< 5 Measuring Customer Health | Home | 7 Customer Success Metrics >
42% complete
* Inserted after section completed. 🙁
- 24 Value Drivers
- 25 Service Outcomes
- 27 Outcome Quality
- Quiz 3: Outcome Quiz
21. A Tour Around the Framework
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20818982#content
A set of measurements, practices, tools and interfaces.
OR(A)EO: Adoption stuffed OREO
- Outcome: Measurement and Practices that ensure the customer value is Understood,Clearly articulated and Shared
- The reason they use my service
- The reason they made the purchasing decision in the first place
- Relationship: Those things I do that build and maintain relationships at all levels
- Adoption: Capturing, analyzing, understanding and improving usage of my service
- Expansion: Activities that identify additional opportunities for my customers to get more value from the service we provide.
- Organization: Brings it all together in a regular systematic review and management of customers, my organization and customer success.
Outcome
- Definitions
- Ensuring that my customer outcome is
- clearly identified
- articulated
- Shared
- Quantified wherever possible
- Ensuring that my customer outcome is
- Activities
- Shared sales value propositions handover
- The reason they made the purchasing decision in the first place
- Outcome Articulation
- A process that involved determining value drivers and connecting value
- This then, will help ensure that everyone is working towards a successful outcome for the customer
- Make Money
- Save Money
- Manage Risk
- Drive Strategy
- Onboarding
- Ensure rapid time to value
- Success Stories/Storyboarding
- Reinforce value
- Shared sales value propositions handover
- Tools
- Outcome Articulation
- Make Money
- Save Money
- Manage Risk
- Drive Strategy
- The work you do from this perspective is the most preemptive work you can do.
- Outcome Articulation
Relationships
- Definition
- The activities in this perspective is essential in building and maintaining relationships at all levels.
- Activities
- Relationship Mapping
- Help you identify the quality of a relationship I really have with my customer and results in a joint action plan to work on the parts of the relationship that require improvement.
- Community
- User Events
- Customer Advisory Board
- Champion Building
- An activity that reinforces persons in my customer’s organization that promote your service.
- Relationship Mapping
- Tools
- Relationship Mapping (TBD)
Adoption
- Definition
- Capture, Analyze, understand and improve usage
- My service was likely purchased by a senior manager and is used by a subset of employees
- This does not mean every user will use my service, or use it in the best possible way, or use it in a way that will provide the best value for them.
- Activities
- Regular monitoring
- Ideally through tight integration with the service
- Adoption assessment
- Education and Enablement
- Shared proven practice
- Promotion
- Regular monitoring
- Tools
- Adoption Assessment Tool
- Help me measure and asses adoption levels and determine the best strategy among the selection of standard strategies to improve it when it is lower than I would like it to be.
- Adoption Assessment Tool
Expansion
- Definition
- Customers that are actively progressing, expanded use of the service I provide are almost certainly going to be retained because they are most likely successful. That’s why they want to expand their success
- But only around half of SaaS companies (54%) treat expansion as a priority.
- This perspective is about taking a systematic customer focused but commercially sound approach to increasing the value that my customer (and in turn my business) are creating.
- Activities
- Gap Analysis
- New Feature Enablement
- keep the customers aligned to new value
- Communities and forums
- Customer Networking
- Build relationships with new teams, new functions and create opportunities to deliver value from a service the customer already has.
- Opportunity Management
- Converts initial, sometimes casual, conversations into opportunities that are progressed from an initial inquiry into expansion.
- Tool
- Gap Analysis
- A rigorous and preemptive practice to identify, help identify opportunities for growth and expansion.
- The approach we then take is to make use of a series of engagement and expansion tactics.
- Gap Analysis
Organization
- Definition
- Customers are most confident in me as a professional Customer Success Manager when I behave in a way that is consistent, predictable and organized.
- This perspective relates to systems, processes and tools I use to manage my customer success.
- Customers will not chase you for meetings. Those that are most happy may remind you, likewise, those whom are most unhappy may also.
- It is up to me that this activity is about the diligent management of my schedule.
- Activities
- Measuring Health
- Constantly!
- Keeps your focus on the right things
- Perpetual Agenda
- Customer Meetings
- Make sure they do
- Discuss the right things
- Internal Meetings to ensure I have
- The resources
- The people, their time and attention
- Internal Reviews (tactical)
- Internal Reviews (strategic)
- Segmentation
- Measuring Health
- Tools
- Perpetual Agenda
- Contains all the things I need to discuss with my customers to make sure I do not miss anything.
- Perpetual Agenda
Summary
- Five Perspectives
- 4 for Outcome, Relationship, Adoption and Expansion
- All related to working with leading indicators of Customer Success
- A 5th, Organization, to drive the management of the other 4 so that what I do is rigorous, methodical and organized.
22. Introduction to the Outcome Perspective
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20962852#content
About ensuring the customer outcome – the reason they originally purchased and continue to use your service, is clearly
- Identifed
- Articulated
- Shared
- Quantified (wherever possible)
This is the most pre-emptive work I can do.
Key Tool – Outcome Articulation
- Outcome Articulation is a process that involves 3 steps
- One: Determining Value Drivers
- Two: Connecting your service outcome to the Value Driver
- Three: Your Connected Outcome should not be a secret
- It should be explicit, agreed and made highly visible.
- A Connected Outcome should be at the forefront of your customer’s mind.
- It is the reason they continue to use the service and invest in it when they reach the next renewal.
23. Disconnected Outcomes
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20243974#content
It is likely that the our Service Outcome – the outcome that our service delivers, is a disconnected outcome.
There are a few potential (and desired) outcomes:
- Increasing retention rate
- Improved acquisition rates
- Increased revenue
- Reduced costs
- Process Improvement
- Employee satisfaction
- Increased profit
- Increased word of mouth (Brand Awareness)
- Increased conversion levels – which could mean anything in terms of
- Web site to purchase
- Inquiry to sales
- Create more expansion or up sell opportunities.
Outcomes and Value Drivers
- Some of these outcomes are Value Drivers
- Some of these are directly connected to value drivers
- Others are not
- The outcome from your solution may be one of these Disconnected Outcomes
Connecting Disconnected Outcomes
- How do I make the value that my service delivers more apparent and more explicit?
How to connect a Service Outcome with a Value Driver
Example 1:
We make an Employee Survey (Voice of the Employee) Tool
- Client overview
- Client has carefully implemented market driven compensation and benefits that have the optimum impact on satisfaction in the workplace for optimum cost.
- Product Purpose: Measure the satisfaction levels of over 50,000 staff, specifically
- How satisfied are they with the compensation packages
- How satisfied are they with the benefits schemes
- Stakehoders: HR Human Resources
- Executive Sponsor – H.R. Director or V.P. of Talent
- Product survey is designed to monitor what people continue to value, so the company can improve its benefits when they need to.
- Usual outcome to achieve this is cost neutral.
- Costs required to gain this information = costs saved
- Expected Outcome
- Maintain employee satisfaction within controlled thresholds
- Scores over 55 produces upper quartile retention levels
- If drops below 48, they start to see attrition and attrition costs them money.
- Quantified Outcome
- Prior to implementing the solution, the Consulting division had seen dramatic cost increases as a result in turnover in their team.
- Costs of implementing solution partially justified by the costs savings associated with increasing staff retention in the Consulting division alone by 5% in the first year.
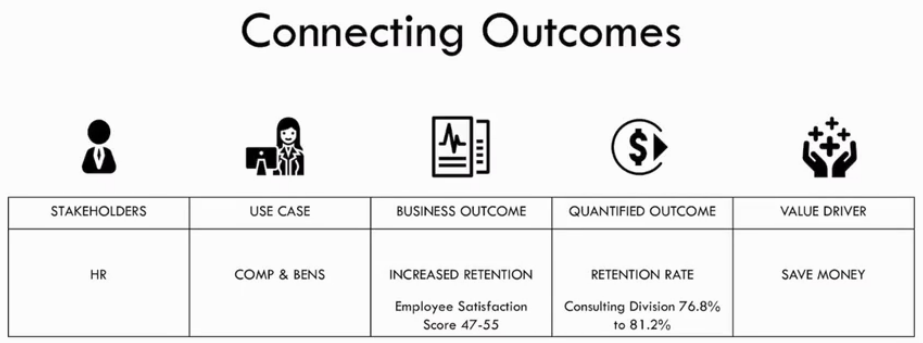
Business / Product summary
- Stakeholders
- HR Dept.
- Use Case
- Compensation and Benefits
- Business Outcome
- Increased retention
- Satisfaction scores over 48
- Quantified Outcome
- Retention Rate Increases
- Value Driver:
- Saving Money
24. Value Drivers
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20962874#content
- It is unlikely that your customers originally came to you unless they had:
- A problem to fix
- An opportunity to capitalize on.
- Most decisions to buy a solution start with these two questions.
- Is it going to make me money?
- Is it going to save me money?
- Actually there are 4 key Value Drivers for any business decision
- Make Money
- Create Revenue
- Save Money
- Reduce Costs
- Improve Profitability
- Reduce Risks
- Comply with regulatory requirements
- It is important for a business to comply with something it is required by law to do.
- This is a cost of doing business
- Think HIIPA
- Comply with regulatory requirements
- Drive Strategy
- Look at any annual report from a large corporation, there will be a number of strategic initiatives.
- These represent commitments they’ve made to the market, shareholders and their employees.
- Usually big picture, visions, perhaps over many years, with sub-goals in the shorter.
- A large company may have a target to reduce their water consumption in their manufacturing process
- These are highly visible and likely to help their business thrive in the long term.
- They can often be seen to be above or beyond short term profits.
- Make Money
Review
- Make Money
- Save Money
- Reduce Risk
- Drive Strategy
Value Drivers |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Make Money | Save Money | Reduce Risk | Drive Strategy |
| Increase Revenue | Reduce Costs | Legal Compliance | Change in Strategic Direction |
| Improve Customer Loyalty | Operating Efficiency | Governance | Experimental |
| Increase Brand Awareness | Reduce Returns | Financial / Operational | Crisis Resources? |
25. Service Outcomes
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/21794284#content
What is the difference between a Feature and a Benefit?
- Feature
- An aspect of my product, service or solution.
- Might enables a customer to do something
- It is not a benefit until it is realized by the customer
- Integration with Salesforce
- Multi-language
- If a client integrates with a different CRM, uses only English, then these are not realized by the customer.
- It is not a benefit until it is realized by the customer
- General Features
- Easy to use
- Available on Mobile
- Specific
- Creates reports in PDF
- Benefit
- Why a customer cares
- What they get out of it
A Feature cannot be a Benefit unless the customer has a need for that feature.
Business Outcomes
- Are specific Benefits that have compelling and positive business results as a consequence of using the service.
Example: Low cost airline
- I am a CSM for a CRM vendor
- Client is a low cost airline.
- Product
- CRM
- They have purchased my service to implement a new contact center platform.
- Use Case
- They have grown rapidly and ignored their systems over the years. Now have 15 different ERP (Enterprise Resource Planner) systems
- These have all been replaced with my CRM and service desk platforms.
- One feature considered was accessibility
- Not a primary business benefit, but is part of their commitment to cultural inclusion, so a priority
- One Outcome is they wanted to move part of their support calls to chat.
- Would reduce costs in their huge contact center.
- Outcome Quantified
- 30% calls moved to chat.
- Saved $75 Million over 3 years
- 30% calls moved to chat.
26. Practice Connecting Outcomes
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20964178#overview
formerly #24
1. Start with an existing customer in mind.
2. What is the service they use? Name it.
3. Who are the stakeholders? Make a note of the function that use it and the role of the most senior individual involved in the original purchase.
4. What is THEIR use case? This may be different to the service in (2) and more specific.
5. What service outcome are they achieving or, perhaps, what service outcome justified the initial selection of your service?
6. Is it quantifiable? If so what quantified outcomes is being targeted or actually achieved?
7. Connect it to one of the 4 Value Drivers
50% Complete!!
27. Outcome Quality
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/21794416#overview
My Notes (Trying to organize where he is going)
Outcome Qualifiers
- Connected (to a Value Driver)
- Connected
- Disconnected
- Identified (Can it be named?)
- Unknown?
- Tacit (Unspoken)
- Inferred or implied from what we know about the general use case
- Explicit and known
- Stated by the customer and not by me.
- Quantified (Measured against mutually agreed benchmarks or targets)
- What were measurements historically? What are you trying to achieve?
- Quantified
- Not Quantified
- It is a must to measure the quality of the outcome and improve it if you want to impact the Renewal.
- Operational (Does it keep the business running?)
- Normal operations
- If your service is about accepting payments, the customer will not shut me off until implementing an alternative solution.
- Strategic Initiative or Change.
- What period, or how long, is the business focused on achieving this?
- Normal operations
- Socialized (Discussed at every QBR, or at least annually)
- This is why the customer works with me… is this still true?
- Never
- Infrequently
- Regularly
- Aligned (To a product or direction)
- Businesses evolve. Sometimes slightly, sometimes significantly.
- Not all customers subscribe because of where I am today, or where we are going tomorrow.
- It might be the right thing for some customers to fall away over time if they are not aligned.
- Service is aligned
- Service is not aligned
- Businesses evolve. Sometimes slightly, sometimes significantly.
Quiz 3: Outcome Quiz
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/quiz/4995186#overview
1. This business has a personalization product. It is being used by Virgin Atlantic to customize pre-flight messaging to include details about their flight and seating preferences. Is personalization a feature or an outcome?
- Feature
- It could be both a feature and an outcome but articulated in this general way it is most likely a feature.
- Outcome
(IMHO, this should be a Benefit)
2. Which of the following is NOT a Value Driver
- Make Money
- Save Money
- Win Customers
- This is an important outcome for most businesses but it is not one of the four value drivers
- Reduce Risk
- Drive Strategy
3. Your SaaS business, Content.ly, delivers a content marketing solution as SaaS. It is being used by a European Healthcare and Wellbeing Business. They have 45,000 customers and are continuing to grow. They are strategically focused on content marketing with a strong following on the subject of wellness. New business originating from content marketing accounts for more than half of their new customers. They use the service to track website visitors based on the content they consume and set up targeted calls to action, forms and workflows. They have seen a 48% growth in Traffic.
Could the outcome be connected?
- Website traffic converts to leads and leads convert to sales. It will most likely be connected to the Make Money value driver.
- The customer is strategically focused on online, content marketing so it is likely to be connected to the Make Money value driver. It should be confirmed with the customer though.
- Marketing in this way is less expensive than tele-marketing, so it will most likely connect to the Save Money value driver.
4. Still with Content.ly and with the same Healthcare and Wellbeing customer strategically focused on content marketing and seeing a 48% growth in website traffic as a result of using your service.
Is the outcome quantified?
- Yes
- Yes it is. They are seeing almost half of much website traffic again
- No
5. Still with Content.ly and with the same Healthcare and Wellbeing customer strategically focused on content marketing and seeing a 48% growth in website traffic as a result of using your service.
Is the outcome operational?
- Yes
- This is more difficult to assess but, on balance, because the business is focused on driving sales through a content marketing strategy, this could be thought of as operational
- No
Assignment 1: Connecting Outcomes to Value Drivers
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/practice/1222880#overview
YOU ARE HERE
1. Start with an existing customer in mind. What is the service they use? Name it.
2. Who are the stakeholders? Make a note of the function that use it and the role of the most senior individual involved in the original purchase.
- Have you included a typical user, a user champion and an economic buyer or executive sponsor.
3. What is THEIR use case? This may be different to the service in (1) and more specific.
- How is the service being used more specifically. This is not the general application of the service but specific to the customers setting.
4. What service outcome are they achieving or, perhaps, what service outcome justified the initial selection of your service?
- This is getting specific now. What is the outcome? This should be something specific and measurable even if it is not, at the moment, quantitative.
5. Is it quantifiable? If so what quantified outcomes is being targeted or actually achieved?
- It may or may not be but ideally you want to know how the outcome is being measured by the customer.
6. Connect it to one of the 4 Value Drivers based on what you know today. Remember, it may not be a direct connection.
- Does it connect to Make Money, Save Money, Reduce Risk or Drive Strategy?
28. Relationship Perspective
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20243976#overview
formerly #25
The activity in this perspective is essential in illuminating customer relationships so:
- They can be maintained
- I will know where they need to be improved.
Activities
- Champion building
- Building 3 events or communities that provide user champions from one customer an opportunity to share with champions from another.
- These forums are great ways to introduce prospective customers to what you do.
- Customer Advisory Boards
Key Tool
- Relationship Mapping
- Used to diagnose my connections with customer so when we say we have a good or bad relationship, we know exactly what we mean.
- Without it, we usually only have a sense of the relationship
- Or only focused on recent events
- Relationship Mapping takes that vague sense of a customer relationship and provides it with precision.
- It assigns qualities to the relationship
- These help me understand what I need to do specifically to maintain or improve it.
- It assigns qualities to the relationship
- Used to diagnose my connections with customer so when we say we have a good or bad relationship, we know exactly what we mean.
29. Relationship Mapping
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20965570#overview
Think of an existing customer. How would I describe my relationship with them today?
- “I have a good relationship with Client X”
- “I have a great relationship with Client Y”
- “My relationship with Client Z is a bit strained”
While the above statements are vague, there is probably a little more behind them.
- Based on general emotions
- Possibly based on something that happened recently
Better to say something like:
- Company Y loves the product.
- They recently attended our last conference
- They just rated a 9 on NPS.
The Basics
- Name
- Role
Now map that relationship to how they are associated with the service
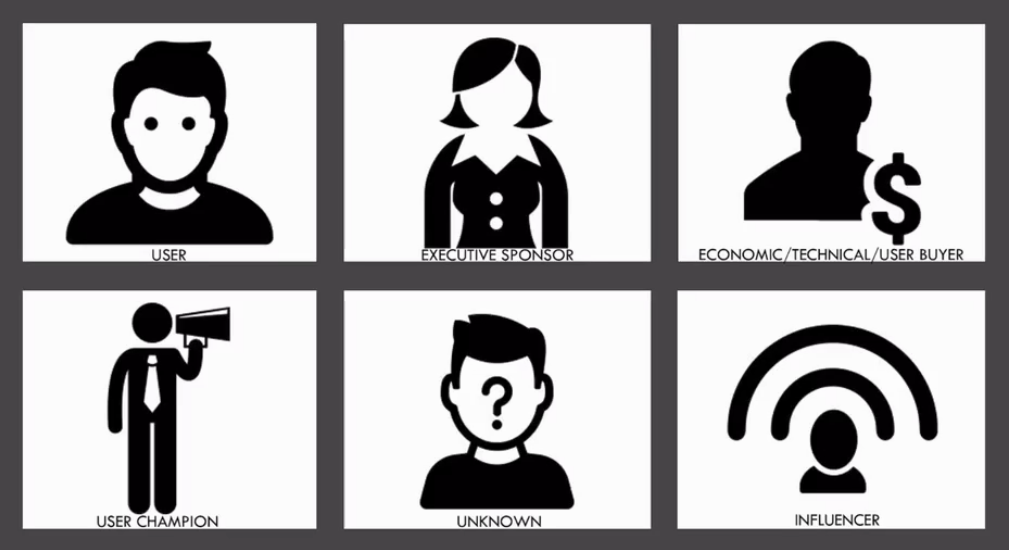
The Relationship Nature
- Users
- Users are literally users of the service, getting direct value.
- There may be different types of users
- CRM
- Salespeople keep track of their accounts, contacts and opportunities
- Sales leader may only consume a summary of the information in the form of reports.
- CRM
- User Champions
- May be part of the team responsible for evaluating and ultimately selecting your service
- These may be users that are more proficient and other users turn to them for help.
- They may be nominated user to represent a team or an office or geography
- Champions generally represent and speak for groups of users and are consulted when decisions are made about my service.
- Buyers (Economic / Technical / User)
- The people that opted to buy my services are likely to be the same people that are responsible for renewing them
- Economic Buyer
- Owner of the budget
- CFO
- Procurement professional
- Technical Buyer
- Does not have budgetary responsibility
- Consultant on technical suitability
- Often part of the IT team
- User Buyer
- Often the same as the User Champion
- Less concerned with the technical suitability
- More concerned with suitability for the Team, Group or Process.
- Executive Sponsor
- May be the same as the Economic Buyer
- Their responsibility will be braoder than just economics
- Possibly concerned with risk
- Business Impact is there are issues with the service.
- Most likely to be the most senior person I’ll be working with.
- Influencers
- Anyone who is not a Champion or buyer, but still influences the decision to buy, expand or renew.
- Unknown
- Placeholder to find out more (Did I miss anyone?)
Quality of the Relationship
From the author of “The Ultimate Question” and creator of NPS
Promoters
- Do they have a tendency to say great things about us and our service?
- Do they see and share the value?
- Do they give us the benefit of the doubt?
- If something goes wrong, will they fight in our corner?
Passive
- Do they usually rely on what others say?
- Do they not show any signs of having a strong opinion
Detractor
- Did they prefer a competitive solution but went along with the group?
- Perhaps they are pretty Senior, and have a history of going with competitors, but went along with my solution this time as an exception
Pulling it together
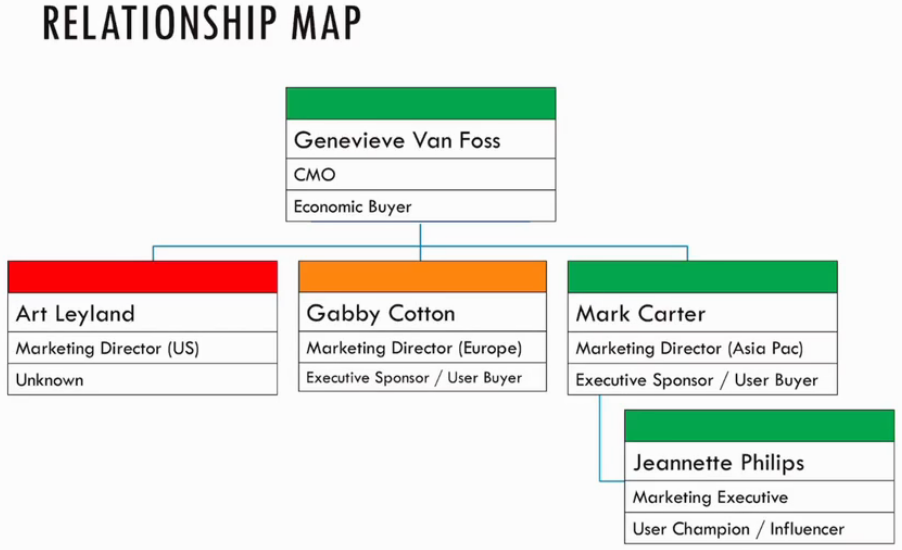
In the above image, we have a clear representation of the contact.
- Name: Charles
- Position: VP Global Services
- Nature of the relationship
- Executive Sponsor
- Economic Buyer
- Quality of Relationship: Passive
Relationship Map
The Relationship Map is likely built with assistance from the Commercial Team
Story focus on Art.
- Joined after the solution was implemented
- Promoted a competitive product as previous company
- Spoke at their last user conference.
Action
- We must find out more about Art.
- His influence on the renewal decision
- Is his influence enough to disrupt my plans for expansion.
30. Adoption Perspective Introduction
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20243988#overview
Introduction
This perspective is the Measurement and Management of Adoption
- Pre-emptive assessment of adoption to understand and respond to activity and feature usage
Why
- My service was likely purchased by someone Senior in the company
- Supported by a small number of users and/or managers that championed me as their preferred solution
- Should have been an onboarding so those that use my services have been well trained and engaged.
- This doesn’t mean all users will
- Use the service
- Use it in the best possible way
- Use it in a way that gets the most value for them
- Make use of the most optimum services/features I provide
Activities
- Generating and maintaining an awareness of my service
- Promoting the service
- Ongoing Education
- Sharing best practices between user communities
31. Adoption Assessment Introduction
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20992220#overview
- Adoption Assessment, a structured technique for measuring adoption, is an advanced warning system.
- Will provide an early indication that either the service is providing value
- If your users are logging into my service and using it, they are doing so for a reason.
- It adds value to what they are doing and ideally they like it also.
- Or there is an issue
- If I analyze adoption and I see my service is not used, or used infrequently, I need to know why.
- This requires further investigation and action.
- Hopefully this before the Champion or Sponsor raises the point.
32. Activity Assessment
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20992222#overview
Measurement
- Track usage and usage patterns
- How many users are active
- Which teams or offices are using it
- What are their usage patterns?
- Daily
- Weekly
- Monthly
- Is this what I was expecting?
- An “Expense Manage” application should be used once weekly, or expect a spike around each monthly expense cutoff date.
- Systems such as a CRM, should be used on a daily basis
- Active usages should be compared against licensed users.
- My service will likely been priced by the number of users, or seats.
- If the customer has 1000 users, they are paying for 1000 users.
- If I routinely see 900 to 1000 active users, then I’m in pretty good place.
- If only 700, then I can expect a conversation about it at the next meeting, certainly by the next renewal.
- Most common use for tracking usage is locating inactive users or teams
- Highly active individuals or teams may be used to help the low
- What are these teams doing that the other is not?
- Can this information/techniques be shared with the other?
Actions – Key Responses for Activity Usage
- Raise Awareness
- “All all your users aware the service is active and available to them?”
- “Do they all have log ins?”
- Promotion
- Do I need to perform some internal marketing to my customer?
- (Seems like there should have been more here)
- Do I need to perform some internal marketing to my customer?
- Training
- Are users finding it difficult to do what they need to do?
- Product
- Does the product require enhancement?
- I should be building a case for the product team to enhance the service.
33. Feature Adoption Assessment
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20998038#overview
Value Features
- Perhaps some features offer more value than others in my service.
- Save more time
- Greater levels of Automation
- Innovations the customer could do without
- Customers using higher value, advanced features are maximizing the use of the service
- Customers only using lower level features is not getting the most value available
- This could be a risk of an adoption issue.
Differentiated Features
- Things my service does that the competitor does not, or does not do it as well.
- Customers using these features understand the advantages of my service.
- Customers not using these features are open to competitive products
- This is also an adoption issue
New Features
- As my product evolves, it can make more value available for my customers’ users.
- However, these create a barrier to usage in terms of awareness and training.
- Users familiar with the service did originally may have blind spots to what the service can do today.
- Hopefully the new product team thought this out and made the enhancements product driven and intuitive
- Analysis can show where there are issues
- Take Action
- Raise awareness
- Are users aware?
- Are they missing information because of poor communication?
- Promotion
- Do I need to do some internal marketing?
- Do I need to sell a new product feature by persuading users or communities though a campaign that new feature is worth the effort required to learn it?
- Training
- Are users missing essential training?
- Is my analysis of user activity telling me that they are not using the service in a way that is optimum?
- Can I offer training or online tutorials that will fix the issue?
- Product Feedback
- Have we discovered a product issue that exposes a problem that will require me to work with the product team to identify improvements that in turn, improve adoption.
- Raise awareness
34. Adoption Assessment Wrap Up
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20992230#overview
Actions for Adoption Assessment
- Activity Assessment
- Identifies problematic levels of usage
- May provide clues to the best way to address them
- Users or teams that are active or inactive
- Feature Assessment
- Tells us much more about the value and adoption risks
- This is a leading leading indicator of Activity Assessment
- If new features, high value features, or differentiating features are being used
- Activity will likely remain constant and adoption will not be an issue
- If these are NOT being used, there is a risk of losing out to a competitor
- Resolutions
- Raise awareness
- Promote
- Train
- Get Feedback/Improve product.
Regular and Frequent measurement and analysis of Adoption underpins everything else I do
35. Expansion Perspective Introduction
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20243982#overview
Customers that are planning to expand, and continue to invest in my service are contented with the service and possibly even delighted. Expanding customers are renewing customers.
- Only ~50% of SaaS treat expansion as a priority
- Activity in this perspective will single me out as a CSM
- Investment here is NOT just about maintaining the customer relationship, it is about Growing It.
Activities
- Building new connections inside my customers’ organizations and networking.
- Enabling customers when there are new features
- Analyzing specific gaps between the service I offered today and the service I could offer
- This will help identify the next most productive conversation on the subject
- Opportunity management will help identify expansions and be rigorous and commercially minded in my management of them.
36. Expansion Process
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20998084#overview
- Many companies do not treat Expansion as a priority may be
- CSMs are motivated by providing excellent customer service
- Might be uncomfortable with some commercial aspects
- May Feel awkward when asking for payments
- Professionals have no trouble asking for value to be returned in the form of payment in exchange for the value of their business provides.
- Expansions of the services process is a Customer Success process
- I’m bringing new sources of value to a customer
- This is also a Sales process
- To be treated proactively, this needs to be treated as a sales process with the following stages:
- Stages that can be ignored
- No Prospecting is required
- Relationship is already built
- If watching the activities in the Relationship perspective, it should be positive
- Stages that need attention. These can be discovered during my regular meetings by ensuring there are placeholders for them to provide updates about their business.
- Customer Need
- Customer Awareness (Or Customer Need met by my Solution)
- Might just be extending the service to other teams
- Qualification – Important
- Is it worth my time and the customer’s time?
- If the customer and I are both aware the customer has a need and I have a solution, I will want to help and they will want my help.
- However, the cost might be too high
- Might have the need but does not have the budget.
- This requires commercial skills to qualify
- Is this worth my time or my client’s time?
- Might be easy or hard
- Client might have budget or authority, maybe they do not.
- No matter what, Qualify.
- If you cannot qualify, work with the Commercial team and ask for help
- Investigation
- Match the customer need to the solution
- Commercial
- Negotiation about costs, terms, conditions and timescales between the customer and my business
- Justification process for the contract and need to secure the budget.
- Closed Implement or Closed Down
- Only after the above have been completed that the expansion opportunity can
- Close, and get ready for implementation and Onboarding
- Close down completely and taken off everyone’s desk
- Only after the above have been completed that the expansion opportunity can
- Stages that can be ignored
Key Takeways
- Customer Success Managers want to help
- Customers often need help
- It’s the right thing to play a long game and consider the long term relationship with the customer
- But must be done through a commercial lens.
37. Organization Perspective
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20243992#overview
- This perspective is different from the others.
- it overlays Outcome, Relationship, Adoption and Expansion with measurement and management activity
- These ensure you are prepared and proactive.
- This perspective helps ME to be diligent, rigorous, thorough
- It helps me to stay proactive
- How this works
- Keep everyone up to date in my own business.
- Make sure I have access to the resources I need when I need them
- Organize with my Customer in a way that elevates their confidence in me.
- Keep everyone up to date in my own business.
Activities
- Health measurement
- Create a meeting schedule that respects both my, and my customer’s time
- Red Flag testing
- A regular desk check to spur me into corrective actions
- Create internal groups to help me review and manage my customers, both tactically and strategically.
38. Red Flag Testing
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/21195032#overview
Red Flags
Red flags, by definition, occur in your regular interactions with customers. Something happens, something changes or something is said that signals that there is an issue but that, for whatever reason, your contact is unable to discuss it openly. Alternatively, they may just not be aware that it requires active management and your participation.
For example, your executive sponsor secures another role in a new organization. Your operational contact may share this with you but will not, understandably, be prioritizing the impact on your relationship with them. They will be rightly supporting the many changes to their own organization. However, you will want to manage the change too. It will, as a minimum, require introductions to the incoming executive.
Investigate, Action or Convert to Risks
Red flags may or may not be an issue but they do require your attention. They should be investigated and actioned until you are confident that either;
- There is no longer a red flag
- There is no more that you can do and it becomes a risk
You will require a consensus from those colleagues that have an interest in the customer relationship that there is nothing more that can be reasonably done to manage the red flag. Most are reluctant to accept significant risks to customer relationships so the process of seeking consensus may raise support from other teams that had not previously been forthcoming. However, some risks may need to be accepted. For example, the customer may have been achieving value from the product in a way that no longer aligns with the rest of the market. To continue to invest in that functionality may not be commercially viable.
Awareness and Proactive Desk Checking
Over time, as a Customer Success Manager, you will develop an instinct for red flags. They will stop you in your tracks in the middle of a call or meeting. However, as part of your routine health measurement, you should remind yourself of your list of red flags. Has something happened over the last period that, on reflection, could be a red flag? For that reason periodically review your portfolio against your list of red flags.
Starter List
There is a list of red flags attached to this article. It will be a reasonably good starting point. Review this list during this course, or soon after, to make it an even better fit for your setting.
Red Flag Testing Checklist
- Outcome unclear
- Product is not a good fit
- Stalled implementation
- Change of people
- “I have been busy” – Low usage or adoption
- “If only it could do this” – High levels of unfulfilled product requests
- “We went another way” – Customer changes strategic direction
- “They don’t get us” – Poor performance or product experience
- We are just not gellin'” – Relationship problems
Assignment 2: Practive Reviewing for Red Flags
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/practice/1217594#overview
Formerly: Assignment 1: Building your own red flag tests
For one of your key customers, ask yourself these questions to identify if there are red flags. Red flags may or may not be indicators of an issue. For example, some customers are naturally over-critical even though they are happy with the service. Red flags though should be examined and investigated to identify if there is (or is not) an underlying issue.
Questions for this assignment
-
- Can your Customer user champion(s) describe the expected business outcome?
- Key users, including your user champions, should be able to naturally describe the reason they use your service. They may not be able to quantify it but if it is clear to them, then it will be clear to the business when they are making decisions at the next renewal event.
- Is your customer lobbying you, the product team, or support for a significant new feature and have hinted that a future renewal would be dependent on it?
- Your product will never meet all the needs of all your users. The product team are maintaining a difficult balance of evolving the service to meet the needs of a set of use cases within a market. A user that is lobbying for a significant enhancement may or may not be aligned with the direction of the product so this may require your intervention to understand if your product and the customer are growing in the same direction.
- Where there are projects (Onboarding or expansion) are they tracking to planned timescales?
- Projects often require additional budget. Your key stakeholders reputation will be impacted by the outcome for the project. If things are going well, it will help them. Everyone understands that projects can go awry but if they do then the problem, the solution and revised expectations should be communicated clearly and in a way that supports your key stakeholders.
- Is your user champion, economic buyer or executive sponsor moving to a new role or new organization? If so, have they committed to an introduction and/or handover to the new individual?
- Ensure that the outgoing stakeholder has handed over to the incoming stakeholder including being introduced to you as their Customer Success Manager.
- Is the business changing in direction in a way that would impact their need for your service?
- Your business review meetings are an opportunity for you to share business updates but also leave space for your customer to update you. It’s a red flag if they are not, if only to persuade them to update you, and it is a red flag if there is a change in strategic direction that will impact the value that they receive from your service.
- Does the customer casually comment on functionality or the performance of your service based on historical issues that you believe to be resolved?
- Perhaps a problem have had a disproportionate impact on your customer, it may have been highly visible, or it may not have been entirely resolved to the customers complete satisfaction. If your business believes it to be resolved but the customer is hinting it is not then it requires investigating.
- Does the customer ask for functionality or features that don’t make complete sense to the use cases that the product has been built to satisfy?
- If the customer has an expectation that is not aligned with your product roadmap then it is likely one of two things. It could be an early warning that their need and your solution are diverging. This does happen from time to time. Or it could be that their requirements are evolving in a way that the market is and it is not visible to the product teams in your business. Dig into the detail with the customer and have open discussions with your product team to determine which.
- The relationship should be able to withstand constructive and positive criticism from the customer. However, is there a key customer contact(s) who is overly critical and/or unforgiving when there are problems?
- An over-reaction to a problem could indicate underlying issues that the customer has not fully communicated to you or that they don’t understand completely themselves.
- Can your Customer user champion(s) describe the expected business outcome?
Now that you have been through this process, how will you adapt the red flag tests for your setting?
39. Customer Portfolio Tracking
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/21197174#content
essentialcsmportfoliotracker202007
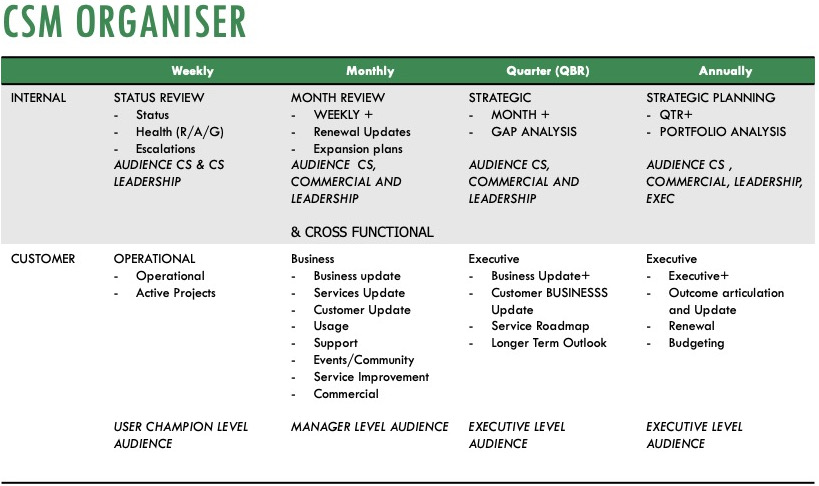
40. The CSM Organizer
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/20998170#content
- The CSM Organizer will help you organizer your week, month, quarters and year.
- The organizer details the internal meetings and customer that should be happening once weekly, monthly, quarterly and annually along with the audience required to make the forums successful.
- For example, a CSM should ensuring they meet with their customers on operational issues weekly or monthly, on business issues monthly and on strategic quarterly.
41. Customer Meeting Template
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/lecture/21197398#content
EssentialCsmCustomerMeetingTemplate202007
Quiz 3: Framework Quiz
https://www.udemy.com/course/essential-customer-success/learn/quiz/4957494#overview
Which of these is NOT a value driver?
- Generates Revenues
- Save Money
- Increase brand loyalty
- This is not a value driver. It is an outcome and would, if successful, lead to increasing revenue (making money) but it is not one of our four value drivers.
- Reduce risk
What is a disconnected outcome?
- It is an outcome that is a leading indicator
- It is an outcome, attributable to the use of your service, which is not connected to a value driver
- It is an outcome of your service that has not been explicitly connected to one of the four key value drivers.
- Is is an outcome that is a lagging indicator
- It is one of Make Money, Save Money, Reduce Risk or Drive Strategy
Which of these is NOT a relationship type
- User Champion
- Economic Buyer
- Partner
- Partner is not a relationship type. They are (1) User, (2) User Champion, (3) Economic/User/Technical Buyer, (4) Executive Sponsor (5) Influencer or (6) Unknown and requiring further investigation
Which of the following is NOT a type of Feature Assessment
- Differentiated Features
- Value Features
- Leading Features
- This is not a type of Feature Assessment. The types of features a CSM should be monitoring and assessing are (1) Value Features (2) Differentiated Features and (3) New Features
Which of the following will NOT improve the number of completed expansion opportunities
- Ensuring you start conversations that relate to potential new needs by ensuring there are placeholders in your business meetings
- Treating an expansion discussion as rigorously as a sales process
- Ensuring you take minutes in every customer meeting, share them and ensure they are agreed.
- It would be a professional approach to take to your meetings but this will not necessarily improve the number of completed expansion opportunities