https://quizlet.com/167611061/cissp-practice-questions-flash-cards/
25 What logical operation is described by the truth table shown here?
| Input 1 | Input 2 | Output |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
A. OR
B. AND
C. XOR
D. NOR
26. How many bits of keying material does the Data Encryption Standard (DES) use for encrypting information?
A. 56
B. 64
C. 128
D. 256
- Cracked in 1998
- Removed as a ‘Standard’
- Triple DES (3DES) uses the same algorithm, but 3 keys. Encrypt with K1, decrypt with K2 and re-encrypt with K3.
27. In the figure shown here, Harry’s request to write to the data file is blocked. Harry has a Secret security clearance, and the data file has a Confidential classification. What principle of the Bell-LaPadula model blocked hist request?
A. Simple Security Property – a subject at a given security level may not read an object at a higher security level.
B. Simple Integrity Property – Biba: a subject at one level of integrity is not permitted to read an object of lower integrity.
C. *-Security Property – a subject at a given security level may not write to any object at a lower security level.
D. Discretionary Security Property – Uses an Access Matrix (therefore, discretionary)
- Top Secret
- Secret
- Confidential
28. Florian and Tobias would like to begin communicating using a symmetric cryptosystem, but they have no prearranged secrey and are not able to meet in person to exchange keys. What algorithm can they use to securely exchange the secret key?
A. IDEA – International Data Encryption Algorithm. (Cracked in 2011)
B. Diffie-Hellman – A system of creating a shared key without reveling your key
C. RSA – Rivest–Shamir–Adleman- One key to encrypt, another to decrypt.
D. MD5 – (Message Digest 5)Hashing system for file integrity.
Keyword: ‘Symmetric’
29. Under the Common Criteria, what element describes the security requirements for a product?
A. TCSEC (The Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria aka Orange Book) American
B. ITSEC (Information Technology Security Evaluation Criteria) European structured set of criteria for evaluating computer security within products and systems.
C. PP (Protection Profile) A PP allows security requirements to be expressed using a template in an implementation-independent way, and is thus reusable.
D. ST (Security Target) contains a set of security requirements that can be stated explicitly. An ST includes detailed product-specific information. It can be viewed as a refinement of the PP, and forms the agreed-upon basis for evaluation.
30. Which one of the following is not one of the basic requirements for a cryptographic hash function?
A. The function must work on a fixed length input. (Requires a fixed length output!)
B. The function must be relatively easy to compute for any input.
C. The function must be one way. (Difficult to find the input based on the output)
D. The Function must be collision free. (Difficult to define two inputs that produce the same output.)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryptographic_hash_function
31. How many possible keys exist for a cipher that uses a key containing 5 bits?
A. 10
B. 16
C. 32 25 = 32
D. 64
32. What cryptographic principle stands behind the idea that cryptographic algorithms should be open to public inspection?
A. Security through obscurity – The presumption that “nobody will ever find it”.
B. Kerckhoffs’ principle – A cryptosystem should be secure even if everything about the system, except the key, is public knowledge.
C. Defense in depth – (aka Castle Approach) is a concept in which multiple layers of security controls (defense) are placed throughout a system.
H. Heisenburg principle – You cannot have complete security and privacy at the same time. If we allow our employees to encrypt their email, we cannot ensure that no confidential information is communicated to untrusted parties at the same time. If you ‘peek’ at the emails to ensure security, you’ve lost privacy.
33. Referring to the figure shown here, what is the name of the security control indicated by the arrow?
(Chapter 10, pg 423)
A. Mantrap – a small space with two sets of interlocking doors, such that the first set of doors must close before the second set opens.
B. Turnstyle – a post with arms pivoted on the top set in a passageway so that persons can pass through only on foot one by one.
C. Intrusion Prevention System – A network security/threat prevention technology that examines network traffic flows to detect and prevent vulnerability exploits.
D. Portal – a set of two interlocking doors where the first set of doors opens before the second set, causing the user to be contained in an enclosed area temporarily. The user must provide valid authorization to pass through the first set of doors into the portal, and may be required to provide secondary authorization credentials (often biometric) to pass through the second set of doors
34. Which one of the following does not describe a standard physical security requirement for wiring closets?
C10, p406
A. Place only in areas monitored by security guards.
B. Do not store flammable items in the closet. True
C. Use sensors on doors to log entries. True
D. Perform regular inspections of the closet. True
35. In the figure shown here, Sally is blocked from writing to the data file by the Biba integrity model. Sally has a Secret security clearance and the file is classified Top Secret. What principle is preventing her from writing to the file?
A. Simple Security Property – A subject at a given security level may not read an object at a higher security level. (No read up)
B. Simple Integrity Property – A subject at one level of integrity is not permitted to read an object of lower integrity. (No read down)
C. *-Security Property – A subject at a given security level may not write to any object at a lower security level. (No write down)
D. *-Integrity Property – A subject at a given level of integrity must not write to data at a higher level of integrity (no write up)
Key: Integrity Principle writing to a higher clearance level.
36. Match each of these following numbered architecture security concepts with the appropriate lettered description:
1. Time of check
2. Covert channel
3. Time of use
4. Maintenance hooks
5. Parameter checking
6. Race condition
A. A method used to pass information over a path not normally used for communication
B. The exploitation of the difference between time of check and time of use.
C. The time at which the subject checks whether an object is available
D. The time at which a subject can access an object
E. An access method known only to the developer of the system.
F. A method that can help prevent buffer overflow attacks
Answers
1 – C
2 – A
3 – D
4 – E
5 – F
6 – B
37. What is the minimum number of independent parties necessary to implement the Fair Cryptosystems approach to key escrow?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
In the Fair Cryptosystems approach to key escrow, the secret keys used in communications are divided into two or more pieces, each of which is given to an independent third party.
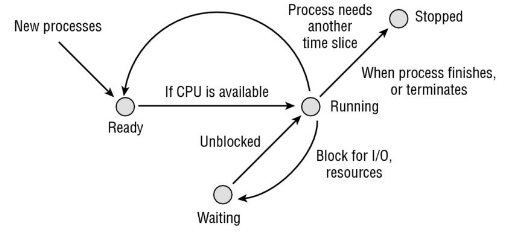
38. In what state does a processor’s scheduler place a process when it is prepared to execute but the CPU is not currently available?
A. Ready – State where a process has been assigned to a CPU.
B. Running – State when a process is executing on the CPU.
C. Waiting – State if it needs a currently unavailable resource, such as user input, or for a file to become available.
D. Stopped – State where a process waits to be removed from main memory.
39. Alan is reviewing a system that has been assigned to EAL1 evaluation assurance level under the Common Criteria. What is the degree of assurance that he may have about the system?
A. It has been functionally tested. (EAL1)
B. It has been structurally tested. (EAL2)
C. It has been formally verified, designed and tested. (EAL7)
D. It has been methodically designed, tested and reviewed. (EAL4)
40. Which one of the following components is used to assign classifications to objects in a mandatory access control system?
A. Security label
B. Security token
C. Security descriptor
D. Security capability
41. What type of software program exposes the code to anyone who wishes to inspect it?
A. Closed source – Non-free computer software for which the software’s publisher or another person retains intellectual property rights.
B. Open source – Software that the general public can access and use and the source code is available for anyone to look at.
C. Fixed source – Same as Closed?
D. Unrestricted source – Whaatt?
42. Adam recently configured permissions on an NTFS filesystem to describe the access that different users may have to a file by listing each user individually. What did Adam create?
A. An access control list – A list of access control entries
B. An access control entry – Monitors access to an object by a specified trustee.
C. Role-based access control – Allows access to objects based on a job function.
D. Mandatory access control – a set of security policies constrained according to system classification, configuration and authentication. (MAC)
43. Betty is concerned about the use of buffer overflow attacks against a custom application developed for use in her organization. What security control would provide the strongest defense against these attacks?
A. Firewall – Device that allow or denies traffic to various systems based on IP addresses and Ports
B. Intrusion detection system – Network device that detects suspicious/malicious traffic based on patterns/activity
C. Parameter checking – A method that can help prevent buffer overflow attacks
D. Vulnerability scanning – A security technique used to identify security weaknesses in a computer system.
Hint: 2 of these simply detect.
44. Which of the following terms is not used to describe a privileged mode of systems operations?
A. User mode – Mode set for non-privileged instructions
B. Kernel mode – Privileged <CPU> instructions can only be executed in Kernel mode.
C. Supervisory mode – aka Kernel mode
D. System mode – aka Kernel mode
45. James is working hard with a Dept. of Defense system that is authorized to simultaneously handle information classified at the Secret and Top Secret levels. What type of system is he using?
A. Single state – Systems that are dedicated to handle one security level at a time. All users must be certified to that security clearance.
B. Unclassified – Information that can be released to individuals without a clearance
C. Compartmented – ???
D. Multistate – Systems are certified to handle multiple security levels simultaneously by using specialized security mechanisms.
46. Kyle is being granted access to a military computer system that uses System High mode. What is not true about Kyle’s security clearance requirements?
A. Each user must have a clearance for the highest level of classification processed by the system regardless of his access.
B. Each user must have access approval for all information processed by the system.
C. Each user must have a valid need to know for some information processed by the system but notnecessarily all information processed by the system.
D. Each user must have a valid security clearance.
Hint: A valid security clearance could be anything.
47. Gary intercepted a communication between two individuals and suspects that they are exchanging secret messages. The content of the communications appears to be the image shown here. What type of technique may the individuals use to hide messages inside this image?
A. Visual cryptography – Encrypting an image into multiple images such that each sub image is required to reconstruct the original image.
B. Steganography – the practice of concealing a file, message, image, or video within another file, message, image, or video.
C. Cryptographic hashing – a string of random-looking characters that uniquely identifies the data in question. One way, used to validate the contents of a file.
D. Transport layer security – (TLS) a protocol that provides communication security between client/server applications that communicate with each other over the Internet.
48. Which of the following terms accurately describes the Caesar cipher?
ABCDEFGHI J KLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
CDEFGHI J KLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZAB
HAIL CEASAR
JCKN EGCUCT
A. Transposition cipher – a system of changing the positions of plain text.
B. Block cipher – Using a set key length to transpose blocks of similar length. These new blocks can then be used as keys to further encrypt additional blocks.
C. Shift cipher – Substitute each character for one x positions away.
D. Strong cipher – Difficult to crack?
Transposition example: WE ARE DISCOVERED FLEE AT ONCE
Rail cypher:
W . . . E . . . C . . . R . . . L . . . T . . . E . E . R . D . S . O . E . E . F . E . A . O . C . . . A . . . I . . . V . . . D . . . E . . . N . .
WECRL TEERD SOEEF EAOCA IVDEN
Route cypher:
W R I O R F E O E E E S V E L A N J A D C E D E T C X
EJXCTEDEC DAEWRIORF EONALEVSE
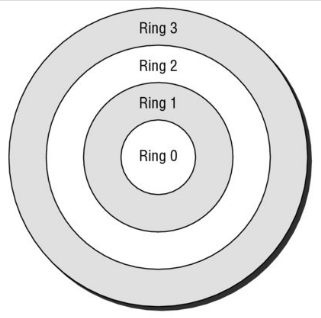
49. In the ring protection model shown here, what ring contains the operating system’s kernel?
A. Ring 3
B. Ring 2
C. Ring 1
D. Ring 0
- Ring 0: OS Kernel/Memory
- Supervisory (Privileged) mode
- Ring 1: Other OS components
- Supervisory (Privileged) mode
- Ring 2: Drivers, Protocols, etc.
- Supervisory (Privileged) mode
- Ring 4: User-Level programs and applications
- User mode
50. In an infrastructure as a service (IaaS) environment where a vendor supplies a customer with access to storage services, who is normally responsible for removing sensitive data from the drives that are taken out of service?
A. Customer’s security team
B. Customer’s storage team
C. Customer’s vendor management team
D. Vendor