< Section 12 | Home | Section 14 >
35% Complete
71: The Cisco Troubleshooting Methodology – Introduction
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605212#overview
72: The Cisco Troubleshooting Methodology
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605222#overview
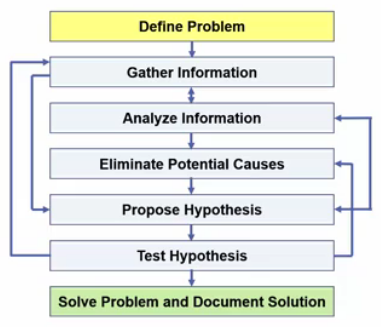
- Define the Problem
- Gather Information
- Analyze Information
- Eliminate Potential Causes
- Propose Hypothesis
- Test Hypothesis
- Solve Problem and Document Solution
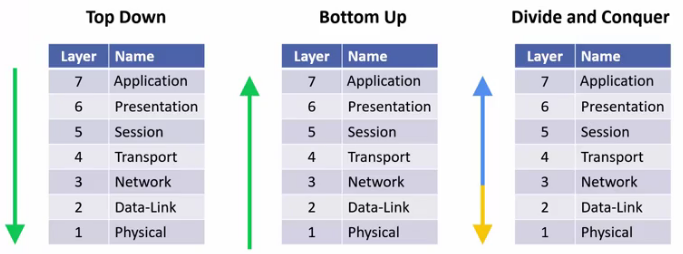
Troubleshooting Methods
- Top Down
- Start at Layer 7 and work your way down to Layer 1
- Bottom Up
- Start at Layer 1 and work your way up to Layer 7
- Divide and Conquer
- Go straight to the most obvious layer and work your way either up or down.
Troubleshooting methods
- Compare configurations
- Trace the path
- Very common
- Start at the source and work your way to the destination
- Swap out components
Common Commands
- Ping
- Uses ICMP
- Verifies 2-way connectivity
- Source sends a PING request
- Destination sends a PING reply
- Traceroute
- Similar to PING but measures hop by hop based on a ‘TTL’ type value
- Each TTL is a hop. First one hop, then two, then 3…
- This way you can tell if something breaks in between
- Many routers are configured NOT to return PING replies, so you may not get values ‘mid stream’ but will get values farther down the path
- Telnet
- Generally used to access command line on a device
- Very similar to SSH, but insecure. All data is sent clear text.
- Telnet can be used to check specific ports. Default is 23, but can be easily set to something else to see if:
- A port is open (not blocked by a firewall)
- A service is ‘listening’ on a specific host, such as:
- 53 for DNS
- 80 for HTTP
- Generally used to access command line on a device
73: Cisco Troubleshooting Methodology – Lab
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605228#overview
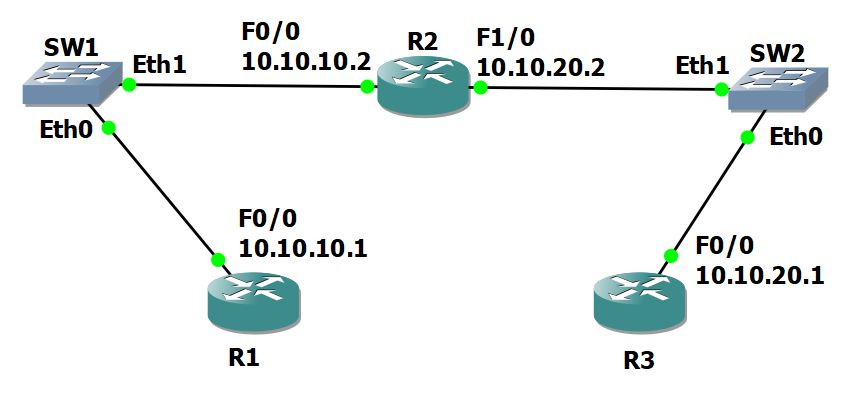
The Issue
- User on PC behind R1 claims DNS isn’t working
- DNS is hosted on R3
Troubleshooting
Ping R3 from R1 using the hostname
R1#ping R3 Translating "R3"...domain server (10.10.30.1) % Unrecognized host or address, or protocol not running
DNS not working confirmed.
Ping the IP to see if connectivity exists
R1#ping 10.10.30.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.30.1, timeout is 2 seconds: ..... Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
Cannot access DNS router confirmed.
Run a traceroute to see where the breakdown occurs
R1#traceroute 10.10.30.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 10.10.30.1 VRF info: (vrf in name/id out name/id) 1 10.10.10.2 4 msec 4 msec 0 msec 2 * in *
R2 is OK, but no response from R3.
Check if R2 can ping R3
R2#ping 10.10.30.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.30.1, timeout is 2 seconds: ..... Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
R2 cannot access R3 confirmed.
Check if there is a route set from R2 to 10.10.30.1
R2#show route .. lots of stuff, but no route to 10.10.30.1 ...
Route does not exist.
Fix the route
R2(config)#ip route 10.10.30.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.20.1
Try Ping gain
R2#ping 10.10.30.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.30.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round trip min/avg/max = 1/3/0 ms
Ping re-established
Verify the issue has been corrected
Attempt Ping from R1 to R3 again
R1#ping 10.10.30.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.30.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
Full connection exists between R1 and R3.
Check if DNS is working now
R1#ping R3 Translating "R3"...domain server (10.10.30.1) % Unrecognized host or address, or protocol not running
DNS still not working.
Check if DNS is running on the router
R1#telnet 10.10.30.1 53 % Connection refused by remote host
DNS Not running on R3 confirmed.
Enable DNS Services on R3
R3(config)#ip dns server R3(config)#exit R3(config)#do telnet 10.10.30.1 53 Trying 10.10.30.1, 53 ... Open [Connection to 10.10.30.1 closed by foregn host]
DNS Service has been re-enabled
Confirm DNS is working on R1
R1#ping R3 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.30.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
Problem Solved!
74: The Cisco Troubleshooting Methodology – Lab Exercises
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605232#content
13 The Cisco Troubleshooting Methodology Lab Exercise
13 The Cisco Troubleshooting Methodology Answer Key
There are at least 3 errors!