< Section 13 | Home | Section 15 >
37% Complete
Including CCNA starting here. Appears to be EXACTLY the same course.
75: Cisco Router and Switch Basics – Intro
77: CCNA: https://www.udemy.com/course/ccna-complete/learn/lecture/7367248#overview
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605258#content
76: Cisco Router and Switch Configuration
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605260#content
Router IP Addresses
- A Router provides connectivity between different IP subnets
- An IP address must be configured on the interfaces in each subnet.
Configuring an IP on a Router
Router>enable Router#show running-config ... interface FastEthernet0/0 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface FastEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! ... Router#configure terminal Router(config)#interface fastEthernet0/0 Router(config-if)ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)no shutdown Router(config-if)end Router#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Prol FastEthernet0/0 10.0.0.1 YES manual up up FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down dow ATM0/0/0 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down dow Serial0/1/0 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down dow Serial0/1/1 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down dow
Switch Management IP Address
- A Layer 2 Switch is not IP routing aware
- It does however support a single IP address for management
- This IP address and subnet mask is configured on the Switched Virtual Interface (SVI) for the default VLAN 1.
- A default gateway also needs to be configured to allow connectivity to other subnets.
Switch(config)#interface vlan 1 Switch(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.101 255.255.255.0 Switch(config-if)#no shutdown Switch(config-if)#exit Switch(config)#ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1
Note: On Switches, Interfaces are UP (not shutdown) by default, so adding ‘no shutdown’ really is not required here.
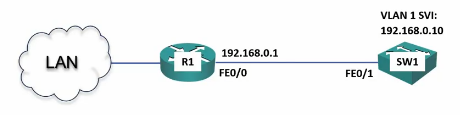
Lab Example
Router Setup
Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0 Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Switch Setup
Switch>enable Switch#configure terminal Switch(config)#interface vlan 1 Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.168.0.10 255.255.255.0 Switch(config-if)#no shutdown Switch(config-if)#end Switch#ping 192.168.0.1 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent...
Configure Switch to reach other networks
Switch#configure terminal Switch(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.0.1
Configure the Hostname
This works for both Routers and Switches (and likely any other Cisco device)
Switch(config)#hostname SW1 SW1(config)#
Configure an Interface Descriptions
This works for both Routers and Switches (and likely any other Cisco device)
This does NOT show up during show ip interface brief, but it does show up in the running-config
SW1(config)#interface FastEthernet 0/0 SW1(config-if)#description Link to R1
77: The Initial Setup Wizard
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605262#content
Router
You will see the “System Configuration Dialog” prompt when you:
- First boot a Router or Switch that has not been configured
- By running ‘setup’ from the enable prompt
In the real world, you will likely never see this used, but you might get tested on it, so you should know what it is going to do.
- Enter host name [Router]: R1
- Enter enable secret: Pas$W0rd
- This password will be stored encrypted in the running config.
- Enter enable password: Pas$W0rd2
- This cannot match the enable secret password.
- To my knowledge, this password is disabled if a secret password had been enabled…
- Enter virtual terminal password: Pas$W0rd3
- Used when telnetting in over a network interface.
- Configure SNMP Network Management? [no]: no
- Can be configured later. Think this is a lengthy subject.
- Enter interface name used to connect to the management network from the above interface summary: fastethernet0/0
- The software will provide a list of the available interfaces before prompting.
- You cannot use shortcut names. You must type the entire interface name.
- Configuring interface FastEthernet0/0:
- Operate in full-duplex mode? [no]: yes
- Configure IP on this interface? [no]: yes
- IP address for this interface: 10.0.0.1
- Do NOT enter the subnet mask here! What??
- Subnet mask for this interface [255.0.0.0]: 255.255.255.0
- Notice that it defaulted to the default net mask for the IP’s Class!
- IP address for this interface: 10.0.0.1
- [0] Go to the IOS command prompt without saving this config.
- [1] Return back to the setup without saving this config.
- [2] Save this configuration to nvram and exit.
- Enter your selection [2]: 2
- This saves your edits to the startup-config
Switch
- Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: yes
- Would you like to enter basic management setup? [yes/no]: yes
- Enter host name [Switch]: SW1
- Enter enable secret: cisco
- Enter enable password: cisco-kid
- Enter virtual terminal password: cisco
- Configure SNMP Network Management? [no]: no (or just press [Enter])
- Enter interface name used to connect to the management network from the above interface summary: vlan1
- Configuring interface Vlan1:
- Configure IP on this interface? [yes]: yes
- IP address for this interface: 10.0.0.101
- Subnet mask for this interface [255.0.0.0] : 255.255.255.0
- Configure IP on this interface? [yes]: yes
- Would you like to enable as a cluster command switch? [yes/no]: no
The setup wizard does not setup a default gateway. You’ll need to do this manually.
SW1>enable SW1#configure terminal SW1(config)#ip default-gateway 10.0.0.1
78: Speed and Duplex Settings
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605266#overview
Interface Speed and Duplex
- Speed and Duplex are set to Auto by default
- Both sides of a link should auto-negotiate to full duplex and the fastest available speed
- Best practice is to manually set the speed and duplex on ports connected to another network infrastructure device such as:
- Firewalls
- Switches
- Routers
- Servers
- This may improve reliability but auto should work also.
- It is important to set matching speed and duplex settings on both sides of the link.
- Both sides set ‘auto’ or both sides set manually.
- Do not set one ‘auto’ and the other manually.
Setting Manually
SW1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 SW1(config-if)#duplex ? auto Enable AUTO duplex configuration full Force full duplex operation half Force half-duplex operation SW1(config-if)#speed ? 10 Force 10 Mbps operation 100 Force 100 Mbps operation auto Enable AUTO speed configuration
Verification Commands
show running-config
show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 10.0.0.101 YES manual up up FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down ... FastEthernet0/12 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/13 unassigned YES unset up up FastEthernet0/14 unassigned YES unset down down ... FastEthernet0/23 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/24 unassigned YES unset down down GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset down down GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down
show running-config interface vlan 1
Building configuration... Current configuration : 79 bytes ! interface Vlan1 ip address 10.0.0.101 255.255.255.0 no ip route-cache end
show interfaces vlan 1
Vlan1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is CPU Interface, address is 0015.6239.5000 (bia 0015.6239.5000)
Internet address is 10.0.0.101/24
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00
Last input 00:00:00, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue: 0/40 (size/max)
5 minute input rate 1000 bits/sec, 1 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 3000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec
1036505 packets input, 173050963 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 278184 broadcasts (0 IP multicast)
0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 91 ignored
1556025 packets output, 950236569 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 4 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
show version
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) C2950 Software (C2950-I6K2L2Q4-M), Version 12.1(22)EA14, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Copyright (c) 1986-2010 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Tue 26-Oct-10 10:35 by nburra
Image text-base: 0x80010000, data-base: 0x80680000
ROM: Bootstrap program is C2950 boot loader
Switch uptime is 1 week, 1 day, 18 hours, 39 minutes
System returned to ROM by power-on
System image file is "flash:/c2950-i6k2l2q4-mz.121-22.EA14.bin"
This product contains cryptographic features and is subject to United
States and local country laws governing import, export, transfer and
use. Delivery of Cisco cryptographic products does not imply
third-party authority to import, export, distribute or use encryption.
Importers, exporters, distributors and users are responsible for
compliance with U.S. and local country laws. By using this product you
agree to comply with applicable laws and regulations. If you are unable
to comply with U.S. and local laws, return this product immediately.
A summary of U.S. laws governing Cisco cryptographic products may be found at:
http://www.cisco.com/wwl/export/crypto/tool/stqrg.html
If you require further assistance please contact us by sending email to
export@cisco.com.
cisco WS-C2950G-24-EI (RC32300) processor (revision L0) with 19911K bytes of memory.
Processor board ID FOC0934Z9V8
Last reset from system-reset
Running Enhanced Image
24 FastEthernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)
2 Gigabit Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)
32K bytes of flash-simulated non-volatile configuration memory.
Base ethernet MAC Address: 00:15:62:39:50:00
Motherboard assembly number: 73-7280-05
Power supply part number: 34-0965-01
Motherboard serial number: FOC09331L5T
Power supply serial number: DAB0933EAAL
Model revision number: L0
Motherboard revision number: A0
Model number: WS-C2950G-24-EI
System serial number: FOC0934Z9V8
Configuration register is 0xF
79: CDP and LLDP
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605272#content
CDP Cisco Discovery Protocol
- CDP is a proprietary Layer 2 protocol
- It is used to share information with other directly connected Cisco equipment, such as the operating system version and IP address
- This aids in troubleshooting by allowing administrators to map out how Cisco devices are connected to each other.
- It is enabled by default on most Cisco devices
- it works at Layer 2, so it is not necessary for the device to have an IP address.
Commands
Enable CDP
(config)#cdp run
Disable CDP
(config)#no cdp run
Disable CDP for a specific interface
Good for enabling on an internal network, but disabling for external networks.
(config-if)#no cdp enable
show cdp
Global CDP information: Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Sending a holdtime value of 180 seconds Sending CDPv2 advertisements is enabled
show cdp neighbors
Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans Bridge, B - Source Route Bridge
S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, P - Phone,
D - Remote, C - CVTA, M - Two-port Mac Relay
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
Switch Fas 0/0 147 S I WS-C2950G Fas 0/1
show cdp neighbors detail
------------------------- Device ID: Switch Entry address(es): IP address: 10.0.0.101 Platform: cisco WS-C2950G-24-EI, Capabilities: Switch IGMP Interface: FastEthernet0/0, Port ID (outgoing port): FastEthernet0/1 Holdtime : 155 sec Version : Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS (tm) C2950 Software (C2950-I6K2L2Q4-M), Version 12.1(22)EA14, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport Copyright (c) 1986-2010 by cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Tue 26-Oct-10 10:35 by nburra advertisement version: 2 Protocol Hello: OUI=0x00000C, Protocol ID=0x0112; payload len=27, value=00000000FFFFFFFF010221FF000000000000001562395000FF0000 VTP Management Domain: '' Native VLAN: 1 Duplex: full
LLDP Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- Came much later than CDP so may not be available on all devices
- Open source standard for various vendors
Commands
- (config)# lldp run
- (config)#no lldp run
- (config)#no lldp transmit
- (config)#no lldp receive
- #show lldp
- #show lldp neighbors
- #show lldp neighbors detail
80: Basic Layer 1 and 2 Troubleshooting
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605274#overview
Layer 1 Troubleshooting
- Copper and Fibre cables are liable to break if not handled correctly.
- The interface is administratively shut down
- The cable is disconnected on either or both ends
- The device on the other end of the cable is powered off.
- Broken connectors which cause loose connections
- Bent or stretched cables which lead to broken wires or fibres.
- Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI) sources such as motors or microwaves which cause errors in transmission. (Newer cables are less susceptible to this)
#show ip interface brief
- administratively down: enable the interface by running ‘no shutdown’
- down/down: Indicates a Layer 1 issues. Check the interface is cabled at both ends and the device on the other side is powered on.
- up/down: Indicates a Layer 2 issue or speed mismatch. Check interface configurations matches on both sides of the link.
#show interface
- If the interface is reporting an excessive amount of errors, it could be either a Layer 1 or Layer 2 issue.
- Check the integrity of the cable
- Check the configurations match on both sides of the link.
Speed and Duplex Mismatches
- Incorrect speed settings can cause the interface to operate below its maximum speed.
- Speed mismatches will typically bring the interface down
- The interface will typically stay up with duplex mismatches but performance will be terrible because of collisions.
- The ‘show interface’ command will report an excessively high number of errors in this case.
- Both sides of a link must be set the same, as either auto or manually configured
- Cisco devices default to auto
- If one side is set to auto and the other is manually configured, this will often result in a mismatch
- Best practice is to manually configure ports attached to other internal network infrastructure devices or servers.
- Remember to manually configure both sides of the link.
- If a device has issues with auto negotiating speed or duplex, manually configuring both sides will normally resolve the problem.
81: Basic Layer 1 and 2 Troubleshooting – Lab Demo
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605278#overview
Speed and Duplex – CDP
CDP should detect a duplex mismatch
- Speed mismatch should bring the interface down.
- Duplex mismatch should not bring the interface down, but will cause horrible performance issues due to collisions.
82: Basic Layer 1 and 2 Troubleshooting – Lab
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605282#overview
14 Cisco Router and Switch Basics Lab Exercise
14 Cisco Router and Switch Basics Answer Key