< Section 21 | Home | Section 23 >
69% Complete
138. Introduction
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8657516#content
139. DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8657522#content
- DHCP is a client/server protocol that automatically provides a host with its IP address and other related configuration information such as the subnet mask, default gateway and DNS server.
- DHCP clients obtain their IP configuration information from a DHCP server, rather than being manually configured.
How DHCP Works
- Client sends a DHCP discover message using broadcast traffic
- Server replies with a DHCP Offer (IP, Subnet, DNS, etc)
- Client replies with a request to keep these settings
- Server responds with an acknowledgement saying the settings have been recorded for that MAC address.
DHCP Benefits – Reduced Network Admin
- Centralized and automated IP configuration, rather than manually assigning and managing IP address for every host.
- DHCP minimizes configuration errors caused by manual IP address configuration
- Typos
- Address conflicts caused by the assignment of an IP address to more than one computer at a time.
- Can assign additional IP configuration values by means of DHCP options.
- IP Phones need to know their server’s address.
- Efficient handling of clients that must be updated frequently, such as laptops that move to different locations on a wireless network.
- IP addresses are automatically updated.
- The forwarding of initial DHCP messages by using a DHCP relay agent, which eliminates the need for a DHCP server on every subnet.
Recommended DHCP Clients
- Desktop PCs and Laptops
- There are generally many of these on a network. – Saves a lot of admin time.
- They do not accept incoming connections so it doesn’t matter if their IP address changes.
Non-Recommended DHCP Clients
- Servers and Network infrastructure Devices
- Mission critical devices which do not move and are required for the network to function
- Their IP address should be manually configured so they do not change and are not dependent on DHCP
- These do require incoming connections
140. Cisco DHCP Server
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8657534#overview
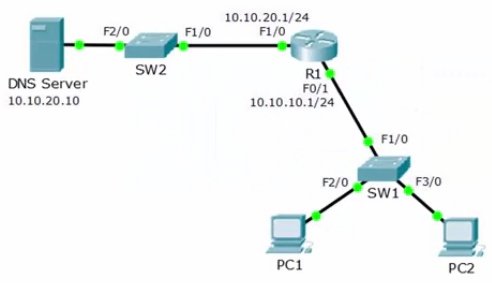
DHCP Server Router Configuration
Usually used for small branch offices
Exclude static address ranges
- It is best to reserve some IP addresses for networking and other static IP devices. This should be done first before clients are accidentally assigned IPs in this range.
R1(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address 10.10.10.1 10.10.10.10
Configure DHCP
- You can name the DCHP pool anything you like.
R1(config)#ip dhcp pool 10.10.10.0_Clients R1(config-dhcp)#network 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 R1(config)#default-router 10.10.10.1 R1(config)#dns-server 10.10.20.10
Verify the DHCP Pool was correctly created
show ip dhcp pool
View which IPs have been auto-assigned using DHCP
show ip dhcp binding
Lab Configuration
Exclude static address first
R1(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address 10.10.10.1 10.10.10.10
Create the DHCP Pool
R1(config)#ip dhcp pool Demo R1(config-dhcp)#network 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 R1(config)#default-router 10.10.10.1 R1(config)#dns-server 10.10.20.10
Verify it is working
show ip dhcp pool
View which IPs have been auto-assigned using DHCP</h3
show ip dhcp binding
141. External DHCP Server
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8657538#overview
Description
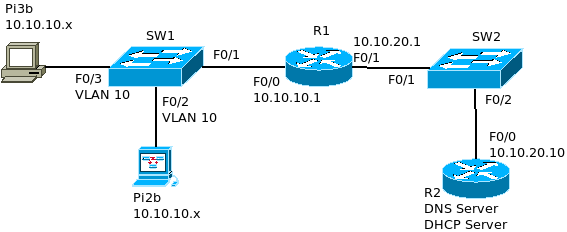
- Pi2b sends a DHCP broadcast request for an IP address
- SW1 sends that request out F0/1 and F/03
- R1 and Pi3b are NOT DHCP servers, so they drop the packets
- Since Routers do not forward broadcast traffic…
- HOW DOES THE REQUEST REACH THE DHCP SERVER?
Solution
R1(config)#int f0/0 R1(config-if)#ip helper-address 10.10.20.10
142. Cisco DHCP Client
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8657546#overview
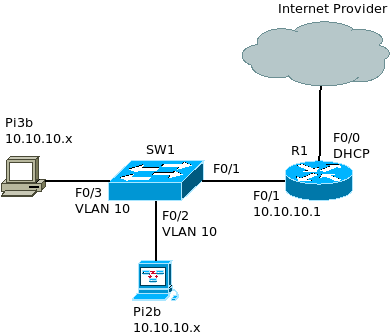
- Cisco routers are typically manually configured with Static IP address
- An exception is where an office is connected to the Internet and they have not purchased a static Public IP.
- They would not have a need for any incoming connections
- The office would still require a public IP to allow internal hosts access to the Internet via NAT.
- In this case, the router will receive the public IP from the service provider via DHCP.
R1(config)#int f0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address dhcp R1(config-if)#no shutdown
To view information regarding any DHCP leases
show dhcp lease
143. DHCP Lab Configuration
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8657550#overview
24-1 DHCP Configuration Lab Exercise
24-1 DHCP Configuration Answer Key
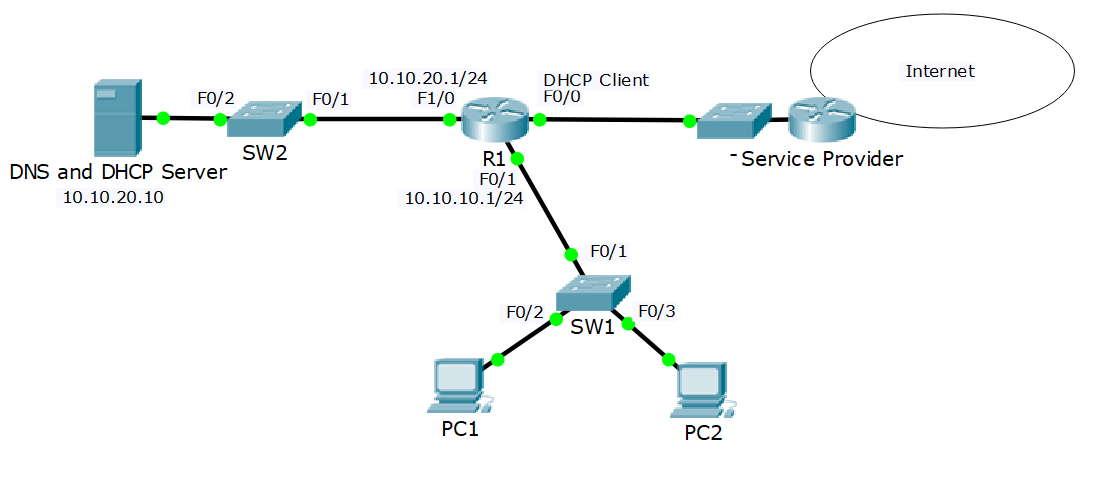
1. You have not acquired a static public IP address from the Internet service provider. Configure the outside interface FastEthernet 0/0 on R1 to receive its IP address using DHCP. The Service Provider is already configured and you have no access to it.
conf t int f0/0 ip address dhcp no shutdow
2. Verify that R1 received its public IP address via DHCP (you may need to wait a few minutes for the address to be assigned).
#2 ways show ip interface brief
3. What is the IP address of R1’s DHCP server?
203.0.113.2
4. Enable the DHCP service on R1 so it gives out IP addresses to the PCs in the 10.10.10.0/24 subnet. Leave IP addresses 10.10.10.1 – 10 free to be assigned to servers and printers. 10.10.20.10 is the DNS server.
conf t ip dhcp exclude-address 10.10.10.1 10.10.10.10 ip dhcp pool Eng network 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 10.10.10.1 dns-server 10.10.20.10
5. Verify the clients received their IP information via DHCP.
PC1
ipconfig ... FastEthernet0 Connection: Link-local IPv6 Address.........: FE80::200:CFF:FEA0:A359 IP Address......................: 10.10.10.11 Subnet Mask.....................: 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway.................: 10.10.10.1
6. Verify the clients can ping the DNS server by its hostname ‘DNSserver’ (it might take some time for DNS to resolve the hostname).
this is not working. everything seem correct. can ping 10.10.20.10 from both pcs
7. On R1, verify both clients received an IP address via DHCP.
sh ip dhcp binding
8. Cleanup – remove the DHCP server configuration on R1. You will use an external DHCP server instead in the next section.
no ip dhcp pool Eng no ip dhcp exclude-address 10.10.10.1 10.10.10.10
9. Enter the command ‘ipconfig /release’ on the PCs to release their IP addresses.
C:\>ipconfig /release IP Address......................: 0.0.0.0 Subnet Mask.....................: 0.0.0.0 Default Gateway.................: 0.0.0.0 DNS Server......................: 0.0.0.0
10. Enter the command ‘ipconfig /renew’ on the PCs and verify they can no longer obtain an IP address via DHCP
C:\>ipconfig /renew DHCP request failed.
11. The server at 10.10.20.10 has been configured as a DHCP server with a scope of IP addresses for the 10.10.10.0/24 subnet, but the PCs there are not receiving IP addresses. Why is this?
The Router interface has not been configured to forward these requests
12. Configure the network to allow the PCs to receive their IP addresses from the DHCP server.
conf t int f0/1 ip helper-address 10.10.20.10
13. Verify the clients received their IP information via DHCP.
PC1
C:\>ipconfig /renew IP Address......................: 10.10.10.101 Subnet Mask.....................: 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway.................: 10.10.10.1 DNS Server......................: 10.10.20.10