What is Active Directory Users and Computers
28: https://www.udemy.com/windows-server-2016/learn/v4/t/lecture/6537816?start=0
Active Directory Users and Computer
- Also known as Active Directory, or AD
- Is a tool that is installed on any Windows Server that has the AD DS role installed.
- May also be installed if DS is NOT installed, but mostly with it.
- Is a live directory (Database) that stores:
- User accounts and their passwords
- Computers
- Printers
- File Shares
- Security Groups
- Etc.
- Permissions for all of the above.
- Each of these is considered it’s own ‘Object’
Security Groups
- Groups only contain other objects (see above)
- Groups of
- Users
- Computers
- File Shares, etc.
- Other Groups!
- Permissions can then be assigned to a ‘Group’ vs. against each object by itself.
Purpose of Active Directory
- Security Authentication
- Only allow authorized users to login to network computers
- Centralized security management of network resources
- User accounts are stored in one place (AD) instead of each individual computer.
Most common task for AD
- Reset passwords
- Create / Delete user accounts
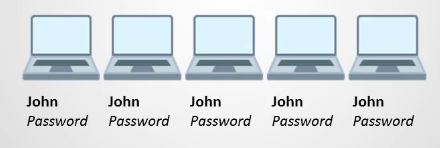
Life without Active Directory
- Create user account for John
- Every time you need to reset John’s password or Delete John’s acct:
- change on every computer!
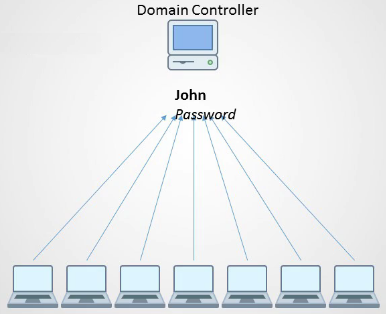
Life with Active Directory
- Central management
- Reset password in one location
- Same principle applies to all objects
- printers, file shares, groups, etc.
The Active Directory Interface
- Server Manager > Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers
- Action tab > Same as Rclick
- View > Good for filtering results
- Help > Versions
- Domain (the domain you’ve choses)
- Delegate Control
- Allow other users to manage AD
- Delegate Control
- Lots more here, but none make sense ATM
Understanding Organizational Units and Containers
29: https://www.udemy.com/windows-server-2016/learn/v4/t/lecture/6637808?start=0
Containers
- A Container is a structural Object included by default with AD
- YOU CANNOT apply Group Policy Objects directly to Containers
- This will make sense later
- You can apply GPOs to the Domain that will then affect the containers, but you cannot apply them directly.
- You cannot create Containers in AD
- There are back doors to this.
- YOU CANNOT create OUs in a Container
- Not mentioned in the class, just an observation.
- Default Containers
- Builtin
- Groups that are required by AD to operate
- Cannot be deleted
- Computers
- Default container for new computers that join the domain
- Best practice not to leave computers here, but to move them to an OU (Orgainzational Unit)
- Place GPOs against the OU
- Domain Controllers
- ForeignSecurityPrincipals
- Only used when a trust is created between your domain and another.
- Managed Service Accounts (MSAs)
- for software?
- Virus scanners – users for these programs
- No passwords for these
- Requires Powershell to create these
- for software?
- Users
- Administrator, Guest and Default Security Groups
- Builtin
Organizational Units (OUs)
- Used to organize and separate Objects within AD
- Objects can be anything AD can store
- Example: If your company has a Marketing team, you can create an OU for marketing users and computers.
- Can assign specific permissions to OUs
- All users in Marketing OU have a special desktop background, or access to a specific file share.
- Creating an OU
- Rclick the domain > New > Organizational Unit
- Protect container from accidental deletion
- To Delete – View > Advanced Features
- Rclick the OU > Properties
- Object tab > Uncheck ‘Protect object…’
- To Delete – View > Advanced Features
- OUs can be created within other OUs
Creating and Managing User Accounts
30: https://www.udemy.com/windows-server-2016/learn/v4/t/lecture/6733684?start=0
You must know how to do this!
This is mostly a lab… Will create a master OU for all of our users, and 2 sub OUs to segrate their permissions
- Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers
- Create an OU for your organization
- Thomas Co
- Create the Sub OUs
- Administrators
- Domain Users
- Create an Administrator
- Rclick Administrators > New > User
- Enter user info > Next
- Enter Password > Next > Finish
- Dclick the username for Properties (or Rclick > Properties)
- [Add…] > Enter ‘Domain admins’ > [Check name]
- When Domain Admins is underlined, you know the system found that group.
- [OK]
- You will now see Domain Admins has been added to the user
- [OK]
Resetting Passwords
- Locate the user (possibly using the hint provided below
- Rclick > Reset Password…
- Enter and confirm the new password
- This is the exact same windows to create a password!
- If selecting ‘Password must be changed at login’, you cannot use the temp. password as the new one.
- If the account is locked, unlock it.
- ** Make sure the user is using the correct login name!
Hint – Finding Users
- To Find a user:
- Find icon (Second from right)
- Find: Users, Contacts and Groups
- In: Entire Directory
- Type in part of the name > [Find Now]
- To search by email address:
- Click Advanced tab > Select ‘Email Address’ under ‘Field’
- Starts with: username
- …
Groups and Memberships
31: https://www.udemy.com/windows-server-2016/learn/v4/t/lecture/7105578?start=0
Lab – Log into your AD Users and Computers Console
Create a users Security Group
- Domain > Domain OU > Rclick ‘Domain Users’ > New > Group
- Group name: Sales
- Group scope (Least accessible to most accessible)
- Domain local
- Only accessible from the local domain
- Cannot be accessed by other domains, even if a trust is established
- Global
- Same as Domain, but CAN be accessed by other domains if a trust is established.
- Universal
- Same as Global, but can be accessed by other Forests if a trust is esablished
- Domain local
- Group type
- Security
- Authentication & access permissions
- Distribution
- Email lists
- Requires an Exchange server
- If the Group name is it-support, if an email is sent to it-support, that email will be distributed among all members of that group! Boom!
- Security
Adding users to a group
- Rclick the group name > Properties > Members tab > [Add]
- Add a user same as if you were searching for one
Adding a group to another group
- Rclick the group name > Properties > Member Of tab > [Add]
- Add the group same as if you were searching for one
- Caution! Any group or user added to another group inherits all of the permissions assigned to that group..
Saved Queries
32: https://www.udemy.com/windows-server-2016/learn/v4/t/lecture/6837032?start=0
Saved Queries are used to make redundant tasks much easier.
Lab 1: Create a query for all users that have not logged in within the last 30 days.
- Active Directory Users and Computers > Rclick Saved Queries > New > Query
- Name: 30 Days Since Last Logon
- Description: List of users that have not logged in within the last 30 days
- Query Root:
- Default should be OK since we only have one domain
- [ X ] Include sub folders.
- Leave this enabled. allows recursive scans into sub folders.
- Ok to disable if you’re sure your data is in a specific OU
- Query String > [Define Query]
- Users, contacts…, Computers, Printers, Shared Folders, Organiz
- These are the same as the ‘find’ search
- Custom Search
- Allows searches based on an Object’s properties
- Specific Fields – Email, Employee ID, etc.
- Allows searches based on an Object’s properties
- Common Queries
- Most common queries for Users, Computers, or Groups
- Select ’30’ from the drop down box next to ‘Days since last logon’ > [ OK ]
- Users, contacts…, Computers, Printers, Shared Folders, Organiz
- The Query String will now display
- “The query is valid but will not be shown here because it contains values that must be computed when the query is run”
- This is because it will use variable values, such as the current date, to create the query string.
- [ OK ]
- To run the query
- Saved Querys > Rclick the Query name > Export list to file
Lab 2: Create a query for all users that are locked out.
This lab will require some LDAP, so don’t expect to understand everything yet.
If a password is entered wrong 3 times, the account will lock.
- Active Directory Users and Computers > Rclick Saved Queries > New > Query
- Name: Locked User Accounts
- Description: Optional
- Query Root: Default
- [Define Query]
- Find: Custom Search > Advanced Tab
- Enter the LDAP query:
- (objectCategory=Person)(objectClass=User)(lockoutTime>=1)
- [ OK ]
- The Query String will display the actual query required
- (&(&(objectCategory=Person)(objectClass=User)(lockoutTime>=1)))
- [ OK ]
Test the Query
- Create a new user with a new password.
- Set a Security rule to lock users after 3 attempts (not explained in class)
- Now attempt to log into the other computer (ws-01) with the new user and an incorrect password.
- After 3 attempts the account should lock.