Video Links
https://www.youtube.com/user/SASsoftware/search?query=Kerberos
Kerberos Overview
Components
KDC Key distribution center
- AS – Authentication Service
- TGS – Ticket Granting Service
Client
- Could be a User’s PC
- Could be a service that wishes to access another
Server
- What the client requires access to.
Keys
- Long Term Keys
- Synonymous with Passwords
- TGS ltk for the Ticket Granting Service
- Service ltk for the service to be connected to
- User ltk
- Session Keys (Short-Term Keys)
- Service Session key
- Limited lifetime
- Unique for the Client’s connection to the service.
- TGS Session key
- Associated with the Client’s connection with the TGS.
- Service Session key
Protocol Overview
Authentication Service Request
Initial Authentication (Not sure about this part)
Client to AS: This is my ID in clear text
AS to Client: Preauth error – You need to authenticate!
KRB_AS REQ: Initial request from the Client (User) to the Authentication Service
- Authenticator encrypted with the User’s LTK
- Information about who is requesting authenticating
KRB_AS_REP: Authenication Service to Client response
- TGS Session Key encrypted using the User LTK
- Use this to talk to the TGS for a limited time.
- TGT (Ticket Granting Ticket) encrypted with the TGS LTK
- Client ID
- Client IP address
- Ticket validity period (sounds like a TTL)
- TGS Session Key (copy of same above)
Ticket Granting Service Request
KRB_TGS_REQ: Client to Ticket Granting Service request
- Authenticator encrypted with TGS Session Key
- Can be decrypted with the Session key sent from the AS
- TGT encrypted with the TGS LTK
- This is decrypted first so the TGS can extract the data in the Authenticator.
- This allows the TGS to NOT need to keep copies of these keys.
KRB_TGS_REP: TGS to Client response
- Service Session Key encrypted using the TGS Session Key (Client has this)
- Service Ticket encrypted with the Service’s LTK
- Client ID, IP, TTL
- Service Session Key
Client/Service Authentication Request
KRB_AP_REQ*: Client to Service request
- Authenticator encrypted with the Service Session Key
- Service Ticket encrypted with the Service’s LTK
KRB_AP_REP*: Service to Client response (optional?)
- Authenticator encrypted with the Service Session Key
- Allows the client to know they’ve connected to the right service!
* These services are unlikely to be viewed via WireShark directly because they are often wrapped within different protocols, such as GSSAPI.
Delegating / Forwarding Authentication
- Delegating: Microsoft AD term
- Forwarding: MIT term
Overview:
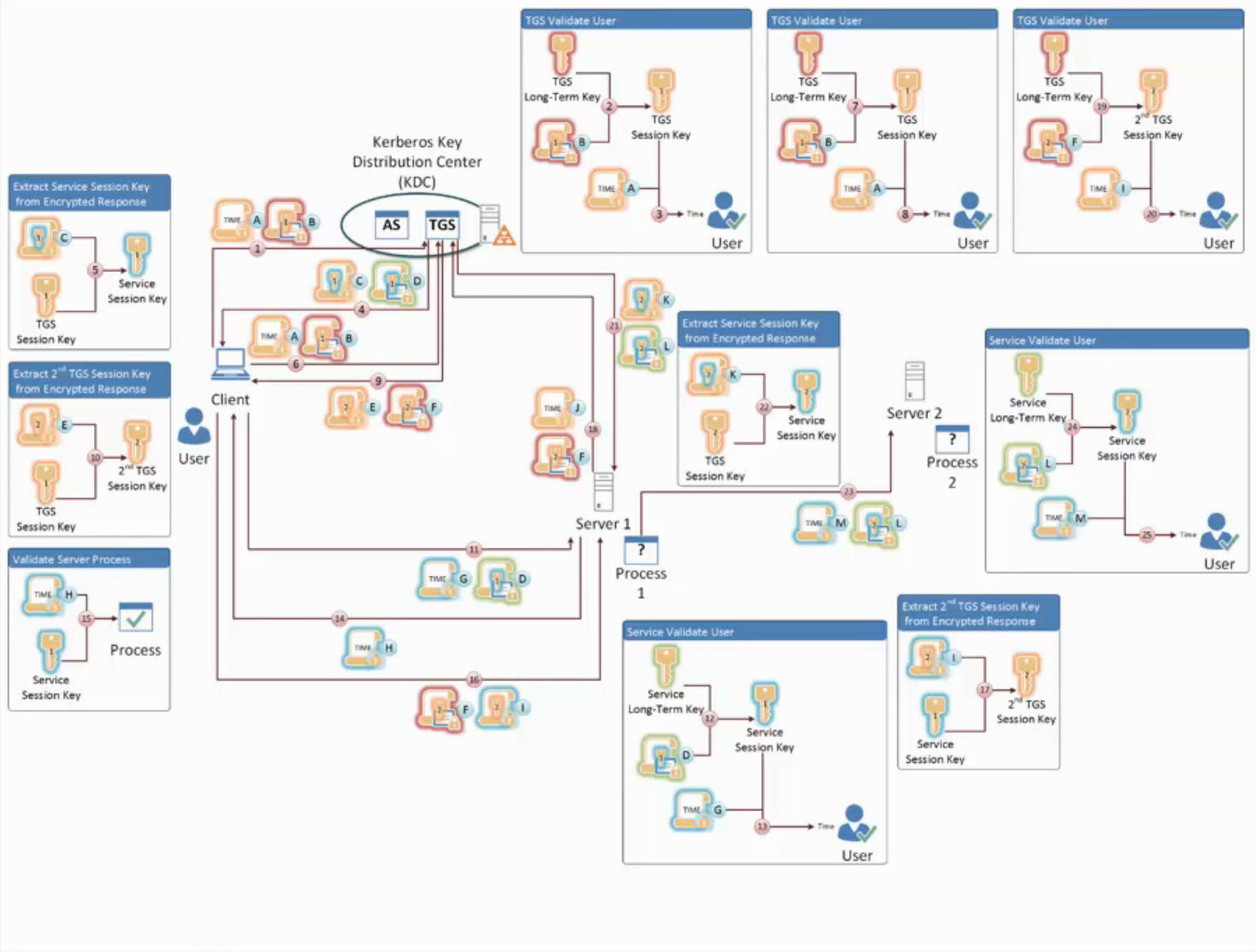
Use the authentication credentials obtained to access the first service to obtain a ticket to access a second service. (Propagate the end user credentials from the first service to the second service.)
Initial Authentication has already taken place.
TGT has been obtained.
(1) KRB_TGS_REQ sent by client for Service #1
- A Authenticator (Client/TGS Session Key)
- B TGT (TGS key)
- Contains the Client/TGS Session Key
(4) KRB_TGS_RES sent by TGS for the first service.
- C Service #1 Session Key (TGS Session Key)
- D Service Ticket (Service #1’s LTK)
(6) KRB_TGS_REQ sent by client for a Forwardable TGT for Service #2
- A Authenticator (Client/TGS Session Key)
- B TGT (TGS key)
- Contains the Client/TGS Session Key
(9) KRB_TGS REP sent by TGS for Service #2
- E Service #2 Session Key (Client/Service #1 Session Key)
- F Forwarded TGT (Service #2 Session Key)
- Client will have access to both keys.
(11) KRB_AP_REQ sent from Client to Service #1 (Wrapped inside connection protocol)
- D Service #1 Service Ticket (Service #1 LTK)
- G Authenticator (Client/Service #1 Session Key)
(14)KRB_AP_RES Sent from Service #1 to Client (Optional)
- H Service #1 Authenticator (Client/Service #1 Session Key)
(16) KRB_CRED sent from Client to Service #1
- F Forwarded TGT (
- I Second copy of TGS Session Key (Client/Service #1 Session Key)
(18) KRB_TGS_REQ sent from Service #1 to TGS
- F Forwarded TGT (TGS LTK)
- 2nd TGS Session Key
- J Authenticator for Service #1 (
(21) KRB_TGS_RES sent from TGS to Service #1
- K 2nd Service Session Key (2nd TGS Session Key from F)
- L Service Ticket for Service #2
(23) KRB_AP_REQ or Protocol used for Service 2 sent from Service #1 to Service #2
- L Service Ticket for Service #2
- M Authenticator for Service #1 (Service #2 Session Key)
(26) KRB_AP_RES sent from Service #2 to Service #1 (Optional)
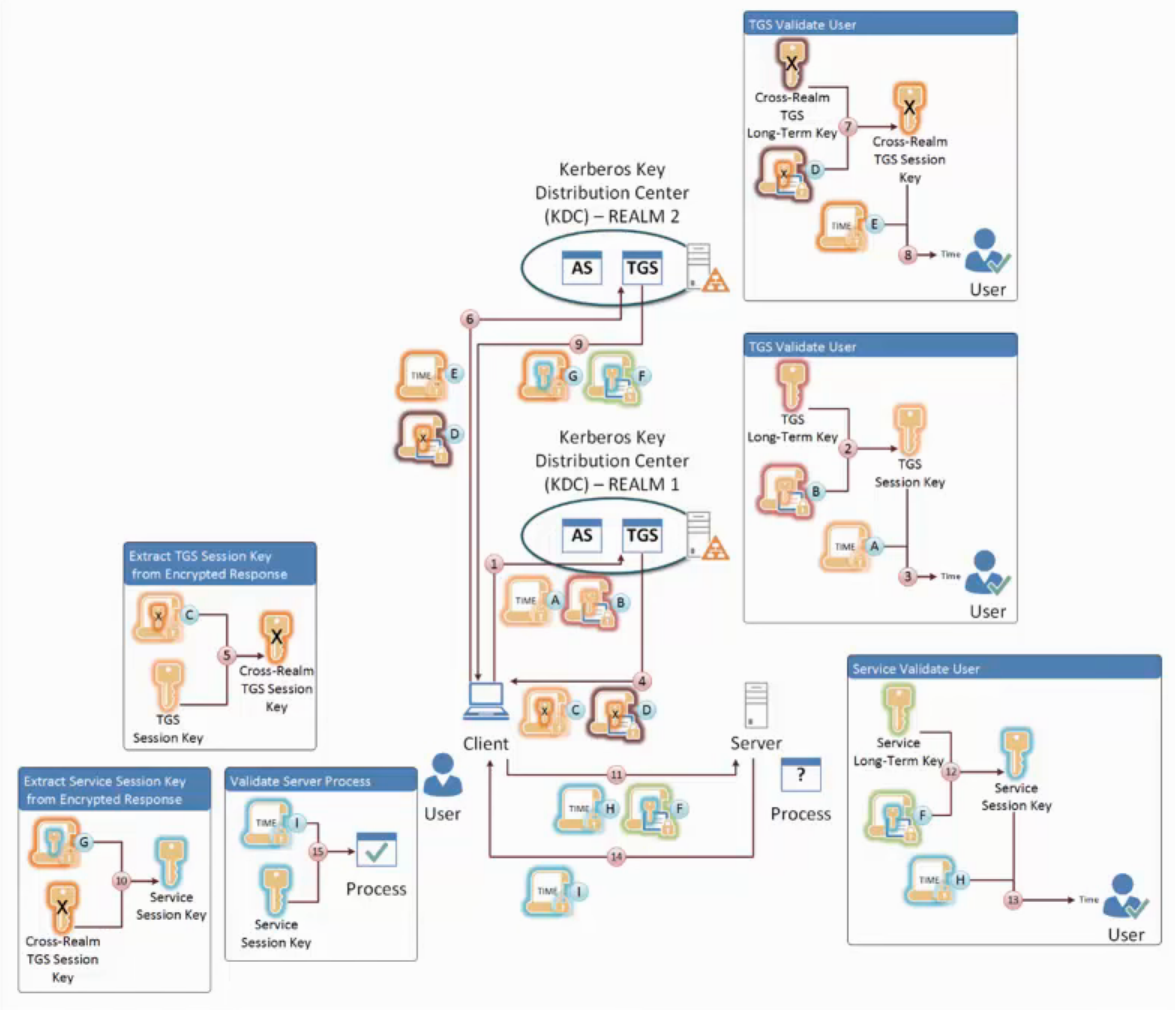
Cross Realm Authentication
12:35
Client and Server are in different Kerberos Realms
A cross-realm trust must be correctly configured prior to performing this successfully