https://channel9.msdn.com/Shows/TechNet+Radio/TNR1670
Return to Main Menu
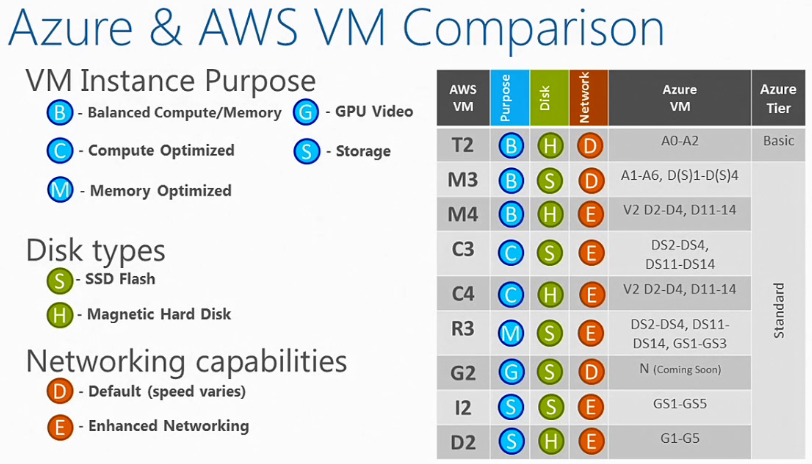
VM Types
- A Family
- Best value
- Basic and Standard Sizes
- General Purpose and High Memory
- High Performance (A8/A9) RDMA Networking
- D Family
- 60% faster CPU
- Up to 112 GB RAM
- Local SSD (Instance???)
- G Family
- Up to 32 CPU
- Up to 448 GB RAM
- 6.5 TB Local SSD (Instance??)
- Latest Gen. Intel Processor – Fastest CPU family available
- DS & GS
- Persistent SSD Storage (via Premium Storage)
- V
- Not discussed yet
- N – GPU
- Coming soon
Sizing
- Start Small – You can always grow
- Azure instances are supported by physical cores, not hyperthreaded.
- Default Core Limit = 20, but can be adjusted. (Soft Limit)
Availability and Service Level Agreements
- 99.95% Monthly Uptime
- 4.38 hours of downtime per year for VMs in an availability set
- What’s included
- Compute hardware failure (disk, cpu, memory)
- Datacenter failures – Network, Power
- Hardware upgrades, Software maintenance – Host OS Updates
- What is NOT included
- VM Guest OS and Applications, VM Guest OS Updates
- Customer on-premises network connectivity and intermediary Internet connectivity
Availability Sets
- Azure uses Availability Sets vs Availability Zones
- These are essentially Tags that push them into different Update and Fault Domains.
- 2 VMs in a set will automatically be provisioned on different hardware.
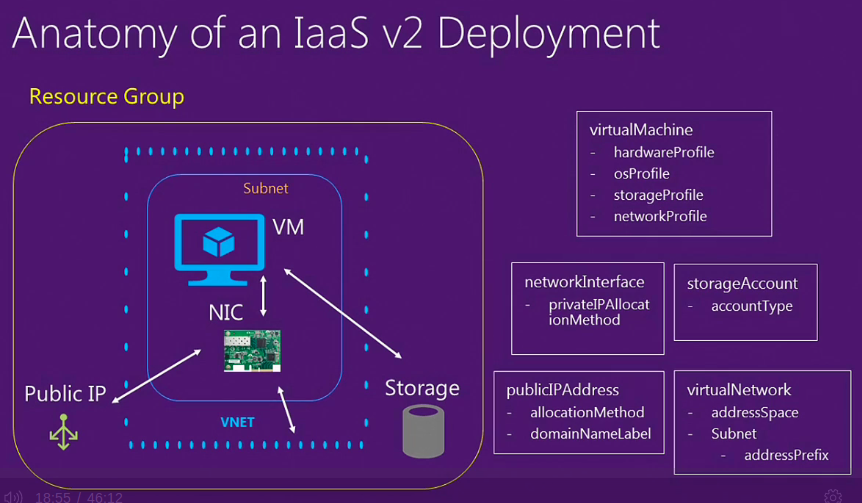
Anatomy of an IaaS v2 Deployment
19 minutes
Return to Main Menu