< 3 Introduction to Active Directory | Home | 5 Group Policy Troubleshooting >
18: What is Group Policy
https://www.udemy.com/course/active-directory-group-policy-2012/learn/lecture/8371484#content
What is Group Policy
Used to deploy configuration changes to thousands of users or computers at one time.
- Restrict some users from accessing specific computers
- Allow access to some users to specific files
- Deploy software to specific computers
How does Group Policy Work
- Applies a GPO (Group Policy Object) to OUs
- GPOs contain User and Computer configuration settings
- When a setting is applied to a GPO, it is instantly applied to all users or computers that are members of that OU
GPO Recursion
- A GPO will apply recursively to all sub OUs and Objects
Accessing Group Policy Management
- Server Manager > Tools > Group Policy Management
- Default Domain Policy
- Group Policy Management >Forest: tas.local >Domains > tas.local >Default Domain Policy > [OK]
- Will apply to ALL OUs & sub OUs under tas.local
- Is actually a link to a Group Policy Object
- Group Policy Objects
- Contains all GPOs in the domain, whether they are active or not.
- WMI Filters
- Allow you to add specific rules when a GPO should or should not be applied
- Example: Apply a specific GPO rule when a computer is running Windows 7 or newer.
- Allow you to add specific rules when a GPO should or should not be applied
- Starter GPO
- Used to import or export GPOs for distribution to other environments.
19: Creating and Linking Group Policy Objects (GPOs)
https://www.udemy.com/course/active-directory-group-policy-2012/learn/lecture/8371614#content
How to Create and Manage Group Policy Objects
- GPOs contain configurations and settings that can be applied to Users or Computers that are stored within Active Directory
- A domain can contain several GPOs
- A single GPO can be linked or applied to several OUs simultaneously
- A GPO could be created to install Anti-virus software, then applied to all computer OUs that need it
- A GPO could be created that prevents access to Internet Explorer, then applied to any user OUs where these users should not have that access.
- Creating a GPO is similar to creating users in AD
- Group Policy Objects [RtClk] > New
- OR
- [RtClk] any OU > “Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…”
Lab: Creating a GPO
Adding directly to an OU
- [RtClk] tas.local > Create a GPO in…
- Name: Test GPO
- Starter: None
- [Ok]
- The GPO will be listed under the tas.local OU
- The GPO will also be listed under the Group Policy Objects OU
- RtClk the link under tas.local and delete
- It will be removed from under tas.local
- The actual Policy will still be listed under Group Policy Objects.
- Delete the Policy
- Group Policy Objects > Test GPO [RtClk] > Delete
Create the Policy, then add to an OU
- Group Policy Objects > Test GPO [RtClk] > New
- Name: Test 2 GPO
- Link it to tas.local
- tas.local [RtClk] > Link an Existing GPO
- Test 2 GPO > [OK]
- Delete the Link
Link Test 2 GPO to both Domain Computers and Domain Users
- Same process as above
- Same Policy, now applied to multiple OUs
GPO Link Options
- Edit
- Where User and Computer settings are configured
- Enforced
- Set it at a higher precedence/priority vs. other GPOs
- Link Enabled
- Like deleting a link, but remains in place for testing.
- Save Report …
- Save settings as a file
- New Window from Here
- Worthless
- Delete
- Rename
- Renames the entire GPO, Source, links, etc.
- Refresh
- Help
GPO Options
- Scope Tab
- Links
- Lists OUs where the GPO is applied
- Security Filtering
- Restricts the GPO from being applied to anything NOT listed here.
- WMI Filtering
- More advanced than Security Filtering
- Only apply to Windows 7 and above…
- More advanced than Security Filtering
- Links
- Details Tab
- General information about the GPO
- Domain
- Owner
- User and Computer versions
- Used for replication
- GPO Status
- All Disabled
- Computer disabled
- User disabled
- Enabled
- Comments
- General information about the GPO
- Settings Tab
- Shows Settings report.
- Uses I.E. to display
- Delegation Tab
- People that can read, edit, modify or delete the GPO
20: Group Policy Precedence
https://www.udemy.com/course/active-directory-group-policy-2012/learn/lecture/8351622#content
Precedence Order (Lowest to Highest)
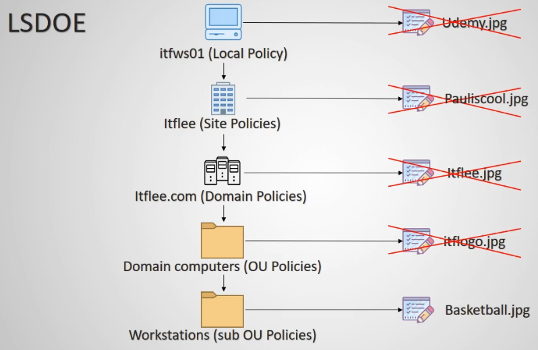
“The closer to the object, the higher the precedence.”
“The setting applied Last wins” (They over-write other settings)
- Local GP
- First Applied
- Site
- Domain
- Organizational Unit
- Sub Organization
- Enforced Group Policy Objects
- Icon displayed with a LOCK
LSDOE
Computer vs User
- Computer applied first
- User applied second
To remember, Computers are listed higher than Users
Blocked Inheritance
- OUs can block inheritance
- Only GPOs inside the OU will apply
- Except for Enforced GPOs above the OU
- Icon displayed with an Exclamation Point
21: Editing Group Policy Objects
https://www.udemy.com/course/active-directory-group-policy-2012/learn/lecture/8371636#content
- Create a GPO
- [RtClk] > Edit
- Computer Configs vs User
- Computer configs only apply to computers
- User configs only apply to users
- Some settings are the same for both, but many are different
- Computer Configs vs User
Lab:
- Computer Configurations > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings >Event Log
- All policies are default ‘Not Defined’.
- Select Policy [RtClk] > Properties
- Select from the list of options available for the Policy
- Click ‘Explain’ tab for deeper explanation of what the Policy does.
- [OK]
- This change will now be visible within the Group Policy reports.
To know which/how to set a policy, Google it!