UML (User Mode Linux)
- VMware vSphere 4.1 update 1 and newer
- Xen (Xen, Citrix XenServer and Xen Cloud Platform (XCP))
- LXC (Linux Containers (through libvirt))
- Bare Metal (via plugin sub-drivers)
- https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/HypervisorSupportMatrix
Key Pairs
- Provides a means of authentication w/o passwords
- Injected to the image with the help of cloud-init process
- Can manage (create/delete/import) key-pairs from dashboard or CLI
- Key-pairs are not specific to openstack
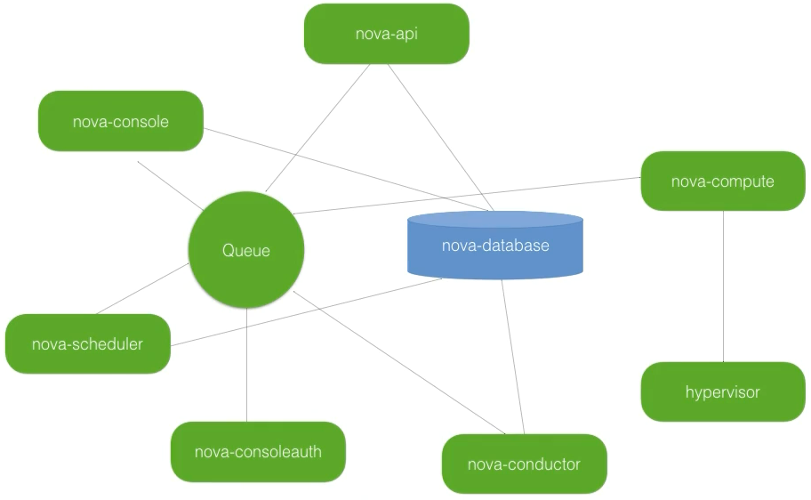
30. Architecture
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729182#overview
- REST API port 8774
- also support aws api
- RabbitMQ but could be any AMQP message bus
- Conductor
- takes build request
- Requests which node to launch on from scheduler
- Interacts with DB and compute nodes
- Schedule – only purpose is to determine which node to build on.
- Compute
- Creates and terminates VM by communicating with the hypervisor
- Database
- stores the data about the vms
Other
- Nova Networking – being replaced by Neutron
- Ceilometer agent
- Used when collecting monitoring information from VMs
- Amazon EC2
31. Launching an Instance
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729192#overview
Minimum Requirements
- Image (pre-built)
- Network
- Flavor
- Resources
- RAM vCPU, Storage
Flavors
openstack flavor list
- https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729192#overview
- Like AWS Instance sizes
- m1.tiny = 512MB RAM, 1 GB Disk, 1 vCPU
- m1.xlarge = 16GB RAM, 160GB Disk, 8 vCPU
Instance Creation
openstack server create --image <image> --flavor <flavor> --nic net-id=<net-id> instance-name
Use the `openstack image show <imageName>` command to see the minimum requirements.
- Using a flavor with less than the minimum required settings will fail.
Flavor Selection
openstack flavor list +----+-----------+-------+------+-----------+-------+-----------+ | ID | Name | RAM | Disk | Ephemeral | VCPUs | Is Public | +----+-----------+-------+------+-----------+-------+-----------+ | 1 | m1.tiny | 512 | 1 | 0 | 1 | True | | 2 | m1.small | 2048 | 20 | 0 | 1 | True | | 3 | m1.medium | 4096 | 40 | 0 | 2 | True | | 4 | m1.large | 8192 | 80 | 0 | 4 | True | | 5 | m1.xlarge | 16384 | 160 | 0 | 8 | True | +----+-----------+-------+------+-----------+-------+-----------+
- Typically each flavor is 2x the previous
- Flavors can be customized by the admin.
- When specifying the flavor with the create command, use the flavor’s ID, not the name.
Network Selection
openstack network list
32. Launching an instance (continued)
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729198#overview
openstack server create --image <image> --flavor <flavor> --nic net-id=<net-id> instance-name
Process Flow
- nova-api
- extracts parameters and validates
- retrieves reference to selected flavor
- retrieves reference to selected boot media
- saves state to DB
- Puts request on bus for conductor
- API call returns with instance status of BUILD and task state SCHEDULING
- Conductor asks scheduler where to create the image
- Filter scheduler kick in
- Schedule applies filters and weights based on config.
- filter examples
- is the compute node on
- Does it have enough free vCPU, vRAM, disk?
- Weight examples
- Give preference to hosts with more free RAM?
- Give preference to hosts with less free RAM?
- If “No Valid Hosts Error” then no hosts were found suitable for the requested VM.
- filter examples
- Database updated with instance state
- Conductor places message on queue for nova-compute on the selected compute node.
- Compute Agent
- prepares for instance creation
- Calls Glance to get boot media
- Calls Neutron for attaching to the network
- Calls Cinder if need to attach persistent volume
- Sets up configuration drive if requested
- Communicates with hypervisor to create the VM
- Udates instance state in DB (using Conductor)
- prepares for instance creation
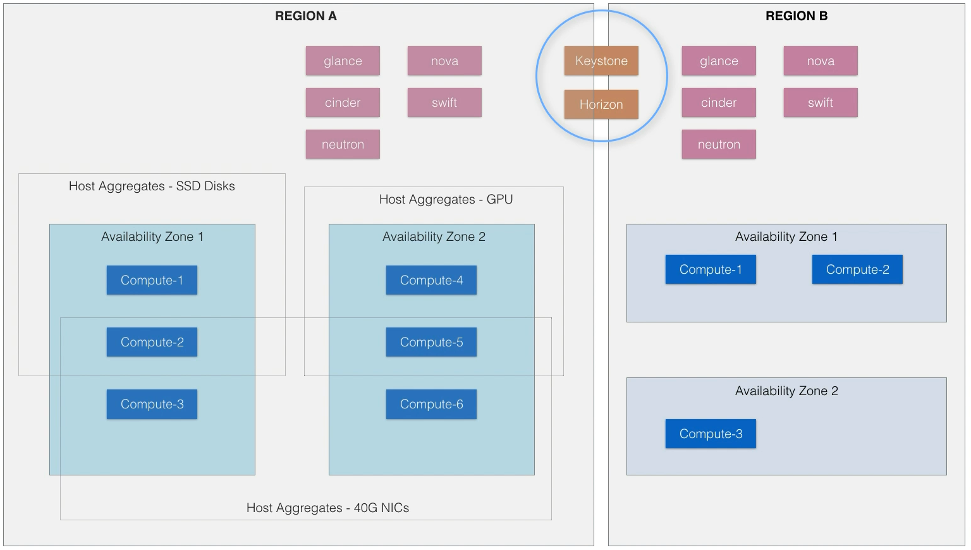
33. Grouping Compute Nodes
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6729206#overview
Segregation of Compute resources
- Provides logical groupings
- Data center, geo region, power source, rack, network resources
- Differentiate specific hardware on compute nodes
- GPU cards, Fast NICs, Storage devices, SSDs
Regions
- Each region get own full openstack deployment where
- Implement their own API endpoints, compute, storage, network, etc
- share as many services as required
- By default, all sservices in one region
- Need to specify a target region for your action.
Host Aggregates
- Logical grouping of compute nodes based on metadata
- Scheduler uses this data to make decisions
- Typically metadata describes capabilities of the nodes
- SSD
- NICs
- GPU
- A compute node can be in multiple host aggregates
- A host with GPU and SSDs might be in both the GPU aggregate and the SSD aggregate
- Implicitly targetable:
- Admin defines host aggregate with metadata and flavor to match
- add commands here
- User selects flavor when requesting instance
- Schedule chooses host matching flavor extra specs with host aggregate metadata
- Admin defines host aggregate with metadata and flavor to match
Availability Zones
- Logical groupings of hosts based on factors like
- Geo-location
- network layout
- Power source
- Explicitly user targetable
- openstack server create –availability-zone <zone-name> …
- if unspecified, will go to default
- Host aggregates are made explicitly targetable by creating them as an Availability Zone
- Unlike host aggregates, hosts cannot be in mulitple AZs!
34. Managing Nova from CLI
https://www.udemy.com/course/openstack/learn/lecture/6738322#overview
View available services
openstack compute service list
Create a flavor
openstack flavor create --id 10 --ram 256 --disk 2 --public m1.tinier
Create a key-pair
openstack keypair create mykeypair >> mykeypair.key
Select Image
openstack image list +--------------------------------------+--------+--------+ | ID | Name | Status | +--------------------------------------+--------+--------+ | 56355c14-2a6b-4980-9af8-7cda2940754c | cirros | active | +--------------------------------------+--------+--------+
Select Network
openstack network list +--------------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------+ | ID | Name | Subnets | +--------------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------+ | 500fcbb8-3a6a-8d03-99c6-b3f442a791a0 | internal | bdb18cac-add9-1e2b-c544-8f592c4246db | | 9c71166f-dc2a-4d9d-25ba-8d0399c6b3f4 | int_net | 246dbbdb-18ca-cadd-91e2-bc5448f592c4 | | 8d0399c6-b3f4-42a7-91a0-500fcbb83a6a | external_network | cadd91e2-bc54-48f5-92c4-246dbbdb18ca | +--------------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------+
Create the Instance
openstack server create --image cirros --key-name mykeypair --flavor 10 --nic net-id=9c71166f-dc2a-4d9d-25ba-8d0399c6b3f4 instance01 ... OS-EXT-STS:vm_state | building ... id | 1a29a750-d010-496e-9f38-597d237d3766b57 ...
Check server status
openstack server show <instance_id> ... OS-EXT-STS:vm_state | active ...
View filters to determine which node to run on
https://docs.openstack.org/developer/nova/filter_scheduler.html
cat /etc/nova/nova.conf | grep filter
Snapshots
openstack server image create --name <snapshot_name> <instance_name>
After a snapshot has been created, it is listed with the images and you can use it to spin up a new instance at any time. 😀
Host Aggregates
openstack aggregate create --property SSD=true agg +-------------------+----------------------------+ | Field | Value | +-------------------+----------------------------+ | availability_zone | None | | created_at | 2022-01-17T15:42:58.000000 | | deleted | False | | deleted_at | None | | hosts | | | id | 1 | | name | agg | | properties | SSD='true' | | updated_at | 2022-01-17T15:42:59.304017 | +-------------------+----------------------------+
Open Instance’s Console
openstack console usr show --novnc <instance_name> ... url | http://IP.ADD.RE.SS:6080/vnc_auto.html?token=<some-long-id>
You can now paste this url into a browser window.
View Console Logs
openstack console log show <instance_name>
Identity Related Commands
openstack command list | grep openstack.compute -A 80
- aggregate *
- managing host aggregates
- compute agent *
- managing hypervisors in the cluster
- computer service *
- Managing Nova services
- console *
- view logs or console url
- flavor *
- Manage flavors
- host *
- View where each nova service is installed
- hypervisor *
- Get information related to hypervisors in the cluster
- ip (fixed|floating) *
- Add or delete IPs
- These are deprecated for the new `server ip` commands.
- keypair *
- Manage key-pairs
- server *
- Manage VM operations
- usage (list|show)
- statistics re: server usage