A View of Network Cards on PCs and Cisco Devices
Cable
- Thin Net
- Would tap into a baseball bat sized with a vampire like connection.
Cat-5: Transceiver
- Category 5: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
- Most Popular
- Higher the Category, the more twists, the more twists, the better the signal strength.
- Connection: RJ-45
- Max Distance: 100 meters
Multi-Mode Fiber
- Allows multiple light signals simultaniously
- Max distance: 275 meters to a few miles
- Connection: Varies
- Less Distance and not as clean as “Single-Mode”
Single-Mode Fiber
- Typically difficult to work with.
- Often requires specialized technicians
- Solid glass core
- Fragile
- Distance: Hundreds of miles
- Connection types also vary and are expensive
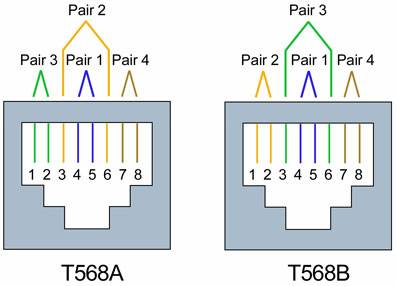
Understanding Ethernet Cabling
- Separate the 8 wires into strands
- Arrange the wires into a standard (T568B Most Common!)
- Slip over the connector and crimp.
- Use the same standard on both ends to create a straight-through cable.
- Used for UNLIKE device connections, PC to Switch, Switch to Router, etc.
- Use BOTH T568-A and T568-B to create a Crossover Cable (aka Null Modem)
- Used for LIKE device connections, PC to PC, Switch to Switch, Router to Router, etc.
- Failure to use one of these standards will result in a cable that will not work reliably over the stated distance.
There are usually “Patch Panels” between wall outlets and the Switch. This makes it much easier to change or move switches.
The Two Types of Ethernet Cables
Straight-Through
- Used for UNLIKE device connections, PC to Switch, Switch to Router, etc.
Cross-Over
- Used for LIKE device connections, PC to PC, Switch to Switch, Router to Router, etc.