Shared Storage
- Multiple computers access data on the same storage device
- In the virtual world, shared storage means VMs
- Most vCenter features require this.
vCenter features that REQUIRE shared storage
- DRS
- DPM
- Storage DRS
- High Availability
- Fault Tolerance
Shared Storage Supported Formats
- Fibre Channel
- Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE)
- iSCSI
- NFS
- Local Storage
Fibre Channel
- Fibre Channel is a high speed network technology generally used for network storage.
- Generally speeds are 2, 4, 8 and 16 Gbps
- It used FCP (Fibre Channel Protocol) similar to TCP
- Often used for SAN (Storage Area Networks)
- Despite its name, it does NOT require fibre, but can run on an electrical interface. (This is why is uses the British spelling!)
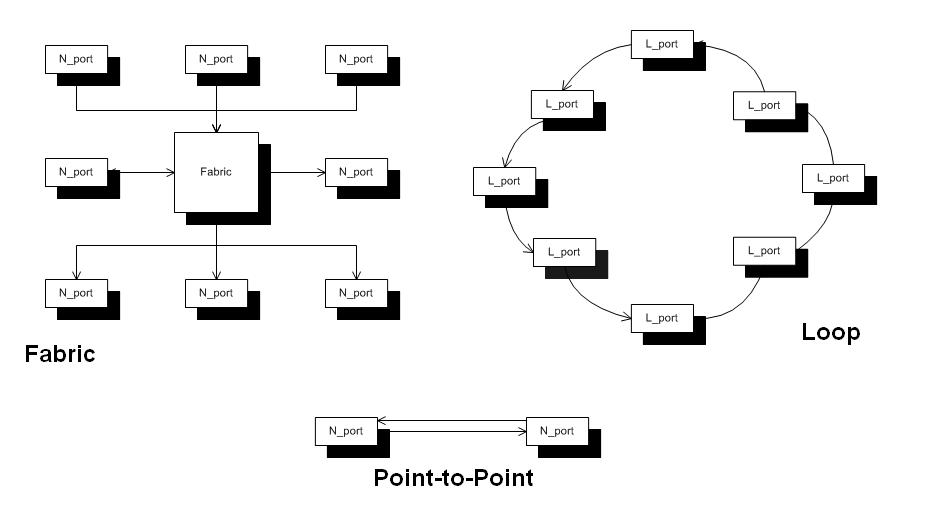
Fibre Channel Topologies
Fibre Channel over Ethernet
- Specification that allows sending FCP over standard Ethernet.
- Generally ran on 10Gbps networks to maintain speed
iSCSI (Internet Small Computer Interface)
- IP Based protocol for linking network based storage facilities. (Protocol sends SCSI commands)
- Can be used with LANS, WANS and Internet.
- Can be used with standard Ethernet technologies
- Requires no dedicated cabling
- Performance can be affected by competition for networking resources
Terminology
- Initiator: The server that acts as the client and communicates with the storage device. Other PCs will connect to the initiator.
- Target: The storage device
NFS (Network File System)
- Standard networking protocol to mount a remote partition as if it was a local drive.
vSphere Storage Appliance (VSA)
- Allows creation of shared storage from the local storage devices in the ESXi hosts
- Provides management and control to share these devices to take advantage of DRS, HA and Fault Tolerance
- Designate disks within ESXi hosts and VSA does the rest.
- Replicates data between ESXi hosts, so if one fails, another can take over.
- Runs as a VM or simply a server on the host?
vFlash
- Good for VMs requiring high speed storage access
- Uses internal SSD drives to accelerate READ performance
- vFlash operates like a read-cache
- VM must be configured to use the vFlash storage
Datastores
- Virtual Machines are stored in containers called “Datastores”
- These are Logical Volumes that allow storage of ESXi host and VMs
- 2 types of Datastores
- Virtual Machine File System (VMFS): Local, iSCSI, Fibre Channel, FCoE
- Network File System (NFS): Network Attached Storage (NAS)