< Section 15 | Home | Section 17 >
For CCNA, these are sections 94 – 100
94: Routing Fundamentals – Introduction
https://www.udemy.com/course/ccna-complete/learn/lecture/7393474#overview
https://www.udemy.com/course/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605340#content
95: Connected and Local Routes
https://www.udemy.com/course/ccna-complete/learn/lecture/7393476#overview
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605342#overview
Router Functions
A router has 2 main functions:
- Determine the best path to available networks
- Forward traffic to those networks
The Routing Table
- The best available path or paths to a destination network are listed in a router’s routing table and will be used to forward traffic.
- A routing table consists of directly connected networks and routes configured statically by the admin or dynamically learned through a routing protocol.
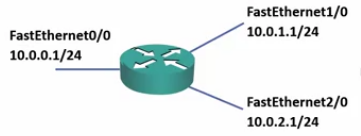
Connected and Local Routes
- The Admin configures IP addresses on the router’s interfaces
- When IP addresses are added to interfaces, it automatically adds those routes to the routing table.
- show ip route
R1#show run
...
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
...
R1#show ip route
...
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
L 10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 10.0.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
L 10.0.1.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
Local Routes
- From IOS 15, local routes will also be added to the routing table
- Local routes always have a /32 mask and show the IP address configured on the interface.
- See above:
- C = Connected route
- L = Local route (direct IP address)
- See above:
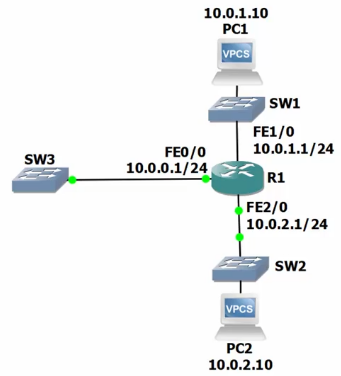
96: Connected and Local Routes Lab Demo
https://www.udemy.com/course/ccna-complete/learn/lecture/7393478#overview
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605344#overview
R1#show ip route
...
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
L 10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
C 10.0.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0
L 10.0.1.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0
C 10.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0
L 10.0.2.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0
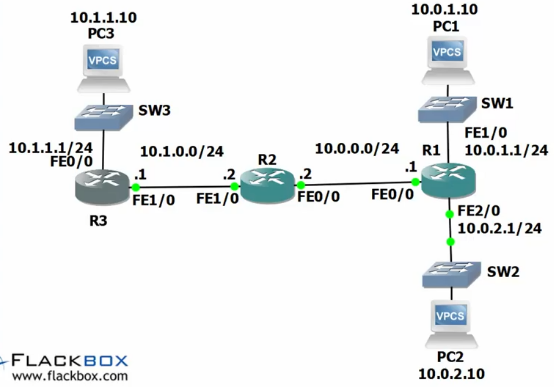
97: Static Routes
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605346#overview
- if a router receives traffic for a network which it is not directly attached to, it needs to know how to get there in order to forward the traffic.
- An Administrator can manually add a static route to the destination, or the router can learn it via a routing protocol.
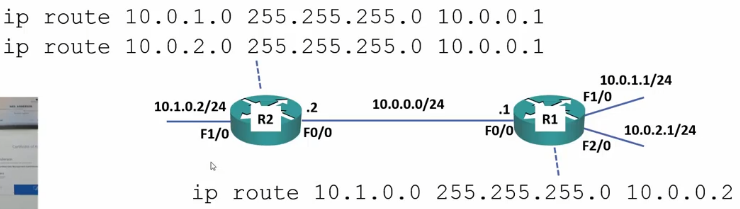
To add a static route:
- ip route <destination network> <Destination Subnet Maks> <Router IP>
- To get to 10.1.0.1 from 10.0.2.1:
- R1(config)#ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.2
- To get from 10.0.1.x and 10.0.2.x from 10.1.0.2
- R2(config)#ip route 10.0.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.1
- R2(config)#ip route 10.0.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.1
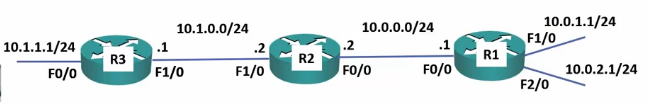
Next Step: Add a middle router
R1(config)#ip route 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.2 R1(config)#ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.2
R2
R2(config)#ip route 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.0.1 R2(config)#ip route 10.0.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.1 R2(config)#ip route 10.0.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.1
R3
R3(config)#ip route 10.0.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.0.2 R3(config)#ip route 10.0.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.0.2 R3(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.0.2
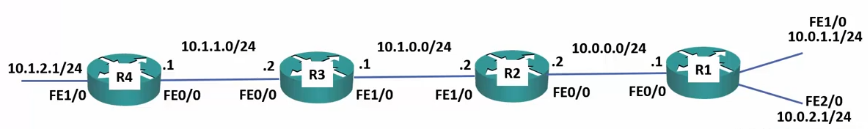
98: Static Routing Fundamentals – Lab
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605350#overview
Example same as above
R1
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 L 10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 C 10.0.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 L 10.0.1.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 C 10.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0 L 10.0.2.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0 S 10.1.0.0/24 [1/0] via 10.0.0.2 S 10.1.1.0/24 [1/0] via 10.0.0.2
R2
R2(config)#ip route 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.0.1 R2(config)#ip route 10.0.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.1 R2(config)#ip route 10.0.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.0.1 R2(config)#ip route 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.0.1
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 L 10.1.0.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 L 10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 S 10.1.1.0/24 [1/0] via 10.1.0.1 S 10.0.1.0/24 [1/0] via 10.0.0.1 S 10.0.2.0/24 [1/0] via 10.0.0.1
R3
R3(config)#ip route 10.0.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.0.2 R3(config)#ip route 10.0.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.0.2 R3(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.0.2
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 L 10.1.1.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 C 10.1.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 L 10.1.0.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 S 10.0.0.0/24 [1/0] via 10.1.0.2 S 10.0.1.0/24 [1/0] via 10.1.0.2 S 10.0.2.0/24 [1/0] via 10.1.0.2
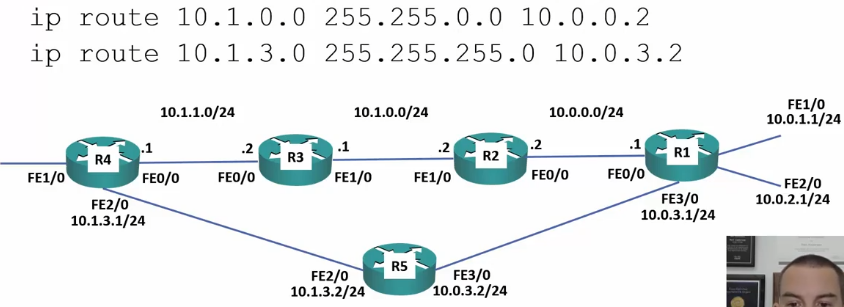
99: Summarization and Default Routes
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605352#overview
Summary Routes
- These can be summarized into a single routing entry per router
- Less routes:
- Less memory consumption
- Reduced errors
- This can be very important on much larger networks.
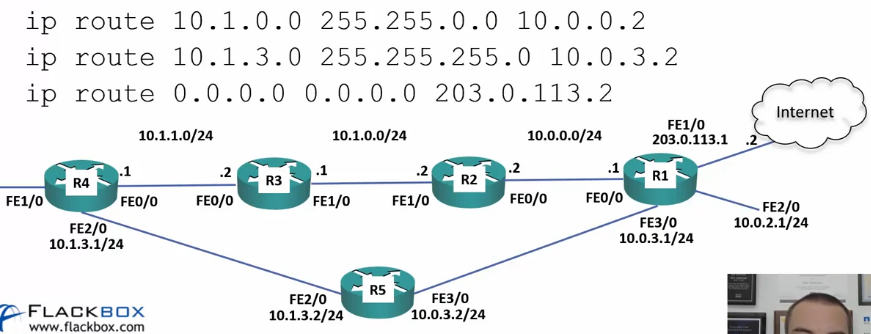
Routes on R1
R1(config)#ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.0.0 10.0.0.2
To Summarize a tighter route (10.1.0.0 – 10.1.3.0)
R1(config)#ip route 10.1.0.0 255.255.252.0 10.0.0.2
Longest Prefix Match
- When there are overlapping routes, the longest prefix route will be selected
- This will be the subnet mask with the most bits
- This can be viewed as ‘the most specific route will win’.
Load Balancing
- When equal length routes are added for the same destination
- The router will add them both to the routing table and load balance between them.
R1(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 10.0.0.2 R1(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 10.0.3.2
Default Route (Gateway of Last Resort)
- When no specific route is located, use the Default Route
- IP: 0.0.0.0
- MASK: 0.0.0.0
- Routing IP: (Probably the Internet provider)
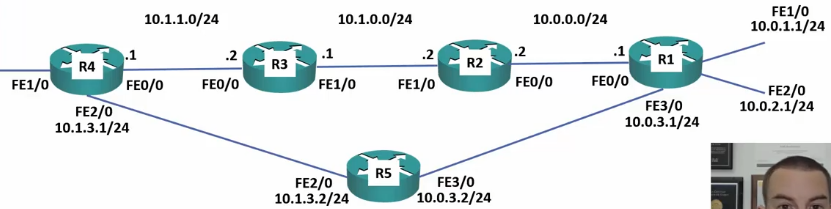
100: Summary Routes and Longest Prefix Match Lab Demo
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605356#overview
- Summary Routes on R1 to 10.1.0.0 255.255.0.0
- Specific Route on R1 to 10.1.3.0 255.255.255.0
- Traceroute to R4 shows hops through R2 and R3
- Traceroute to R5 shows direct hop.
101: Direct Routes and Load Balancing Lab Demo
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605358#overview
- Setup All routers to push all internet traffic toward R4
- R1 setup to load balance between R2 and R5
- R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.2
- R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.3.2
- R4 setup to load balance back to R1 via R3 and R5
- R4(config)#ip route 10.0.1.0 255.255.255 10.1.1.2
- R4(config)#ip route 10.0.1.0 255.255.255 10.1.3.2
- R4(config)#ip route 10.0.2.0 255.255.255 10.1.1.2
- R4(config)#ip route 10.0.2.0 255.255.255 10.1.3.2
How Load Balancing Works
- Traffic from one host will always take the same route.
- This is to help ensure all packets are received in the correct order.
- Traffic from a second host might take the alternate route
- This traffic will continue to take the second route
- This is shown in the lab by traceroutes from PC1 and PC2, both originating from R1
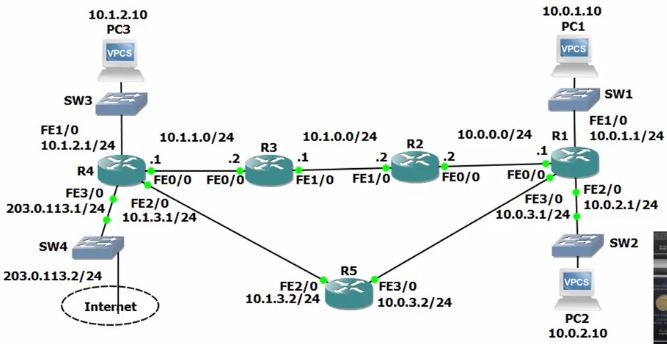
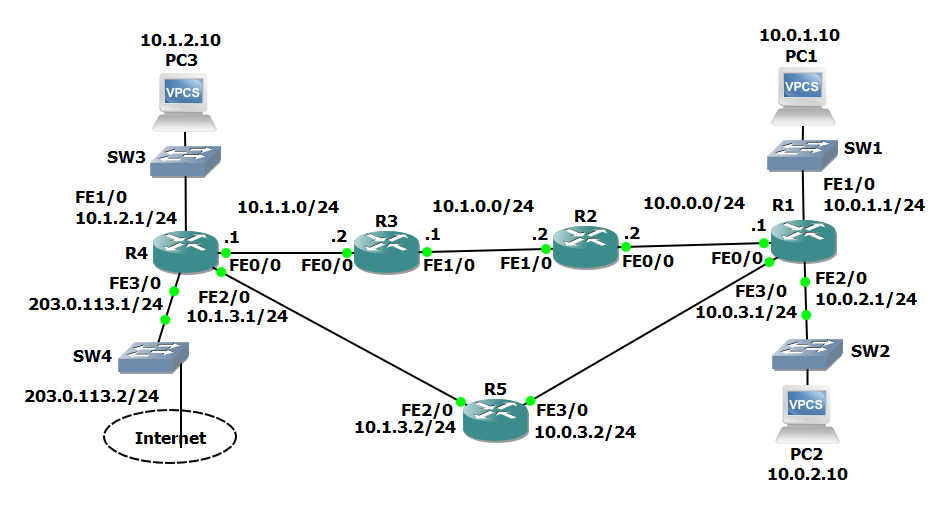
102: Routing Fundamentals – Lab Exercises
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605370#overview
16 Routing Fundamentals Lab Exercise
16 Routing Fundamentals Answer Key
Connected and Local Routes
Configure PC’s with IPs
- Console > ip IP.AD.RE.SS /24 DEF.AULT.GATE.WAY
- done
- show ip route – OK
- Yes – done
- ping from both, ok.
- No, no route. done
Static Routes
7. done
8. done
9.done
10. 10.0.1.1 > 10.0.0.2 > 10.1.0.1 > 10.1.1.1 > 10.1.2.10
11.
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 8 subnets, 2 masks C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 L 10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 C 10.0.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 L 10.0.1.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 C 10.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0 L 10.0.2.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0 C 10.0.3.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet3/0 L 10.0.3.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet3/0
12. Ping fails
13. R3(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 10.0.0.2
14. Verified
15. Verified
Longest Prefix Match
16. done
17. no, no route back to PC1 from R5!
18. R5(config)#ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 10.0.3.1
– ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.252.0 10.0.3.1 = tighter
19. long way
20.
R5#traceroute 10.0.1.10 1 10.0.3.1 ... 2 10.0.1.10
21.
R1(config)#ip route 10.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.3.2
22. Verify that traffic between PC1 and R5 fe 2/0 takes the most direct path in both directions.
R5#traceroute 10.0.1.10 1 10.0.3.1 52 msec 48 msec 24 msec 2 10.0.1.10 72 msec 68 msec 56 msec PC1> trace 10.1.3.2 1 10.0.1.1 30.758 ms 15.639 ms 15.136 ms 2 10.0.3.2 47.374 ms (ICMP type:3, code:3, Destination port unreachable)
Default Route and Load Balancing
23. done
24. done
25.
R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.2 R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.3.2