Lesson 3 of 6
< Lesson 2 | Lesson 4 >
Main Menu
Overview of Certificate Services
- What is a Certificate Authority
- A Certification Authority is an entity entrusted to issue certificates to:
- Individuals/Users
- Computers
- Organizations
- Network Devices
- Services
- These certificates verify the identity and other attributes of the certificate subject to other entities.
- A Certification Authority is an entity entrusted to issue certificates to:
- How CA Hierarchies Work
- CA Hierarchies include a root CA and one or more levels of subordinate CAs (option)
- Reasons for deploying more than a single server CA hierarchy
- Usage
- secure emails, web servers, etc.
- Organizational divisions
- Geographic divisions
- Load balancing
- High Availability
- Restrict administrative access
- Allows very granular control
- Usage
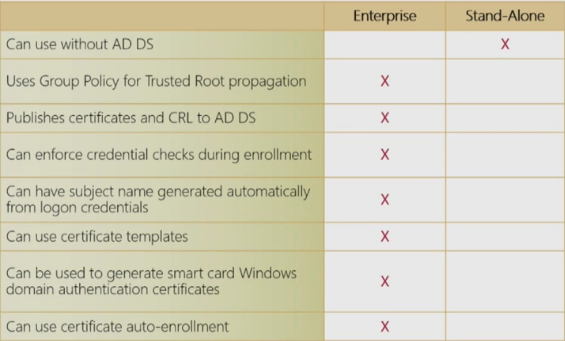
- Options for Implementing CAs
- When implementing a CA solution, you can
- Use an internal private CA
- Internal CAs are less expensive and provide more administrative options, but the issued certificates are not trusted by external clients.
- Use an external public CA
- Managed by a 3rd party.
- Use an internal private CA
- When implementing a CA solution, you can
- Options for Integrating AD CS and AD DS
- Demonstration: Tools for Managing AD CS
- This demonstration shows you how to install CS, but NOT how to configure it, making it impossible to follow along after the installation process completes. LAME!
- Certification Authority Tool
- Revoked Certs
- Issued Certs
- Pending requests
- Failed requests
- Cert. templates
- Right click > Manage = Cert. Template Console
- From here, you can modify the Templates for the certs that can be issued by the Cert. Authority.
- You do not use this page to determine which certs to issue.
- Online Responder Configuration
- Alternative to certification revokation list.
- Enterprise PKI
- provides information about your certification authority.
Understanding Active Directory Certificate Services Certificates
- What are Digital Certificates?
- A certificate is a digital file with 2 parts
- Basic information about the Certificate and the Holder
- Name
- Location
- Organizational Information
- Key (might be public or private)
- Public keys are distributed to all clients that request it.
- Private keys are only stored on the computer from which it was requested.
- Basic information about the Certificate and the Holder
- A certificate is a digital file with 2 parts
- How Public Keys and Private Keys Work
- Demonstration: Using Certificates to Secure Data
- What are Certificate Templates?
- Define what certificates can be issued by the CAs
- Define certificates used for various purposes
- Define which security principles have permissions to read, enroll and configure the certificate template.
Implementing Certificate Enrollment and Revocation
- Options for Implementing Certificate Enrollment
- What methods are used for certificate enrollment?
- Web Enrollment
- Manual/Offline Enrollment
- Automatic Enrollment
- What methods are used for certificate enrollment?
- Demo: Using Web Enrollment to Obtain Certificates
- In this demonstration, you will see how to use web enrollment to obtain certificates.
- Administering Certificate Enrollment
- To obtain a cert. using manual enrollment
- Create a cert. request
- Submit cert. request to CA
- Obtain administrative approval for certificate
- Retrieve cert. from CA and install on client.
- To obtain a cert. using manual enrollment