https://channel9.msdn.com/Shows/TechNet+Radio/TNR1669
Azure Storage
Overview
- Possibly the #1 use for Aure
- Multi-petabyte
- 2 Flavors
- Azure Standard
- Azure Premium
- Standard Storage Account (Magnetic based)
- Durable and HA
- Blob Object
- Page Blobs
- Acts as a Virtual Hard Disk
- VHD Format
- Compatible with Hyper-V and other technologies
- 1 TB Max per disk, but can stripe multiple disks for more storage.
- Up to 64 TB with G-Series VMs
- Exact same storage technology/system used by Blob storage, so 3 copies, very durable.
- Up to 64 TB with G-Series VMs
- Up to 500 IOPs per disk
- Very fast with striping – IOPs are added together.
- Page B
- Page Blobs
- File Storage
- Table Storage
- Queue Storage
- Premium Storage
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/windows/premium-storage
- B-series, DS-series, DSv2-series, DSv3-series, GS-series, Ls-series, M-series and Fs-series
- High IOPs, SSD Based
- Block Storage
HA
- Every block of data sychronously written to 3 separate physical “fault domains” within a Storage Stamp, within a Region.
- Eliminates any Single Point of Failure
- If one of the fault domains storage units fails, the remaining 2 continue to read and write while simultaneously rebuilding the failed drive.
- Geo-Replicated
- Good for Disaster Recovery
- Copies data Asychronously across different regions.
- Remote copies also have 3 physical storage devices.
Page Blobs
- AWS EBS
- Acts as a Virtual Hard Disk
- VHD Format
- Compatible with Hyper-V and other technologies
- 1 TB Max per disk, but can stripe multiple disks for more storage.
- Exact same storage technology/system used by Blob storage, so 3 copies, very durable.
- Up to 64 TB with G-Series VMs (Via striping)
- Up to 500 IOPs per disk
- Very fast with striping – IOPs are added together.
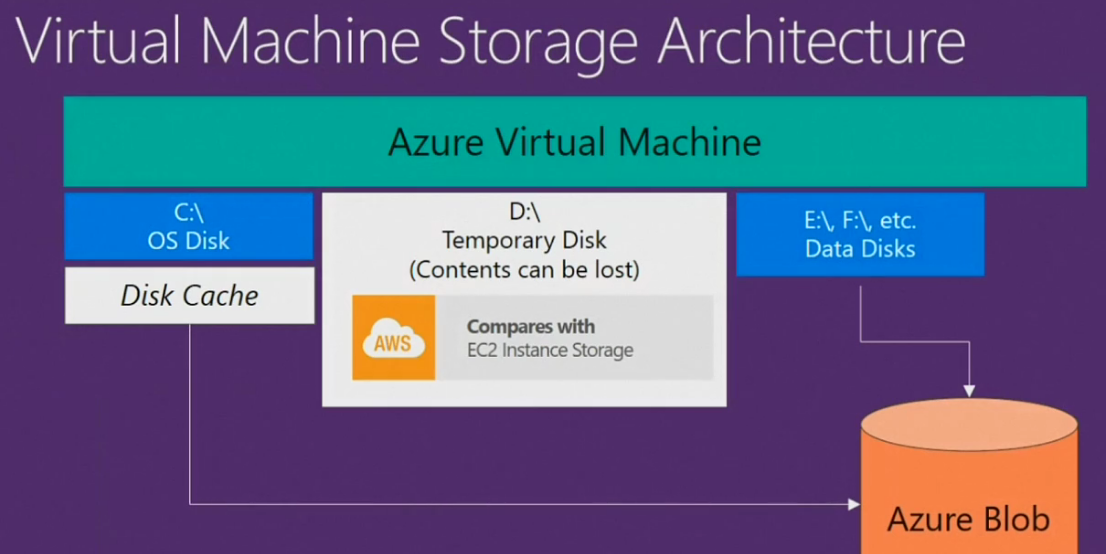
VMs & Page Blobs
- Root storage is stored as a Page Blob (Windows C:\ or Linux /)
- Includes a Host Level disk cache for frequently accessed data
- VM gets a Temporary Disk (Windows D:\ or Linux ‘swap’)
- Ephemeral – lost on reboot
- Not persistently backed to Blob Storage
- Do Not Use for anything you need to keep!
- Persistent data should be stored to additional Page Blob disks: E:\, F:\, etc.
- Possible to Terminate a VM or just shut it down (deallocated state) but keep the data disks
- In De-allocated state:
- Not reserving any CPU, Memory, IP addresses, etc.
- No ‘Compute’ costs
- In De-allocated state:
- Possible to Terminate a VM or just shut it down (deallocated state) but keep the data disks
Azure Files
- AWS EFS
- SMB 3.0 or CIFS
- The Common Internet File System (CIFS) is the standard way that computer users share files across corporate intranets and the Internet. An enhanced version of the Microsoft open, cross-platform Server Message Block (SMB) protocol, CIFS is a native file-sharing protocol in Windows 2000.
- No need to spin up File Servers – works automatically
- Shared location between VMs
- Configurations
- Common Logs
- Web Applications
- Maps the same as any other mount location (G:\, /mnt/share, etc.)
Azure Premium Storage
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/windows/premium-storage
- AWS Provisioned IOPs
- All SSD
- Low Latency, predictable IO throughput
- Single digit millisecond latencies
- Up to 1TB blob/disk size
- Stripe up to 64 disks for 64TB
- more than 84,000 IOPs
- Stripe up to 64 disks for 64TB
- Designed to be used with specific classes of VMs
- DS & GS
- ‘S’ stands for SSD
- These have high speed connectivity back to the storage devices.
- DS & GS
| Disk Types | P4 | P6 | P10 | P20 | P30 | P40 | P50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disk Size | 32 GB | 64 GB | 128 GB | 512 GB | 1024 GB | 2048 GB | 4095 GB |
| IOPs/Disk | 120 | 240 | 500 | 2300 | 5000 | 7500 | 7500 |
| Throughput/Disk | 25 MBps | 50 MBps | 100 MBps | 150 MBps | 200 MBps | 250 MBps | 250 MBps |
Storage Accounts
- 500 TiB MAXIMUM per Storage Account
- To increase storage, you need more Storage Accounts
- Max 200 Storage Accounts per subscription
- To increase storage, you need more Storage Accounts
- Require a unique name (globally?)
- Deployment Model
- Resource Manager or Classic
- Account Kind
- General Purpose
- V1
- All types discussed above
- Cannot do Hot/Cool
- Slightly lower cost per transaction than v2
- Works in Classic model
- V2
- All types discussed above
- CAN do hot / cool
- Recommended
- Does not work in Classic Model (ARM only)
- V1
- Blob Storage (S3?)
- Access Tier
- Cool – Infrequently Accessed (Lower cost tier)
- Same Durability and Performance
- Charge per GB Read – Pay to access (AWS IA)
- Hot – Standard S3
- Cool – Infrequently Accessed (Lower cost tier)
- Access Tier
- General Purpose
- Performance
- Standard or Premium
- Grayed out when not available
- Standard or Premium
- Replication
- Locally-redundant storage (LRS) (Default, 3 synchronous writes)
- Fastest
- Zone-redundant storage (ZRS)
- For Block Blob storage
- Stored in multiple zones within an Azure Region (something like “multi-AZ”?)
- Geo-redundant (GRS)
- Read-Access Geo-Redundant (RA-GRS)
- Use Cases
- Objects (Block blobs, queues, tables)
- GRS or RA-GRS
- VHDs (Especially with high IOPs requirements)
- LRS
- Images or backup copies of VHDs
- GRS
- Objects (Block blobs, queues, tables)
- Locally-redundant storage (LRS) (Default, 3 synchronous writes)
Managed Disks
Azure Managed vs Unmanaged disks : The choice
This is not part of the training, due to the age of the course.
| Category | Managed | Storage Account |
|---|---|---|
| Management | Azure Resource Manager object | Storage Account .vhd file on a blob |
| Size | Pre-determined sizes only | Variable |
| Cost | Pay per size | Pay for what you use |
| Performance | Predictable 500 IOPs | 500IOPs but might be impacted by Storage Account Limits/throttling |
| Availability | Guaranteed different Availability Sets | Not guaranteed |
| Redundancy | LRS | LRS, GRS |
| Encryption | ADE, SSE (coming soon) | ADE, SSE |
Managed Disks
Storage CLI
List all available commands
azure storage --help
View all available storage accounts
azure storage account list
Create a new Storage Account
azure storage account create --resource-group --sku-name <GRS/LRS/etc> --location --kind <storage>