< Section 17 | Home | Section 19 >
57% Complete
116. Introduction
https://www.udemy.com/course/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605642#overview
- Ping
- Traceroute
117. Basic Connectivity Troubleshooting
https://www.udemy.com/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8605640#overview
Ping
- Uses ICMP
- Internet Control Message Protocol
Message Replies
- ! (Exclamation Point): The Ping reached its destination and returned successfully.
- It is not uncommon to miss the first 1 (or even 2) pings if a devices has not updated its ARP cache.
- . (Period): Indicates the Ping has failed.
- Router does not have a corresponding route
- Destination IP address is not responding
- U (Unreachable): The packet has been discarded
- Blocked by an Access Control List
Extended Ping
PC1> ping 10.1.2.10 10.1.2.10 icmp_seq=1 timeout 10.1.2.10 icmp_seq=2 timeout ... 10.1.2.10 icmp_seq=5 timeout
R1> ping 10.1.2.10 Sending 5 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.2.10, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100% (5/5)
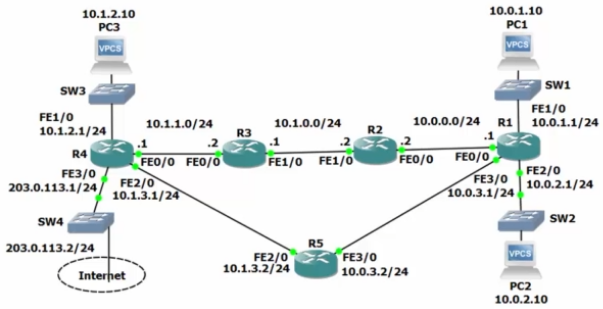
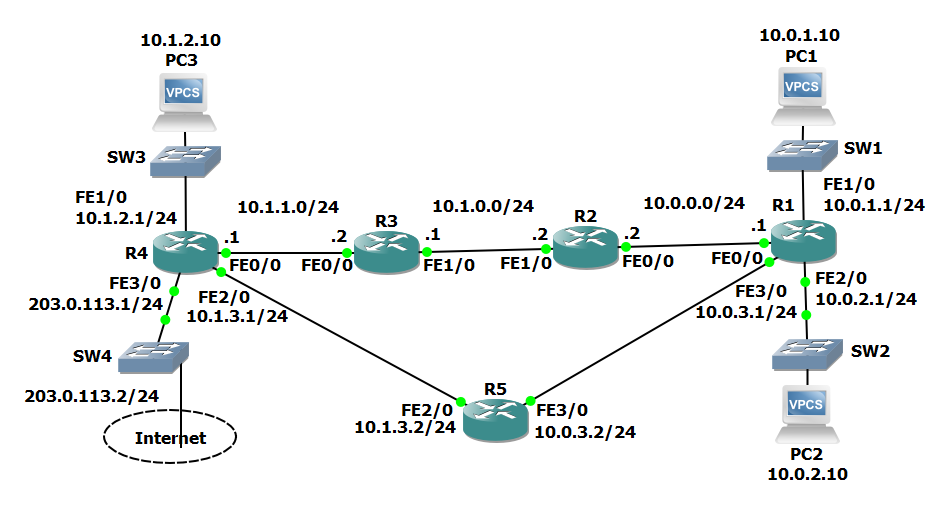
Scenario:
- PC1 complains he cannot access services on PC3
- R4 does not have a route to 10.0.1.0/24
- Traffic which originates from a router always uses the IP address on the outgoing interface as the source address.
- A ping from R1 to 10.1.2.10 will succeed because R4 has a route to 10.0.0.1
Solution:
- Force the PING to source from the same subnet the PC is on (10.0.1.0/24)
- You should always do this when checking connectivity from a subnet!
R1#ping Protocol [ip] Target IP address: 10.1.2.10 Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 10.0.1.1 ... (Default the remaining options) Sending 5 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.2.10, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 10.0.1.1 ..... Success rate is 100% (5/5)
Extended Ping option descriptions
- Repeat count: Set this to a higher value if you suspect a connection is going up and down
- Datagram size [100]: Good to troubleshoot a suspected MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) issue.
- This allows you to set the packet to different sizes to check this.
- Timeout in seconds [2]: Possibly increase this if running over very slow connections.
- Extended commands [n]: Required ‘y’ if you want to manually set a source address or interface.
- Source address or interface: Use the IP address of the interface that corresponds to the subnet experiencing the issue.
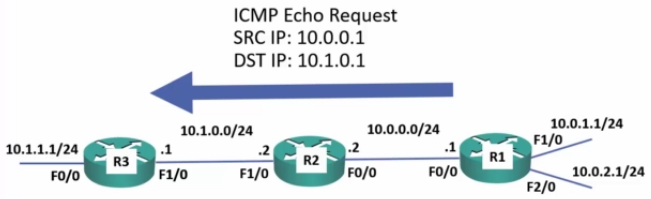
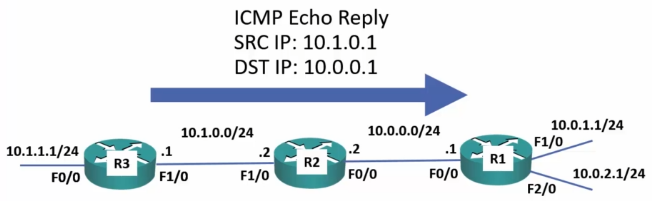
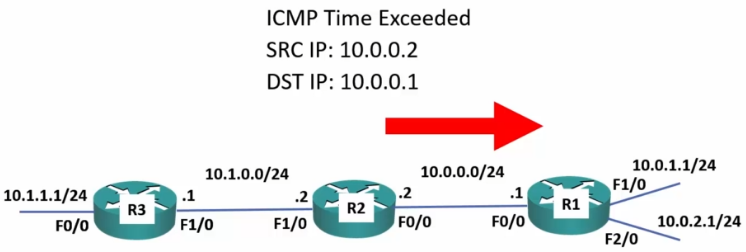
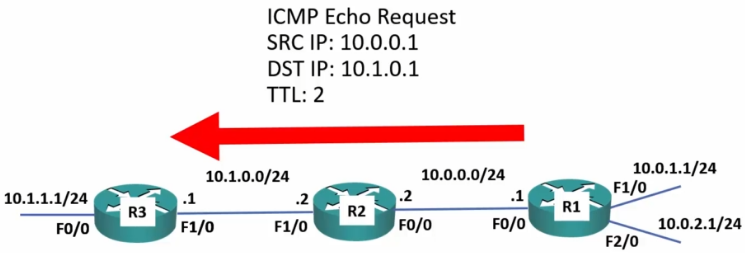
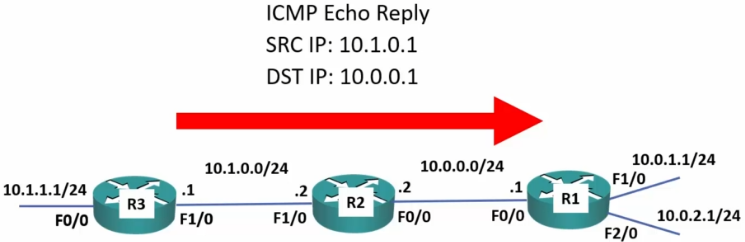
Traceroute
- Very similar to PING.
- Great for checking connectivity issues between 2 points.
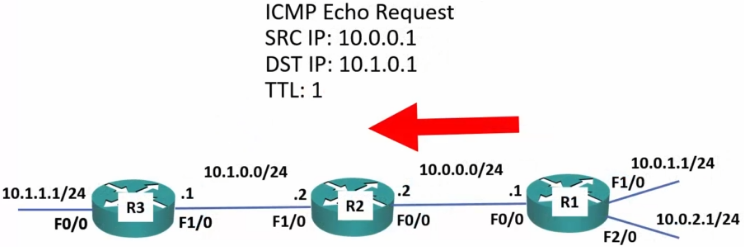
- 1st. attempt is set with a TTL (time to live, although really means ‘maximum hop count’) of 1
- TTL is actually used as a route loop prevention mechanism.
- This prevents a packet from getting stuck in eternal loops.
- Each time a packet is passed, it decrements the TTL by one.
- Once the TTL reaches 0:
- The router drops the packet
- It replies to the sender with a ‘time exceeded’ message
- Each successive attempt adds one more to the TTL.
- 2nd attempt = 2 hops
- 3rd attempt = 3 hops
- Each ‘hop’ replies with the IP address it reached before returning and total time taken to run reach and return.
Successful Traceroute:
R1#traceroute 10.1.2.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 10.1.2.1 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 10.0.0.2 20 msec 16 msec 16 msec 2 10.1.0.1 36 msec 40 msec 40 msec 3 10.1.1.1 60 msec 54 msec 60 msec
Traceroute Responses
- First run Ping to verify the connection is failing
- Then run Traceroute to find out where the failure starts.
- In this example, the packet gets as far as 10.1.0.1. Start troubleshooting there.
- Press <Ctrl><Shift><6> to abort.
R1#traceroute 10.1.2.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 10.1.2.1 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 10.0.0.2 28 msec 16 msec 16 msec 2 10.1.0.1 36 msec 36 msec 40 msec 3 * * * 4 * * *
Other basic tools
- Layer 1
- show ip interface brief
- show interface
- Layer 2
- show arp
- show mac address-table
- Layer 4
- telnet <destination IP> <destination Port>
- DNS
- nslookup (like dig)
- Ping by FQDN
118. Connectivity Troubleshooting – Lab Exercises
https://www.udemy.com/course/cisco-icnd1/learn/lecture/8631424#overview
18 Connectivity Troubleshooting Lab Exercise
18 Connectivity Troubleshooting Answer Key
1. Use ping to test connectivity from PC1 to PC3.
PC1> ping 10.1.2.10 *10.1.0.1 icmp_seq=1 ttl=253 time=108.341 ms (ICMP type:3, code:1, Destination host unreachable) *10.1.0.1 icmp_seq=2 ttl=253 time=82.847 ms (ICMP type:3, code:1, Destination host unreachable) *10.1.0.1 icmp_seq=3 ttl=253 time=98.612 ms (ICMP type:3, code:1, Destination host unreachable)
2. Use traceroute to determine where the problem is likely to be.
PC1> trace 10.1.2.10 trace to 10.1.2.10, 8 hops max, press Ctrl+C to stop 1 10.0.1.1 33.801 ms 16.563 ms 26.429 ms 2 10.0.0.2 50.240 ms 98.177 ms 75.777 ms 3 10.1.0.1 121.613 ms 121.023 ms 109.946 ms 4 *10.1.0.1 106.448 ms (ICMP type:3, code:1, Destination host unreachable
Problem between R3 and R4
3. Determine the issue and fix it to restore connectivity between PC1 and PC3
Check R3 Interfaces Up – OK
R3#sh ip int bri Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol FastEthernet0/0 10.1.1.2 YES NVRAM up up FastEthernet1/0 10.1.0.1 YES NVRAM up up FastEthernet2/0 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down down FastEthernet3/0 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down down
Check R3 for routes to 10.1.2.0/24 – FAIL
R3#show ip route 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 9 subnets, 2 masks S 10.0.0.0/24 [1/0] via 10.1.0.2 S 10.0.1.0/24 [1/0] via 10.1.0.2 S 10.0.2.0/24 [1/0] via 10.1.0.2 S 10.0.3.0/24 [1/0] via 10.1.0.2 C 10.1.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 L 10.1.0.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 L 10.1.1.2/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 S 10.1.3.0/24 [1/0] via 10.1.1.1
Add static route to 10.1.2.0/24 via 10.1.1.1
R3#conf t R3(config)#ip route 10.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.1.1
Verify ping from PC1
PC1> ping 10.1.2.10 84 bytes from 10.1.2.10 icmp_seq=1 ttl=60 time=170.952 ms 84 bytes from 10.1.2.10 icmp_seq=2 ttl=60 time=122.586 ms 84 bytes from 10.1.2.10 icmp_seq=3 ttl=60 time=93.745 ms 84 bytes from 10.1.2.10 icmp_seq=4 ttl=60 time=146.945 ms 84 bytes from 10.1.2.10 icmp_seq=5 ttl=60 time=141.337 ms
Done!