< Section 14 | Home | Section 16 >
Quick Notes
41% Complete
83: Cisco Device Management – Introduction
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605296#overview
CCNA #85: https://www.udemy.com/course/ccna-complete/learn/lecture/7393416#overview
84: The Boot Up Process
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605304#overview
Cisco Device Memory
- ROM – Read Only Memory
- Flash
- Similar to a solid state disk.
- Retains data even when powered off. Does not require battery
- Newer devices use removable CompactFlash
- NVRAM – Non-Volatile RAM
- Battery powered, so it retains its memory even when the device is powered off.
- RAM – Random Access Memory
- External USB devices can be used.
ROM Read Only Memory
- Power on self test (POST) checking for any initial errors.
- Load the bootstrap
- Bootstrap looks in Flash for an IOS image to load
- If Flash image cannot be found, the device will display the ROMMON (ROM Monitor) prompt at the command line.
- The ROM Monitor can be used to recover a missing or corrupted software image.
- In this case, you can boot from USB or an external TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server
- Search for ‘Cisco ROMMON Recovery’ for your device model.
Flash Memory
- System will load the first IOS image found in Flash by default
- You can override this with the ‘boot system’ command
- This is a Global Configuration command
- You can copy additional IOS system images to Flash via TFTP or USB
NVRAM Non-Volatile RAM Memory
- Once the system finishes loading the IOS system image from Flash, it will load the startup-config configuration file from NVRAM
- The saved startup-config becomes the current running-config in RAM
- If no startup-config file is found, the device will load the Setup Wizard.
- Whenever you enter a command in IOS, it takes effect immediately and goes into the running-config
- To make your changes permanent across a reboot:
- copy running-config startup-config
RAM Random Access Memory
- The IOS image and startup-config are loaded from Flash and NVRAM into RAM during bootup.
- RAM is used as the normal working memory of the device
- ROM, Flash and NVRAM are permanent memory, their contents are not lost when the device is powered off or rebooted.
- RAM is volatile memory. Its contents are lost when the device is powered off.
The VLAN Database
- On a switch, the VLAN database (vlan.dat) is saved in either Flash or NVRAM, depending on the model of the switch.
Booting from TFTP
- The system can also load a system image and/or startup-config from an external TFTP server instead of Flash/NVRAM
- This is NOT recommended because the device will not be able to boot if it loses connectivity to the server.
- It is usually only used where the device does not have enough capacity in Flash to save the system image.
85: The Boot Up Process Lab Demo
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605310#overview
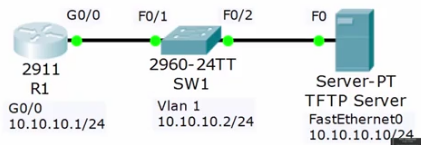
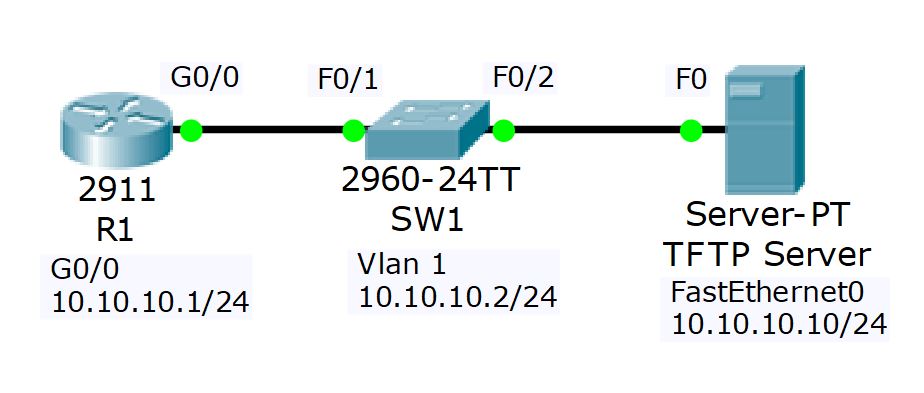
Lab Example
Using Packet Tracer
Delete the system image – This is UGLY!!
show flash:
Directory of flash:/
2 -rwx 3722814 Mar 01 1993 00:08:12 +00:00 c2950-i6k2l2q4-mz.121-22.EA14.bin
# delete the file
delete flash:c2950-i6k2l2q4-mz.121-22.EA14.bin
Delete filename [c2950-i6k2l2q4-mz.121-22.EA14.bin]? <enter>
Delete flash:c2950-i6k2l2q4-mz.121-22.EA14.bin? [confirm] <enter>
# system will continue running until you reboot
# Reboot the system
reload
Reboot the system
Switch
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/switches/catalyst-2950-series-switches/41845-192.html
Router
The system is unable to boot automatically. The BOOT environment variable needs to be set to a bootable image. switch: IP_ADDRESS=10.10.10.5 IP_SUBNET_MASK=255.255.255.0 DEFAULT_GATEWAY=10.10.10.1 TFTP_SERVER=10.10.10.20 TFTP_FILE=c2950-i6k2l2q4-mz.121-22.EA14.bin
Summary: he deleted the IOS from flash, searched for his devices ‘cisco ROMMON recovery’ and found the required commands to configure the system to locate the TFTP server and download the IOS.
- ROMMON commands are CASE SENSITIVE!!!
86: Factory Reset and Password Recovery
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605312#overview
Factory Reset
- write erase
- This will erase the startup-config
- Reload to boot up with a blank configuration
- The Setup Wizard will run at next boot.
The Config Register
- The configuration register can be used to change the way the router boots
- use the ‘config-register’ command from global configuration mode (config), or ‘confreg’ from the ROMMON prompt.
- Example: config-register 0x2142
- 0x2102: boot normally (default)
- 0x2120: boot into ROMMON
- 0x2142: ignore contents of NVRAM (Startup-config)
- There are more!
Router Password Recovery Procedure
Part 1 – Access the enable prompt
- Press <Ctrl>+<Break> at power on to break into rommon prompt
- <Ctrl> +<A> then <F> for minicom!
- Enter ‘confreg 0x2142’ to ignore the startup-config on boot.
- The startup-config is still there with the full configuration including the unknown enable secret, but the router does not use it when it boots.
- Enter ‘reset’ to reload
- The router will boot up with no configuration.
- Type ‘no’ to bypass the setup wizard
- Enter enable mode. You will not be prompted for the enable secret as it is not in the running configuration.
Part 2 – Reload the startup-config
- Copy the startup-config to the running-config
- DO NOT FORGET THIS STEP!
- This will copy the entire previous configuration into the running config, inclnonouding the unknown enable secret. Since you are already in enable mode, you don’t need to know what it is.
- Enter a new enable secret in global configuration mode. to over write the old one. This will go into the running-config.
- Enter ‘config-register 0x2102’ so the router will boot normally on the next restart.
- Enter ‘copy running-config startup-config’ to save the new enable secret.
Switch Password Recovery Procedure
- Likely very similar to the router password recovery procdure, but you may have to physically press the ‘Mode’ button on the front of the switch to break into the switch loader.
- Search for ‘Cisco Password recovery’ for your model of switch for full instructions.
87: Password Recovery Lab Demo
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605314#overview
Lots of fun in this lecture. Pay attention and see if you can catch his mistakes before he tells you he made them.
88: Backing Up the System Image and Configuration
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605320#overview
Caution – do not perform this at home!
It will take several hours to restore a system image if you delete it.
Backing up the System Image and Config
- Copies of the device’s IOS system image and configuration can be saved to Flash FTO, TFTP or USB
- If you copy a config file into the running-config, it will be merged with the new configuration.
- This seems incorrect, but who am I to know.
- To replace a configuration, factory reset and then copy the new configuration into the startup-config
Common commands
- Backup files from Flash to TFTP
- copy flash tftp
- You will be prompted for the file name.
- You will be prompted for the tftp server’s IP address
- You will need to enter a file name that you’re saving as. It is recommended to enter the same name.
- copy flash tftp
- Backup the running-config to TFTP
- copy running-config tftp
- You will be prompted for the tftp server’s IP address
- You will need to enter a file name that you’re saving as. This time it is recommended to incorporate a save date.
- copy running-config tftp
- Backup the startup-config to USB
- copy startup-config usb
- Restore a saved backup
- To the Startup Config
- (config)#write erase
- #copy flash start
- Enter the complete filename as saved in flash
- Press [Enter] when prompted to save as startup-config
- #reload
- To the running config
- #copy flash run
- Enter the complete filename as saved in flash
- Press [Enter] when prompted to save as startup-config
- #copy flash run
- To the Startup Config
89: Upgrading IOS
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605324#overview
Upgrading the IOS System Image
- IOS software images can be downloaded from: https://software.cisco.com
- After downloading, copy the file to the device’s flash using TFTP
- copy tftp flash
- Delete the old system image or use the ‘boot system’ command
- (config)#boot system flash:<full file name>
- Make sure you ‘reload’ to ensure you reboot to the new version.
90: Licensing
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605326#overview
Router IOS Licensing
- Prior to IOS 15.0, different IOS system images were available for different feature sets, such as Security (firewall or IPS) or Telephony.
- Licensing was not enforced.
- A universal system image is provided from IOS 15.0
- License codes must be entered to activate the Technology Packages
Licensing Procedure
IMPORTANT! You will be tested on this!
- When you purchase a license you will be provided with a Product Activation Key (PAK) code
- The license will be tied to an individual device. To get the device’s Unique Device Identifier (UDI) enter:
- show license udi
- Go to the Cisco License portal http://www/cisco.com/go/license and enter the PAK code and UDI to generate the license.
- Copy the license to Flash on the router using TFTP or similar, then activate it as shown below
- license install flash:
- license show
91: Cisco Device Management – Lab Exercises
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605328#overview
- Basically just copying files back and forth using tftp
- Restoring Startup Config
# erase all files in nvram write erase # now copy the restore copy <flash/tftp> start # enter the file to copy # Destination filename startup-config reload
15 Cisco Device Management Lab Exercise
15 Cisco Device Management Answer Key
c2900-universalk9-mz.SPA.151-4.M4.bin
c2960-lanbasek9-mz.150-2.SE4.bin