< Section 22 | Home | Section 24 >
71% Complete
ICND1 Exam Topic!
Know this section for the exam!
Resources:
144. Introduction
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8676906#content
Access Layer Switch Security Mechanisms
145. DHCP Snooping
https://www.udemy.com/course/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8676916#content
Access Layer Switch Security Mechanisms
- DHCP Snooping
- DAI Dynamic ARP Inspection
- 802.1X Identity Based Networking
- Port Security – MOST IMPORTANT
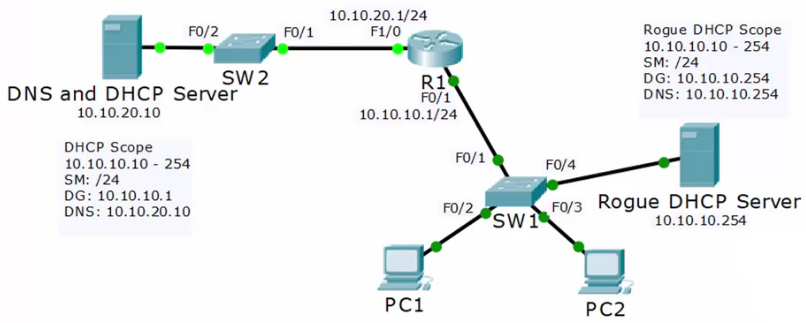
Rogue DHCP Server
- The rogue server would catch the DHCP request before it reaches the external one and will assign itself as the router to receive all traffic from the hijacked PCs.
- This would knock the PCs off the primary network.
- Odds are this was not a malicious attack, but someone connecting a server that had a DHCP server running on it.
DHCP Snooping
- When DHCP Snooping is enabled, DHCP server responses are dropped if they don’t arrive on a trusted port
- I had difficulty configuring this on my lab. It appears trust only works on trunk interfaces and not on access. Additionally, once DHCP was blocked by disabling the trust on the trunk, re-enabling it would sometimes still not allow that traffic through.
- I FINALLY GOT THIS TO WORK!!! For my switches, I had to use one final global command: no ip dhcp snooping information option
SW1(config)#ip dhcp snooping SW1(config)#ip dhcp snooping vlan 10 # Add the following command to disable Option 82, which prevents this from working! SW1(config)#no ip dhcp snooping information option SW1(config)#int f/01 SW1(config-if)#ip dhcp snooping trust
146. DAI Dynamic ARP Inspection
https://www.udemy.com/course/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8676920#questions
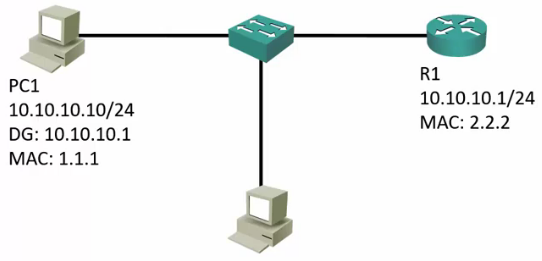
ARP Address Resolution Protocol
- PC1 wants to send a request to its Default Gateway at 10.10.10.1
- PC1 send an broadcast ARP request.
- This is seen by PC2 and R1
- R1 sees the request is for its IP:
- R1 caches PC1’s MAC
- R1 replies with its MAC address
- PC1 receives the reply
- PC1 caches R1’s MAC
- PC1 sends its packet.
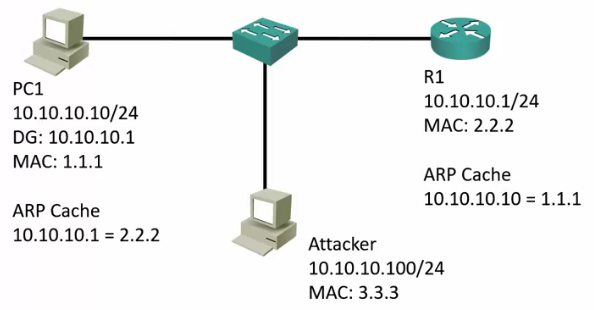
Man in the Middle ARP Spoofing
- This is almost always malicious!
- Can be used for packet sniffing/manipulation
- Can be used for denial of service: Drops the packet after it is received.
- Attacker sends unrequested ARP reply with R1’s IP and Attacker’s MAC
- All traffic from PC1 to R1 will flow through the Attacker.
- Attacker sends unrequested ARP reply with PC1’s IP and Attacker’s MAC
- All traffic from R1 to PC1 will flow through the Attacker.
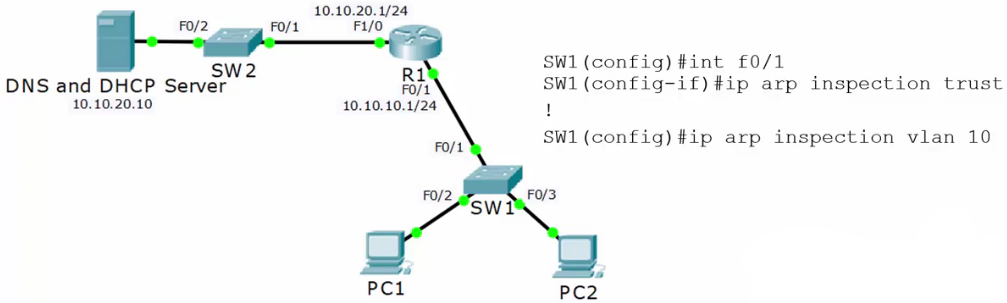
Dynamic ARP Inspection DAI
- When you enable DHCP snooping, the switch inspects the DHCP traffic and keeps track of which IP addresses were assigned to which MAC addresses
- Example: PC1 with MAC 1.1.1 was assigned 10.10.10.10
- If invalid ARP traffic tries to pass through the switch, for example, 3.3.3 says it is 10.10.10.10, the switch will drop the traffic.
DAI Configuration
- Enable IP DHCP Snooping Trust on all non-DHCP clients
- Servers, switches, routers, anything with a static IP.
- Do not set any ports that require DHCP as trusted
SW1(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/1 SW1(config-if)#ip arp inspection trust SW1(config-if)#exit SW1(config)#ip arp inspection vlan 10
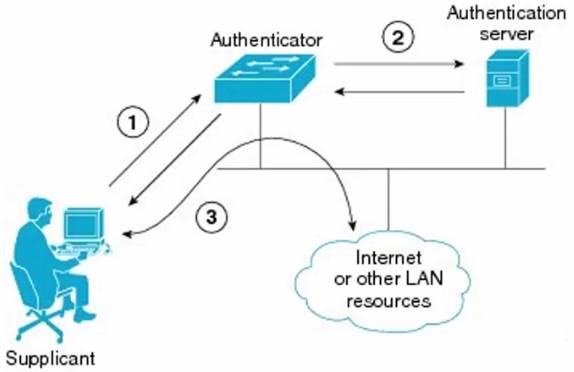
147. 802.1X Identity Based Networking
https://www.udemy.com/course/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8676940#content
- When 802.1X is enabled, only authentication traffic is allowed on the switch ports until the host and user are authenticated.
- When the user has entered a valid username and password, the switch port transitions to a normal access port in the relevant VLAN
- The PC (Supplicant) must have 802.1X authentication enabled in its Operating System.
- The PC will only have access to the Authentication Server until it has been authenticated.
- The authentication server is connected to (or might be?) an Active Directory server.
- Once authenticated, the switch will grant access to the other ports on its relevant VLAN.
148. Preventing Unauthorized Devices with Port Security
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8676960#content
Shut Down Unused Interfaces
- Best practice is to administratively shut down unused switch ports
- This stops somebody from getting access to the network if they physically connect to the port.
SW1(config)#int f0/1 SW1(config-if)#shutdown
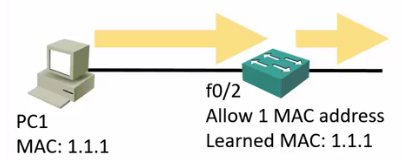
Port Security
- Port Security enables an administrator to specify which MAC address or addresses can send traffic in to an individual switch port.
- This can be used to lock a port down to a particular host or hosts.
- Unfortunately, it is easy to spoof a MAC address, so locking ports down to a specific host is not usually Port Security’s main role in production networks.
- Port Security can also configure individual switch ports to allow only a specific number of source MAC addresses so send traffic in to the port
- This prevents users from adding Wireless Access Points or other shared devices.
- If you allow only a single MAC, you would not be able to connect a switch to that port.
- It can learn connected MAC addresses.
Port Security Configuration
- Configured at the Interface level
SW1(config)#int f0/2 SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security
Port Security Default Behavior
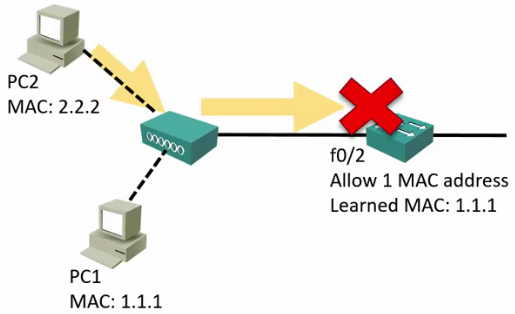
- If you configure Port Security with no additional parameters then only one MAC address is allowed to transmit on the port.
- The current MAC address can be disconnected and replaced. The port is NOT locked down to a particular MAC address.
- If a shared device is connected and multiple hosts try to transmit, the port will be shut down.
Port Security Verification – Defaults
SW1#show port-security interface f0/2 Port Security : Enabled Port Status : Secure-up Violation Mode : Shutdown Aging Time : 0 mins Aging Type : Absolute SecureStatic Address Aging : Disabled Maximum MAC Addresses : 1 Total MAC Addresses : 1 Configured MAC Addresses : 0 Sticky MAC Addresses : 0 Last Source Address : b827.eb62.35b2 Security Violation Count : 0
Security Violation Actions
- There are 3 options when an unauthorized MAC address tries to send traffic in to a protected port:
- Shutdown (Default): The interface is placed into the error-disabled state, blocking all traffic.
- Protect: Traffic from unauthorized addresses is dropped. Traffic from allowed addresses is forwarded.
- Restrict: Traffic from unauthorized addresses is dropped, logged and the violation counter incremented. Traffic from allowed address is forwarded.
Violation Action Configuration
SW1(config)#int f0/1 SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security violation protect SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security violation ? SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security violation shutdown
protect Security violation protect mode
restrict Security violation restrict mode
shutdown Security violation shutdown mode>/pre>
Error-Disabled Interfaces
- If the Violation Action is set to Shutdown and a violation occurs, the port will move to an error-disabled state.
- To bring an error-disabled interface back into service:
- Remove the host with the offending MAC address
- Manually shutdown, then ‘no shutdown’ the interface.
Error-Disabled Auto Recovery
Notice these are executed at the Global Configuration level and NOT on the interface!
SW1(config)#errdisable recovery cause psecure-violation SW1(config)#errdisable recovery interval 600
149. Preventing Unauthorized Devices with Port Security Lab Demo
ps://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8676970#content
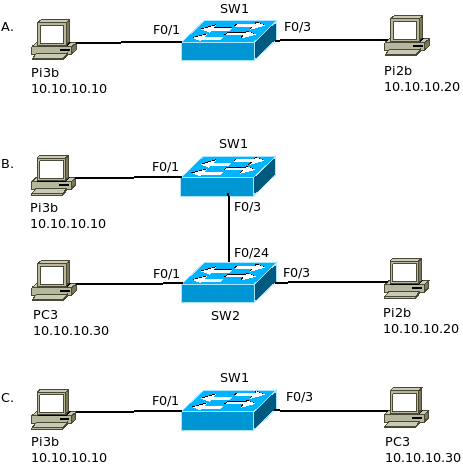
A: Port Security Enabled
SW1(config)#int range f0/1 - 3 SW1(config-if-range)#switchport mode access SW1(config-if-range)#switchport port-security
Verify PCs can talk
Pi2b $ ping 10.10.10.10 PING! PING! PING!
Pi3b $ ping 10.10.10.20 PING! PING! PING!
Verify SW1 Ports up
SW1#show ip int brief FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/3 unassigned YES unset up up
B. FastEthernet 0/3 replaced with switch connecting to both Pi2B and PC3
Verify PCs can no longer talk
Pi3b $ ping 10.10.10.20 Destination host unreachable
Verify Pi2B can reach PC3
Pi2b $ ping 10.10.10.30 PING! PING! PING!
Verify Port F0/3 now shut down
SW1#show ip int brief FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/3 unassigned YES unset down down
C: Remove Pi2b and Re-enable SW1-F0/3 to show new PC3 MAC can replace Pi2B’s MAC
Re-enable Sw1 F0/3
SW1(config)#int f0/3 SW1(config-if)#shutdown SW1(config-if)#no shutdown
Verify Pi3b can talk to PC3
Pi3b $ ping 10.10.10.30 PING! PING! PING!
150. Locking Ports to Hosts with Port Security
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8676988#content
Maximum MAC Addresses
- When Port Security is enabled the maximum number of MAC addresses allowed to send traffic into the interface is 1 by default
- This can be increased if multiple hosts share the port, for example, an IP phone with a PC plugged into the back of it.
SW1(config)#int f0/1 SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 2
Manually adding MAC Addresses
- You can statically configure allowed MAC addresses if you want to lock the port down to a particular host
SW1(config)#int f0/1 SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address 1111.2222.3333 SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 1
MAC Address Learning
- Scenario: You have 1000 authorized hosts connected to the network. You want to lock the ports down to these particular hosts.
- Manually adding hosts is not a scalable solution
- Sticky MAC address add the learned MAC address to the running configuration. Save to the startup config to make them permanent.
SW1(config)#int f0/1 SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security SW1(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address sticky
151. Locking Ports to Hosts with Port Security Lab Demo
https://www.udemy.com/course/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8676990#content
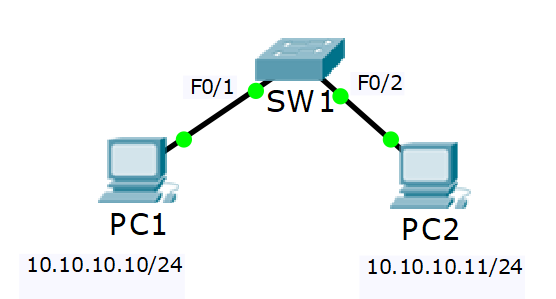
1. Lock down f0/1
Will use absolute address
SW1
configure terminal int f0/1 switchport mode access switchport port-security switchport port-security mac-address 0000.1111.1111 ! Following command is optional. 1 is the default switchport port-security maximum 1
2. Lock down f0/2
Use sticky
SW1
int f0/2 switchport mode access switchport port-security switchport port-security mac-address sticky ! Put some traffic on the port to add the address end
PC2
ping 10.10.10.10 ping! ping! ping!
152. Port Security Configuration – Lab Exercises
https://www.udemy.com/course/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8677000#content
1) Disable all unused ports on SW1. This prevents unauthorized hosts plugging in to them to gain access to the network.
conf t int range f0/3 - 24 shut int range g0/1 - 2 shut
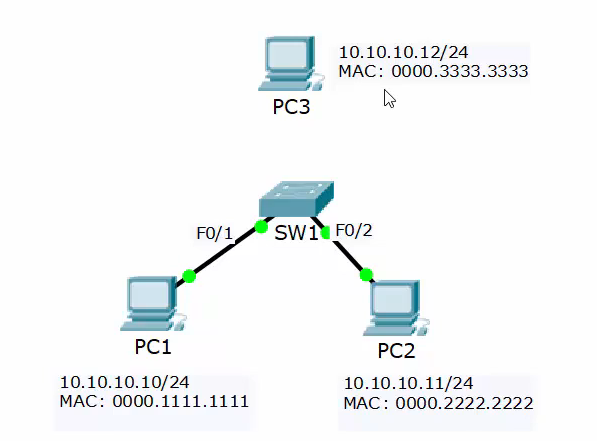
2) Configure port security on interface FastEthernet 0/1. Allow a maximum of two MAC addresses and manually add PC1’s MAC address to the configuration.
int f0/1 switchport mode access switchport port-security switchport port-security maximum 2 switchport port-security mac-address 0000.1111.1111
3) Enable Port Security on interface FastEthernet 0/2 with the default settings.
int f0/2 switchport mode access switchport port-security
4) Use a ‘show port-security’ command to verify the MAC address on PC2.
end show port-security int f0/2 ... Last Source Address: Vlan : 0000.0000.0000:0 ! Did not. Need to see some traffic. PC2> ping 10.10.10.10 ping! ping! ping! ! Try again show port-security int f0/2 ... Last Source Address: Vlan : 0000.2222.2222:1
5) Verify the full Port Security configuration on both interfaces.
SW1#show port-security interface f0/1 Port Security : Enabled Port Status : Secure-up Violation Mode : Shutdown Aging Time : 0 mins Aging Type : Absolute SecureStatic Address Aging : Disabled Maximum MAC Addresses : 2 Total MAC Addresses : 1 Configured MAC Addresses : 0 Sticky MAC Addresses : 0 Last Source Address:Vlan : 0000.1111.1111:1 Security Violation Count : 0 SW1#show port-security interface f0/2 Port Security : Enabled Port Status : Secure-up Violation Mode : Shutdown Aging Time : 0 mins Aging Type : Absolute SecureStatic Address Aging : Disabled Maximum MAC Addresses : 1 Total MAC Addresses : 1 Configured MAC Addresses : 0 Sticky MAC Addresses : 0 Last Source Address:Vlan : 0000.2222.2222:1 Security Violation Count : 0