Very important to know this! 20% of the exam!
https://d0.awsstatic.com/whitepapers/Security/AWS_Security_Whitepaper.pdf
https://d0.awsstatic.com/whitepapers/Security/AWS_Security_Best_Practices.pdf
https://aws.amazon.com/security/security-resources/
Part 1
https://www.udemy.com/aws-certified-solutions-architect-associate/learn/v4/t/lecture/2050752?start=0
Shared Security Model
- AWS is responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure that supports the cloud.
- You’re responsible for anything you put on the cloud or connect to the the cloud
AWS Security Responsibilities
- AWS is responsible for protecting the global infrastructure that runs all of the services offered in the AWS cloud. This infrastructure is comprised of the hardware, software, networking and facilities that run AWS
- AWS is also responsible for the security configuration for all of their Managed Services products. Examples of these include:
- DynamoDB
- RDS
- Reshift
- Elastic MapReduce
- WorkSpaces
Customer Security Responsibilities
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) are the responsibility of the customer. Examples of these are:
- EC2
- VPC
- S3
- In Managed Services
- AWS is responsible for patching, antivirus, etc.
- Customer is responsible for Account Management and User access
- MFA (Multifactor Authentication) is strongly recommended
- Communication with these services should be performed using SSL/TLS encryption.
- API User activity should be logged using CloudTrail
Storage Decommissioning
- When a physical storage device has reached the end of its useful life, these are used to destroy the data as part of the decommissioning process:
- DoD 5220.22-M (National Industrial Security Program Operating Manual) or
- NIST 800-88 (Guidelines for Media Sanitization)
- All Magnetic storage devices are degaussed and physically destroyed in accordance with industry standard practices.
Network Security
Transmission Protection
- SSL (Secure Socket Layer): A cryptographic protocol that is designed to protect against eavesdropping, tampering and message forgery.
- Use VPCs and a private subnet to isolate services that do not need to be publicly accessible.
- Use VPNs to create an encrypted tunnel between the VPC and your datacenter
- Use DirectConnect between the VPC and your datacenter
Amazon Corporate Segregation
- The AWS network and Amazon.com are logically separated.
Network Monitoring and Protection
- DDoS
- MITM (Man In The Middle) attacks
- IP Spoofing
- AWS Host based firewall infrastructure will not permit an instance to send traffic with a source IP or MAC address different from its own.
- Port Scanning
- Scanning against other customers is a violation of the AWS AUP.
- Vulnerability scans are limited to your own instances and must not violate the AUP
- You must request permission to run a vulnerability scan in advance!
- Packet Sniffing by other tenants
AWS Credentials
Study These Again!
- Passwords for users to access the Management Console
- MFA (Multi-factor Authentication) to access the Management Console
- Access Keys
- Digitally signed requests to the AWS APIs (using AWS SDK, CLI or REST/Query APIs)
- Key Pairs
- SSH Logins
- CloudFront Signed URLs
- Amazon Generated Keys are 1024 bit SSH-2 RSA keys.
- X.509
- X.509 Certificates are only used to sign SOAP-based requests (currently used only with S3). You can have AWS create an X.509 cert and private key, or you can upload your own using the Security Credentials page.
- Digitally signed SOAP requests to AWS APIs
- SSL server certs for HTTPS
AWS Trusted Advisor
Administration & Security > Trusted Advisor
- Inspects your AWS environment and makes recommendations that may help to:
- Save Money
- Improve System Performance
- Close Security Gaps
- Provides alerts on most common security misconfigurations
- Leaving ports open
- Neglecting IAM accounts for internal users
- Public access to S3
- Not enabling user activity logging (CloudTrail)
- Not using MFA on the root AWS acct.
- Provides alerts on most common security misconfigurations
PART 2
https://www.udemy.com/aws-certified-solutions-architect-associate/learn/v4/t/lecture/2195620?start=0
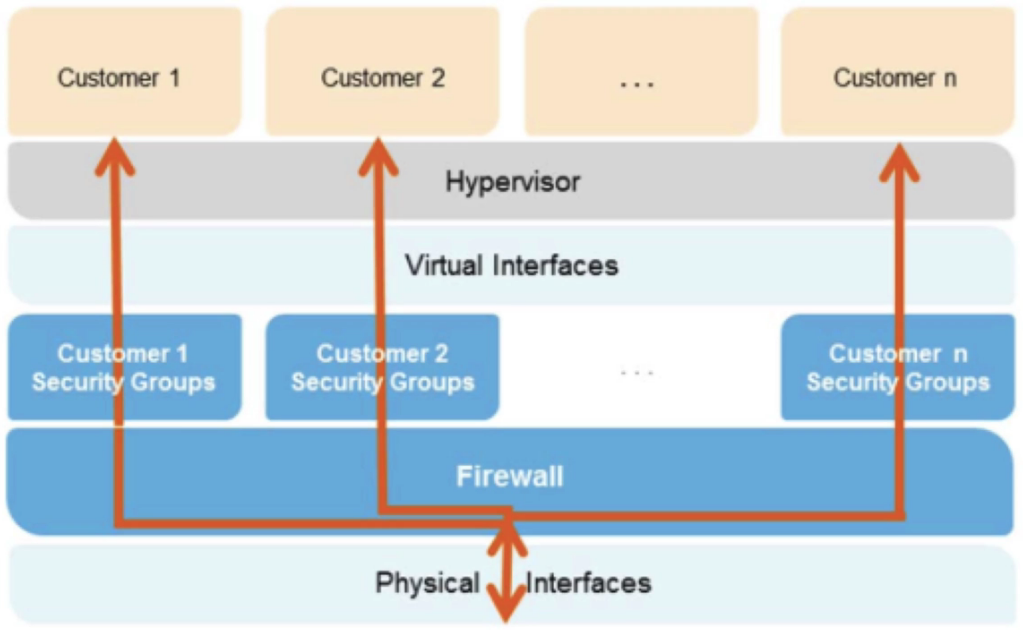
Instance Isolation
Networking
- Instances are isolated on the same physical machine via the Xen hypervisor.
- A Firewall exists between the hypervisor’s physcial NIC and the instances virtual NICs
- All packets are routed through this firewall
- An instance’s neighbors have no more access to the instance than any other host on the Internet.
- RAM is segregated similarly. (An instance has no access to another instance’s RAM)
Disk Storage
- Instances have NO access to raw disk devices, but only to virtual disks.
- AWS automatically resets every block of storage used, so that one customer’s data is never unintentionally exposed to another.
- Memory is scrubbed (set to Zero) when it is unallocated to a guest.
- Memory is not returned to the pool of free memory until this scrubbing is complete.
Guest Operating System
- Instances are COMPLETELY controlled by the client. You have full root access and administrative control over accounts, services and applications.
- AWS doe NOT have ANY access rights to your instances or the Guest OS – NO BACKDOORS!
- Encryption is available between EC2 instances and EBS volumes with AES-256.
- Encryption occurs on the host servers.
- Only available on powerful instance types
- M3
- C3
- R3
- G2
Firewall
- EC2 instances are protected by a mandatory firewall (security group)
- Configured by default to Deny ALL for all ingress (inbound) traffic.
- Any required ports must be explicitly opened.
Elastic Load Balancers
- SSL Termination is supported
- Allows you to identify the source IP of a client connecting to your servers whether you’re using HTTPS or TCP load balancing.
- Some types of load balancing with SSL termination do NOT have this feature.
Direct Connect
- Bypass Internet providers between you and AWS
- Uses industry standard 802.1q VLANS
- Can be partitioned into multiple virtual interfaces.
- Connect to public resources such as S3
- Connect to private resources like EC2 instances running within a VPC using private IP space.
- Maintains network separation between public and private environments.
Part 3 – Overview of Risk and Compliance
https://www.udemy.com/aws-certified-solutions-architect-associate/learn/v4/t/lecture/2050754?start=0
(This is mostly a summary of the above information, so they say)
AWS Management re-evaluates their strategic business plan bi-annually (once every 2 years).