https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sB2iQSvrcG0
What is software engineering?
- A standardized, structured and thorough approach to writing code.
- Treating the whole development process in a standardized manner.
Why bother?
- Ensure you are building the right product.
- Design code to a certain standard.
- Conventions and coding styles become important when working in a team.
- Ensure the code meets a level of rigor.
- Must be correct
- Efficient
- Secure
Stage 1: Requirements Gathering and Analysis
Understanding what the customer wants
Gathering
Customer provided list
- Have customer provide a list of requirements
- List could be long, but not useful for development
Conversational
You take the notes and results will be more productive.
- Surveys
- Interviews
- Focus Groups
- Observations
- If an existing package exists, watch how your client uses it.
- Watch for pain points
Use Case Analysis
- Have client describe a real usage scenario
- Point of view of the user, no jargon or technical info.
- Written as a list, emphasizing End Results and Steps taken.
- Extensions: “What if” error detection and how to handle
- Preconditions: Requirements to run the software
- Postconditions: What measures success?
Use Case Analysis Example:
- Use Case: Record a sale onto the system
- Role: Sales Staff
- Main Success Scenario:
- User initiates an “Add Sale” operation
- Software request the name and quantity of the item sold.
- User inputs name and qty and confirms the action
- Software stores the new entry into the system
- Extensions:
- User inputs qty less than 1
- Software indicates the qty is invalid
- Use case returns to step 2
- Preconditions
- User is logged in as Sales staff
- Postconditions
- Entry is stored in the system.
User Stories
A simpler, though less detailed, formulation of the requirements.
User stories should contain the 3 pieces of information
- Who they are
- What they want to do
- Why they want to do it
User Story Example
- As a Sales Staff, I want to be able to add new sales to the system, such to have a record of all transactions.
Analysis
Functional requirements
What we need the system to do
- Ex: Strore and retrieve information about sales
Non-Functional requirements
A characteristic or property of the system. Describes something about the process.
- Performance
- Ex: Records must be retrieved within 3 seconds
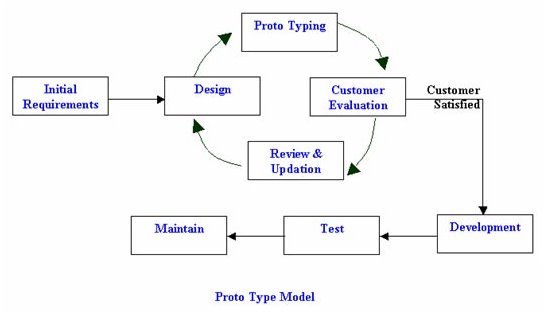
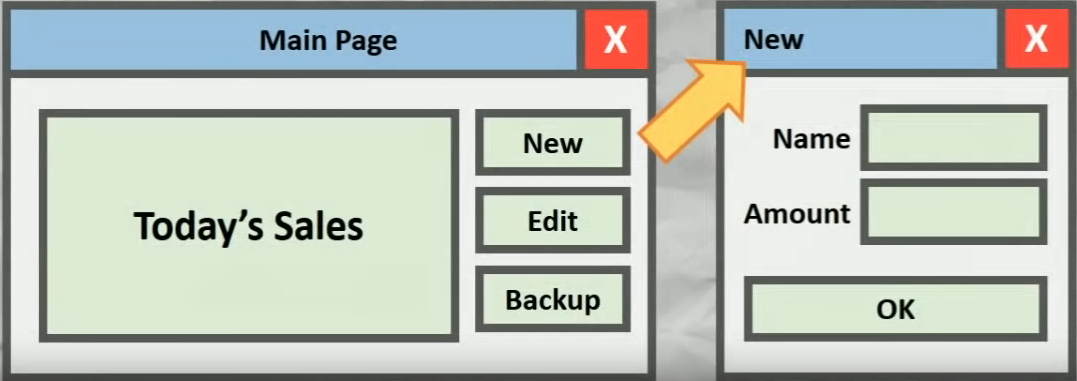
Prototyping
- Build a (usually non-functional) system that represents the visual layout and linkage of features.
- Might be some type of code
- Power Point slides
- Give the client a good idea of how the software will look, feel and perform prior to design
- There may be a lot of back and forth in this stage.
- Only once this has been completed can you move forward into serious development.
Stage 2: Planning
- Decide how you want to do things over the coming weeks and months.
- This provides a road map that defines how the different parts are going to interact with each other
- How to approach developing them
Modularization
- Breaking large programs/projects into smaller parts