Types of Wireless Networks
- PAN: Personal Area Network – Wireless Mouse, Bluetooth, very short distance
- LAN: Local Area Network – replace or suppliment your wired LAN
- MAN: Metropolitan Area Network – Uses Point to Point Wireless Bridges to allow network to extend several miles.
- WAN: Wide Area Network – Cellular.
Wireless LAN Facts
- Wireless Access Points (WAP) communicate like a Hub
- Shared Signal
- Half Duplex
- Use “Unlicensed” bands of Radio Frequency (RF)
- Is both a Physical and Data Link Standard
- Uses CSMA/CA Instead of CSMA/CD: Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance vs Collision Detection (Sends request to send before sending)
- Faces connectivity issues because of interference – Susceptible to neighbors, appliances, etc.
Unlicensed Frequencies
These are basically worldwide ranges. While these ranges are available for free use, “hogging” the bandwidth is illegal.
Lower frequencies get longer range, but slower bandwidth.
Higher frequencies get shorter range, but greater bandwidth.
- 900 MHz Range: 902 – 928
- 2.4 GHz Range: 2.400 – 2.483
- 5 GHz Range: 5.150 – 5.350
Understanding RF
- RF waves are absorbed (passing through walls) or reflected (by metal).
- Higher data rates have shorter ranges. (The closer you are, the faster you can send)
- Higher frequencies (RF) have higher data rates (bandwidth)
- Higher frequencies (RF) have higher data rates (bandwidth)
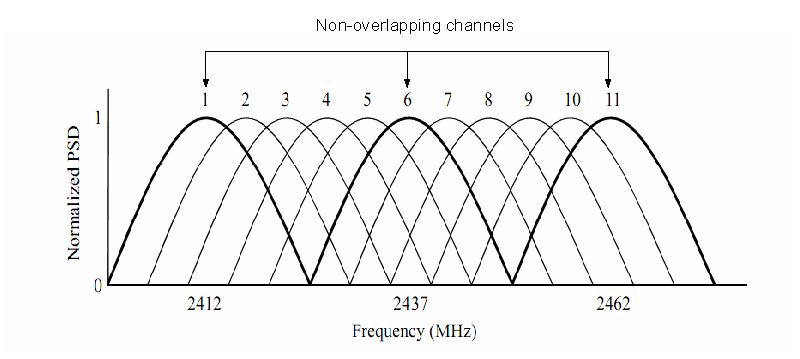
- Each channel is 5 MHz apart and 22 MHz wide.
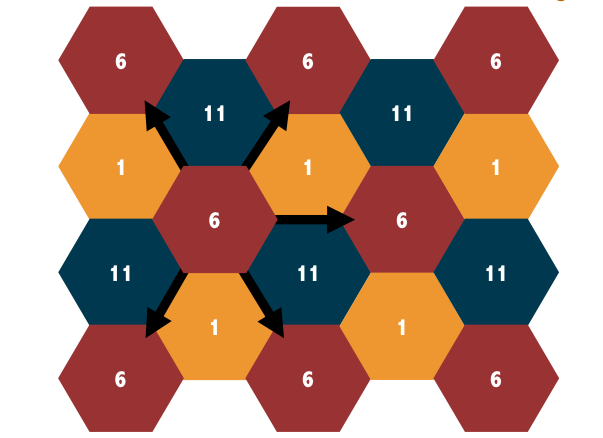
- Only channels 1, 6 and 11 are ‘clean’ and do not overlap each other.
The 802.11 Line Up
802.11B (2.4 GHz)
- Official as of Sept. 1999
- Up to 11 Mbps (1, 2, 5.5, 11 Data Rates)
- Most popular standard
- Three ‘clean’ channels
- Won out over .11A due to manufacturing issues.
802.11G (2.4 GHz)
- Offical as of June, 2003
- Backwards compatible with 802.11B
- Up to 54 Mbps (12 Data Rates)
- Three ‘clean’ channels
802.11A (5.8 GHz)
- Official as of Sept. 1999
- Up to 54 Mbps
- Not cross compatible with 802.11B/G
- 12 – 23 ‘clean’ channels
802.11N (2.4 & 5.8 GHz)
- Official as of Oct., 2009
- 100+ Mbps
- Uses MIMO (Multiple Inputs, Multiple Outputs)
- Multiple antennas
Designing Your Wireless Coverage
Wireless Ranges = ~300′ (150′ Radius)
The Powers Over the Wireless World
International Telecommunication Union – Radio Sector (ITU-R)
- Regulate the radio frequencies used for wireless transmission.
Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE)
- Maintains the 802.11 wireless transmission standards
Wi-Fi Alliance
- Ensures certified interoperability between 802.11 wireless vendors
- This makes sure products from different vendors work together seamlessly.