Section 11: Views in BigQuery
47. Introduction to Views & their Advantages
https://www.udemy.com/course/bigquery/learn/lecture/22757841#questions
View Overview
- Views do not contain any data of its own
- Can be created by selecting any number of rows or columns of it base table/tables
- Views can reflect the results of a JOIN query on any number of tables.
- Once created, views become independent of the base table.
- The View schema is frozen and will not reflect changes made to the base table schema
- To change a View schema, you have to change the underlying view definition query
- Changing a View schema will not change it’s base table’s schema
- Views are read only
- Drop the base table and you cannot run queries against the view, since Views do not contain their own underlying data.
Advantages of Views
- Protect base table from being accidentally dropped or altered.
- Can help turn lengthy and complicated query into a one-liner.
- No additional storage costs
- Again, no data exists in the view.
- Queries are still charged
- Views prevent direct access to tables for security reasons.
- Users are restricted to getting data from Views only
- Different users should be provided different data accesses
- Higher users would have access to to all columns in our tables data,
- Others are only provided limited access to limited columns
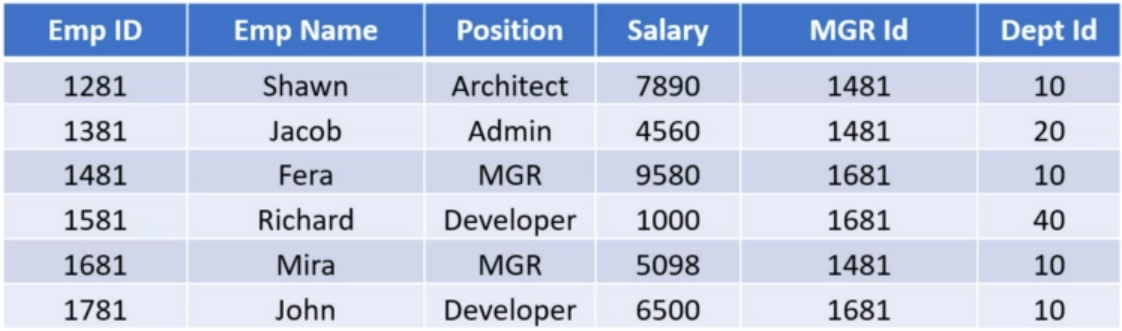
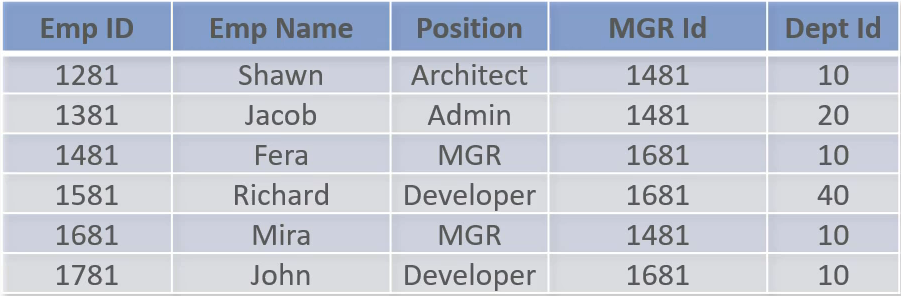
View Access Example
- Access to this table required by users in various depts.
- HR
- Requires access to all columns
- Support
- Only need Emp ID, Name, Position, Mgr and Dept Id
- HR
Support View
48. Create Views in BQ
https://www.udemy.com/course/bigquery/learn/lecture/22757847#questions
- Create a view with 2 columns and 100 rows
- select names, gender from `proj.ds.table` limit 100
- Click [ Save View ]
- Views must be stored in the same region as the table data
- Provide a name for the view
- You cannot add a Description, Expiration or Labels at creation time using the UI
- Possible with CLI or API
- Possible after creations
- Expiration dates are default to the Table’s, but can be set shorter.
Limit Access to Views
- To limit access to a few columns, create a view with only those columns
- To limit access to a View
- Views are treated as Table resources in BQ
- There is no option to assign access controls directly to Tables or Views
- The lowest level of BQ that you are able to grant access is the dataset level
- Therefore, you cannot granularly grant access to specific tables and views in that dataset.
- To grant access to a Dataset
- Create a Cloud IAM role to an entity at the dataset level or higher (Project?)
- Users with that role will only be able to perform the set of operations on all tables and views present in that dataset.
- Limiting access to only Views
- Create the View in a different Dataset than the source tables!
- Creating the View in the same dataset would not make sense… the user would have access to the tables also!
- Always create Views in a different dataset than the source tables!
Copying and Renaming Views
- Copy
- Currently only available via UI
- Not available via API, CLI or client libraries
- You will need to recreate the view if using these
- View > [ Copy View ]
- Currently only available via UI
- Rename
- This option is not available.
- Copy the view to a new name, then delete the current view.
- Deleting a view cannot be undone.
49. Restrict rows at User level in Views
https://www.udemy.com/course/bigquery/learn/lecture/22758315#overview
Restricting Rows
session_user() = email address of current user
- Create a new table with user email address assigned to groups
- group_id, email
- Create a new column on the source table that include the access group ID
- Create a view that joins both tables
select data.* from `proj.ds.data` as data JOIN `proj.ds.groups` as group ON data.group_id=group.group_id where group.email="john.doe@johndoe.com"
50. View Limitations and Quotas
https://www.udemy.com/course/bigquery/learn/lecture/22758305#overview
Limitations
- Datasets containing the View and Table must be in the same location
- Data from a View cannot be exported
- A standard SQL query cannot reference a view defined using legacy SQL syntax
- You cannot reference query parameters in Views
- To be discussed later
- You cannot include a User-defined function in View definition
- You cannot reference a view in a wildcard table query
Quotas
- Maximum nested views = 16
- A view created from another view
- select * from `proj.ds.view`
- If you delete a parent view, the child views will not work
- A view created from another view
- Maximum number of views in a dataset = 2500