50% Complete!!
Section 12: Materialized Views in BigQuery
51. What are Materialized Views
https://www.udemy.com/course/bigquery/learn/lecture/22758503#overview
Materialized Views
- Stored physically on disk
- These do occupy space and you will be charged
- They do not rely on the base table unless you re-run or refresh the view query
- Must be in the same Dataset at the source tables!
- Inherit the expiration times of the source
- Provide the latest data including streaming tables
- Faster than normal views
- Smart tuning
- If a query or subquery on a table can be served with an already created Materialized View, BQ reroutes the query to use Materialized view for efficiency.
- SELECT name, SUM(count) as total FROM `proj.ds.table` GROUP BY name
- If this or a subquery of this can use a materialized view (mv), it will
- Uses less bytes
- Use Cases
- ETL or BI pipelines
- Highly computational queries like aggregations
Views vs. Materialized Views (Not part of the class)
Views
- A short/simplified version of the query used to create the view.
- Every time you run a query against the view, you are actually running the query that created the view in the background, then running your query against those results.
- Your data is always up to date
- If the “creation query” is expensive or slow, so will all queries against the view.
- You can create a View in a different dataset than the original table(s)
- This allows you to set different access permissions on the View
- Example: You can grant access to the View while blocking access to the actual table
Materialized Views
- Also a short/simplified version of the query used to create the view.
- Materialized Views are actual tables created using the “create query”
- Queries against the MV are ran against the table created, so are faster than Views
- Your data can get stale if the MV are not refreshed
- You cannot create a MV in a different dataset than the original tables.
- You can use Partitioned Tables and Clustering
52. Create a Materialized View
https://www.udemy.com/course/bigquery/learn/lecture/22758507#overview
Note: Materialized Views are still in Beta and features and functionality are still under development
Create the view
- Standard SQL
- Cannot use Table Joins
- Limited set of aggregation functions
- APPROX_COUNT_DISTINCT
- ARRAY_AGG
- HLL_COUNT.INIT
- MAX, MIN, SUM, COUNT, AVG
- Stacked functions are not supported
- ROUND(AVG(count))
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW proj.ds.table_mv as SELECT name, SUM(count) as total FROM proj.ds.table group by name- I don’t see any back-tics on the table names….
- You cannot use `HAVING` clause. To use this, use it on the MV.
- UNLESS Auto-refresh is disabled, an auto-refresh will start running as soon as the initial build query runs.
- Once it completes creation, it will appear in the table list.
- You can create Partitioned and Clustered MVs
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW proj.ds.mv PARTITION BY date AS SELECT name, SUM(count) as total, _PARTITIONDATE as date FROM proj.ds.partitioned_table WHERE _PARTITONDATE = "YYYY_MM_DD" GROUP BY 1,3
- 1, 3 refers to the position of the columns being returned
Smart Tuning Demonstration
- Locate the code for the MV
- MV > Details > Scroll down to Query
- Copy/paste the query into the editor and run it.
- Note that the source table is the original table and not an MV
- Once the query completes, click the “Execution Details” tab near “Results”
- Scroll down and expand a job. You’ll see it used the MV and not the original source table
To prevent smart tuning:
- Add a where clause to the query
SELECT name, SUM(code) as total_count FROM proj.ds.table WHERE rand() < 1 GROUP BY name
53. ALTER a Materialized View
https://www.udemy.com/course/bigquery/learn/lecture/22759071?start=0#overview
Allowed
- CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW…
- ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW `proj.ds.mv` SET OPTIONS…
- (enable_refresh = true)
- DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW `proj.ds.mv`
No others are allowed
Not allowed
- Running COPY, IMPORT or EXPORT jobs where either the source or the destination is a materialized view
- Writing query results into a materialized view
- Using the BQ Storage API
54. Design an optimized query for Materialized View
https://www.udemy.com/course/bigquery/learn/lecture/22759107#overview
How to design a query such that it always hits the MV
Sub queries are supported
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
proj.ds.mv
AS SELECT
name,
total_count
FROM (
SELECT
name,
count(*) as total_count
FROM
proj.ds.table
GROUP BY
name
)
Use the grouping keys from the MV
- Notice how you are actually calling the Table, not the Materialized View
- The field ‘total_count’ does not exist on the table, so it will use the Materialized View instead.
SELECT name, total_count FROM proj.ds.table
Performing computation on grouping keys
SELECT name, AVG(total_count) as ave_count FROM proj.ds.table
Ad-hoc query contains filters on grouping columns OR direct filters of MV definition
Create MV
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW proj.ds.mv AS SELECT DATE(shipdate) as shipdate, SUM(price) as sum_price FROM proj.ds.table WHERE shipping_mode = "land" GROUP BY 1
Ad-Hoc Query
SELECT shipdate, SUM(price) as sum_price FROM proj.ds.table WHERE [optional filter AND ] shipping_mode = "land" GROUP BY 1
Ad-hoc query contains a filter which is a subset filter of the MV definition
- While the filter is not exactly the same, it is a subset of the Create view.
Create MV
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW proj.ds.mv AS SELECT price, COUNT(*) as cnt FROM proj.ds.table WHERE price IS NOT NULL GROUP BY 1
Ad-hoc Query
SELECT price, COUNT(*) as cnt FROM proj.ds.table WHERE price > 100 GROUP BY 1
55. Auto and Manual Refreshes of Materialized Views
https://www.udemy.com/course/bigquery/learn/lecture/22766733#overview
Updates
- If an update (alter) is performed prior to the next refresh
- The portions that have changed will be invalidated and reread
- If on a partition, only the partition will be invalidated and reread
- If only inserts
- The changes are added to the materialized view
Manual Refresh
- REFRESH_MATERIALIZED_VIEW
- BQ looks for the changes in the base table and applies those changes to the MV
CALL BQ.REFRESH_MATERIALIZED_VIEW('proj.ds.mv_table_name')- BQ is literal. It is not an abbreviation for ‘BigQuery’ in this case
- The table name in the command is in single quotes, not back ticks.
- View ‘Details’ to see the refresh time
Automatic
- By default, Materialized Views are updated within 5 minutes of changes to the base table
- Not ‘Every 5 minutes’
- If constant changes are made to the base table
- Refreshes are performed per Refresh Interval (ms) which is default 1,800,000 ms (30 minutes)
- ‘Details’
Setting the Refresh Interval
- Minimum refresh cap = 1 minute
- Maximum = 7 days
At time of creation
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW proj.ds.mv OPTIONS (enable_refresh = true, refresh_interval_minutes = 60) AS SELECT ...
Alter an existing MV
ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW `proj.ds.mv` SET OPTIONS (enable_refresh = true, refresh_interval_minutes = 60)
Keeping the MV up to date
- BQ ensures your query replies are ALWAYS up to date
Appends Only
- Fetch all materialized data
- Read the delta
- Adjust the aggregations as per delta
- Show results
Updates or Deletions
- Materialized View might not be scanned
- Query will hit the base table only
- You might have to wait until the next refresh before the queries start using the MV again.
56. Limitations and Quotas of Materialized Views
https://www.udemy.com/course/bigquery/learn/lecture/22766737#overview
- You cannot copy a MV either as a source or destination of a copy job
- Cannot export data
- Cannot load data into MVs using load query
- Cannot write data to it – READ ONLY
- No DML statements
- SHOULD be in the same dataset location
- Supports limited aggregation functions in query definitions
- Only 1 reference table. No joins during creation
- Cannot be nested
- Only Standard SQL
- Maximum 20 MVs per base table
57. Best Practices
https://www.udemy.com/course/bigquery/learn/lecture/22766743#overview
- Do not create Materialized views for every permutation of a query
- Create them for broader use.
- If your users often filter on a date range, add a date range filter on your query that includes that set of dates.
- if the base table is large and partitioned, your MV should be partitioned as well.
- If the MV is about the same size or larger than a partition, then partition the MV
- Refreshes are expensive. Do some analysis to determine the necessary refresh interval
- if the base table is updated relatively infrequently, then refresh less often.
- Batch DML statements and manual refresh your MVs after.
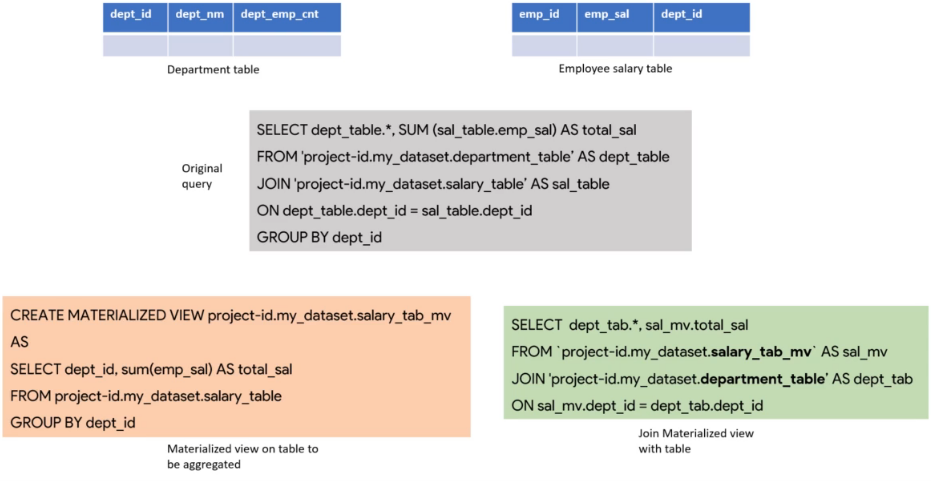
Work around for Joins on Materialized Views
- Create the MV on the aggregated view
- Run your query as shown