< 8 Docker on Windows and Mac | 10 Conclusion >
44: Container Orchestration
https://www.udemy.com/course/learn-docker/learn/lecture/15828644#content
- You can only deploy a single container with the docker run command.
- What if the container fails? You’ll need to manually relaunch the container.
- What if the load increases? You’ll need to manually launch additional containers.
- What if the Host fails? Who will sit and monitor that?
This is what Orchestration solves
Options for Orchestration
- Docker swarm
- Easy to setup
- Lacks advanced features
- kubernetes
- Slightly difficult to set up
- Provides a lot of options to setup and customize.
- MESOS
- Difficult to configure
45. Docker Swarm
https://www.udemy.com/course/learn-docker/learn/lecture/7894030#content
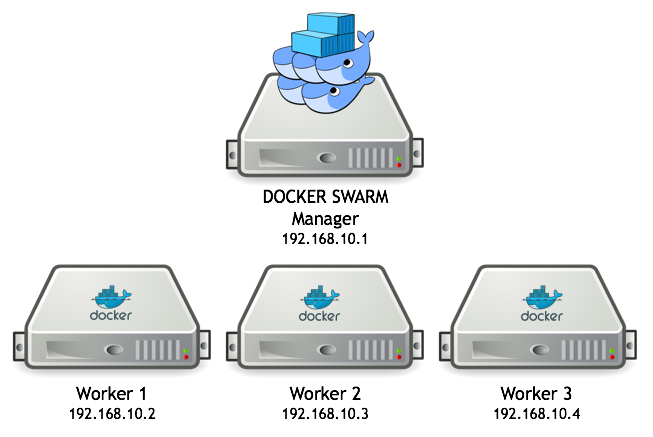
Docker swarm allows you to arrange your containers into clusters
- Manage across hosts
- Scalability
- High Availability
Swarm Setup
Create the Swarm manager using
docker swarm init
Join the worker nodes
docker swarm join --tocken <token>
Docker service
A Docker Services are one or more instances of a single application that run across the nodes in a cluster.
On Master
docker run my-web-server docker service create --replicas=3 <-e> <-p> <--network> my-web-server
46: Kubernetes Introduction
https://www.udemy.com/course/learn-docker/learn/lecture/15828702#content
Kubernetes actually requires it own courses. (5?)
kubectl scale --replicas=2000 my-web-server kubectl run --replicas=1000 my-web-server
Rolling upgrades / downgrades
kubectl rolling-update my-web-serve --image=web-server:2 kubectl rolling-update mys-web-server --rollback
Testing upgrades
Possible to test upgrades by only rolling out the upgrade to a percentage of instances in your cluster.
Open Architecture
- Almost every vendor you can think of provide plugins for Kubernetes.
- Storage
- Networking
- Available on all popular Cloud hosts
- Works with various containerization systems
- Docker
- rkt (Rocket)
- Others
Understanding Kubernetes Architecture
- A Kubernetes cluster consists of a set of nodes
- A Node
- Is a physical or virtual machine on which the Kubernetes tools are installed
- Is a worker machine where containers will be launched.
- For HA, you need to have more than 1 node.
- A Cluster is a set of Nodes grouped together.
- A Master
- Is a Node with Kubernetes Control Plane Components installed.
- Watches over the Nodes and is responsible for the orchestration of the containers.
Components
- API Server
- Acts as the front end for Kubenetes
- Management devices, CLIs, all communicate with Kubernetes via the API
- ectd
- Key: Value store
- Stores all data used to manage the cluster
- Stores all information about all nodes and masters in a distributed manner.
- Responsible for implementing logs to ensure there are no conflicts between the masters
- scheduler
- Distributes the work across multiple nodes
- Looks for newly created containers and assigns them to nodes
- Controller
- Brains behind orchestration
- Responsible for noticing and reacting when Nodes, Containers or Endpoints go down.
- Controllers make decisions to bring up new containers in such instances.
- Container Runtime
- The underlying software used to run containers.
- Docker, etc.
- The underlying software used to run containers.
- kubelet
- Agent that runs on each node in the cluster
- Makes sure the containers are running on the nodes as expected
kubectl (kube control tool)
- Kubernetes CLI used to
- Deploy and manage applications on a cluster
- Get cluster related information
- Get status of nodes
- etc
kubectl run
Run an application on the cluster
kubectl run hello-minikube
kubectl cluster-info
Get information about the cluster
kubectl cluster-info
kubectl get nodes
List all nodes in the cluster
kubectl get nodes
Kubernetes Deployment Example
To run hundreds of applications across all nodes in the cluster, run a single command:
kubectl run my-web-app --image=my-web-app --replicas=1000